Abstract
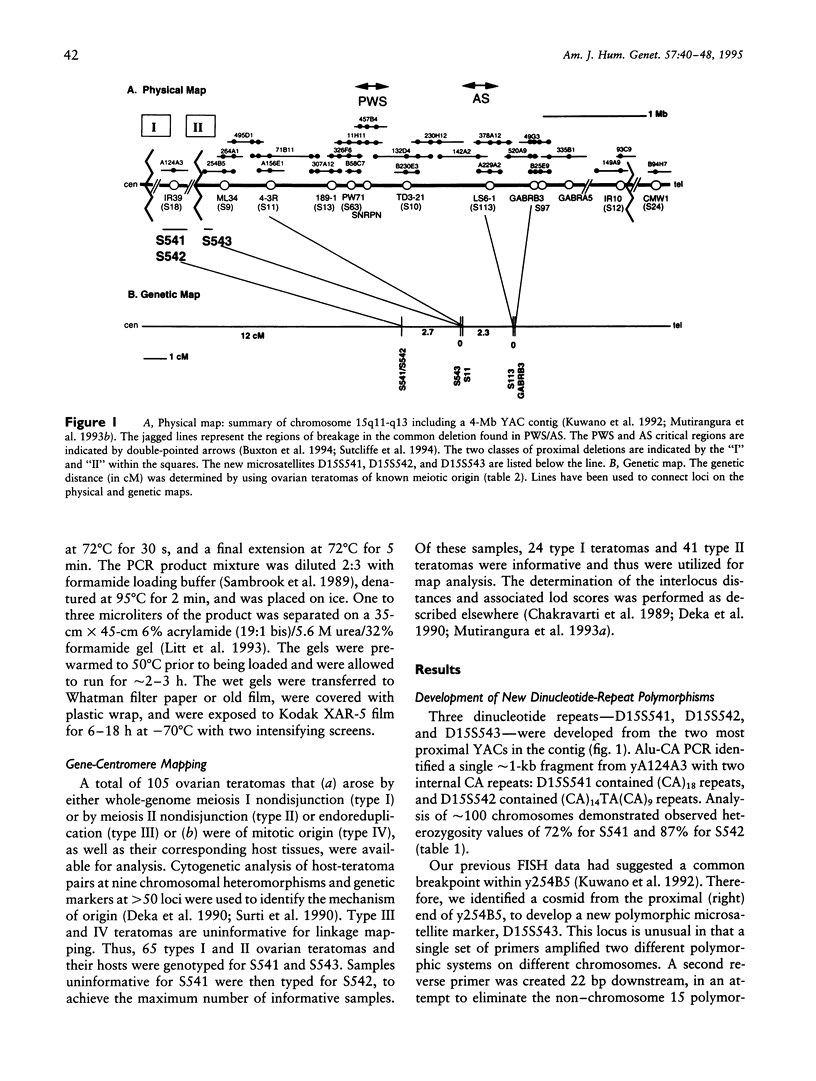
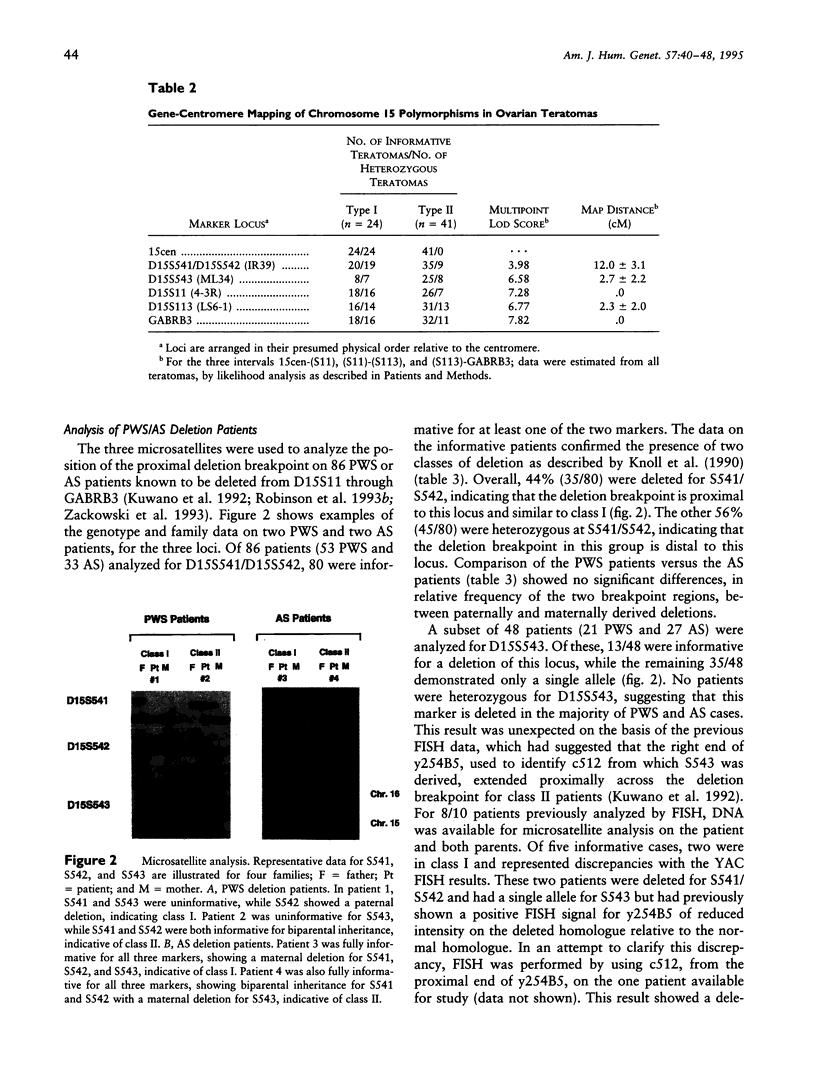
Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) and Angelman syndrome (AS) are distinct mental retardation syndromes caused by paternal and maternal deficiencies, respectively, in chromosome 15q11-q13. Approximately 70% of these patients have a large deletion of approximately 4 Mb extending from D15S9 (ML34) through D15S12 (IR10). To further characterize the deletion breakpoints proximal to D15S9, three new polymorphic microsatellite markers were developed that showed observed heterozygosities of 60%-87%. D15S541 and D15S542 were isolated from YAC A124A3 containing the D15S18 (IR39) locus. D15S543 was isolated from a cosmid cloned from the proximal right end of YAC 254B5 containing the D15S9 (ML34) locus. Gene-centromere mapping of these markers, using a panel of ovarian teratomas of known meiotic origin, extended the genetic map of chromosome 15 by 2-3 cM toward the centromere. Analysis of the more proximal S541/S542 markers on 53 Prader-Willi and 33 Angelman deletion patients indicated two classes of patients: 44% (35/80) of the informative patients were deleted for these markers (class I), while 56% (45/80) were not deleted (class II), with no difference between PWS and AS. In contrast, D15S543 was deleted in all informative patients (13/48) or showed the presence of a single allele (in 35/48 patients), suggesting that this marker is deleted in the majority of PWS and AS cases. These results confirm the presence of two common proximal deletion breakpoint regions in both Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes and are consistent with the same deletion mechanism being responsible for paternal and maternal deletions. One breakpoint region lies between D15S541/S542 and D15S543, with an additional breakpoint region being proximal to D15S541/S542.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballabio A., Andria G. Deletions and translocations involving the distal short arm of the human X chromosome: review and hypotheses. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Jul;1(4):221–227. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.4.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballabio A., Bardoni B., Guioli S., Basler E., Camerino G. Two families of low-copy-number repeats are interspersed on Xp22.3: implications for the high frequency of deletions in this region. Genomics. 1990 Oct;8(2):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann J. S., Tomfohrde J., Barnes R. I., Williams M., Broux O., Richard I., Weissenbach J., Bowcock A. M. A linkage map of human chromosome 15 with an average resolution of 2 cM and containing 55 polymorphic microsatellites. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Dec;2(12):2019–2030. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.12.2019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beuten J., Mangelschots K., Buntinx I., Coucke P., Brouwer O. F., Hennekam R. C., Van Broeckhoven C., Willems P. J. Molecular study of chromosome 15 in 22 patients with Angelman syndrome. Hum Genet. 1993 Jan;90(5):489–495. doi: 10.1007/BF00217446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buiting K., Greger V., Brownstein B. H., Mohr R. M., Voiculescu I., Winterpacht A., Zabel B., Horsthemke B. A putative gene family in 15q11-13 and 16p11.2: possible implications for Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5457–5461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler M. G. Prader-Willi syndrome: current understanding of cause and diagnosis. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Mar;35(3):319–332. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320350306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton J. L., Chan C. T., Gilbert H., Clayton-Smith J., Burn J., Pembrey M., Malcolm S. Angelman syndrome associated with a maternal 15q11-13 deletion of less than 200 kb. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Aug;3(8):1409–1413. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.8.1409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarti A., Majumder P. P., Slaugenhaupt S. A., Deka R., Warren A. C., Surti U., Ferrell R. E., Antonarakis S. E. Gene-centromere mapping and the study of non-disjunction in autosomal trisomies and ovarian teratomas. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1989;311:45–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance P. F., Abbas N., Lensch M. W., Pentao L., Roa B. B., Patel P. I., Lupski J. R. Two autosomal dominant neuropathies result from reciprocal DNA duplication/deletion of a region on chromosome 17. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Feb;3(2):223–228. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.2.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton-Smith J., Pembrey M. E. Angelman syndrome. J Med Genet. 1992 Jun;29(6):412–415. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.6.412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton-Smith J., Webb T., Cheng X. J., Pembrey M. E., Malcolm S. Duplication of chromosome 15 in the region 15q11-13 in a patient with developmental delay and ataxia with similarities to Angelman syndrome. J Med Genet. 1993 Jun;30(6):529–531. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.6.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crolla J. A., Harvey J. F., Sitch F. L., Dennis N. R. Supernumerary marker 15 chromosomes: a clinical, molecular and FISH approach to diagnosis and prognosis. Hum Genet. 1995 Feb;95(2):161–170. doi: 10.1007/BF00209395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deka R., Chakravarti A., Surti U., Hauselman E., Reefer J., Majumder P. P., Ferrell R. E. Genetics and biology of human ovarian teratomas. II. Molecular analysis of origin of nondisjunction and gene-centromere mapping of chromosome I markers. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Oct;47(4):644–655. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donlon T. A., Lalande M., Wyman A., Bruns G., Latt S. A. Isolation of molecular probes associated with the chromosome 15 instability in the Prader-Willi syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4408–4412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feener C. A., Boyce F. M., Kunkel L. M. Rapid detection of CA polymorphisms in cloned DNA: application to the 5' region of the dystrophin gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Mar;48(3):621–627. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greger V., Woolf E., Lalande M. Cloning of the breakpoints of a submicroscopic deletion in an Angelman syndrome patient. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jul;2(7):921–924. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.7.921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoll J. H., Glatt K. A., Nicholls R. D., Malcolm S., Lalande M. Chromosome 15 uniparental disomy is not frequent in Angelman syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jan;48(1):16–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoll J. H., Nicholls R. D., Magenis R. E., Glatt K., Graham J. M., Jr, Kaplan L., Lalande M. Angelman syndrome: three molecular classes identified with chromosome 15q11q13-specific DNA markers. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jul;47(1):149–154. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwano A., Mutirangura A., Dittrich B., Buiting K., Horsthemke B., Saitoh S., Niikawa N., Ledbetter S. A., Greenberg F., Chinault A. C. Molecular dissection of the Prader-Willi/Angelman syndrome region (15q11-13) by YAC cloning and FISH analysis. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Sep;1(6):417–425. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.6.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter S. A., Garcia-Heras J., Ledbetter D. H. "PCR-karyotype" of human chromosomes in somatic cell hybrids. Genomics. 1990 Dec;8(4):614–622. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90247-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litt M., Hauge X., Sharma V. Shadow bands seen when typing polymorphic dinucleotide repeats: some causes and cures. Biotechniques. 1993 Aug;15(2):280–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutirangura A., Greenberg F., Butler M. G., Malcolm S., Nicholls R. D., Chakravarti A., Ledbetter D. H. Multiplex PCR of three dinucleotide repeats in the Prader-Willi/Angelman critical region (15q11-q13): molecular diagnosis and mechanism of uniparental disomy. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Feb;2(2):143–151. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.2.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutirangura A., Jayakumar A., Sutcliffe J. S., Nakao M., McKinney M. J., Buiting K., Horsthemke B., Beaudet A. L., Chinault A. C., Ledbetter D. H. A complete YAC contig of the Prader-Willi/Angelman chromosome region (15q11-q13) and refined localization of the SNRPN gene. Genomics. 1993 Dec;18(3):546–552. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(11)80011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaoka H., Ozawa K., Matsuda F., Hayashida H., Matsumura R., Haino M., Shin E. K., Fukita Y., Imai T., Anand R. Recent translocation of variable and diversity segments of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain from chromosome 14 to chromosomes 15 and 16. Genomics. 1994 Jul 1;22(1):189–197. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao M., Sutcliffe J. S., Durtschi B., Mutirangura A., Ledbetter D. H., Beaudet A. L. Imprinting analysis of three genes in the Prader-Willi/Angelman region: SNRPN, E6-associated protein, and PAR-2 (D15S225E). Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Feb;3(2):309–315. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.2.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls R. D., Knoll J. H., Butler M. G., Karam S., Lalande M. Genetic imprinting suggested by maternal heterodisomy in nondeletion Prader-Willi syndrome. Nature. 1989 Nov 16;342(6247):281–285. doi: 10.1038/342281a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pentao L., Wise C. A., Chinault A. C., Patel P. I., Lupski J. R. Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1A duplication appears to arise from recombination at repeat sequences flanking the 1.5 Mb monomer unit. Nat Genet. 1992 Dec;2(4):292–300. doi: 10.1038/ng1292-292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettigrew A. L., Gollin S. M., Greenberg F., Riccardi V. M., Ledbetter D. H. Duplication of proximal 15q as a cause of Prader-Willi syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Dec;28(4):791–802. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis A., Dittrich B., Greger V., Buiting K., Lalande M., Gillessen-Kaesbach G., Anvret M., Horsthemke B. Imprinting mutations suggested by abnormal DNA methylation patterns in familial Angelman and Prader-Willi syndromes. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 May;54(5):741–747. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. P., Binkert F., Giné R., Vazquez C., Müller W., Rosenkranz W., Schinzel A. Clinical and molecular analysis of five inv dup(15) patients. Eur J Hum Genet. 1993;1(1):37–50. doi: 10.1159/000472386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. P., Bottani A., Xie Y. G., Balakrishman J., Binkert F., Mächler M., Prader A., Schinzel A. Molecular, cytogenetic, and clinical investigations of Prader-Willi syndrome patients. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Dec;49(6):1219–1234. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. P., Spiegel R., Schinzel A. A. Deletion breakpoints associated with the Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes (15q11-q13) are not sites of high homologous recombination. Hum Genet. 1993 Mar;91(2):181–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00222722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saadallah N., Hultén M. Chiasma distribution, genetic lengths, and recombination fractions: a comparison between chromosomes 15 and 16. J Med Genet. 1983 Aug;20(4):290–299. doi: 10.1136/jmg.20.4.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh S., Harada N., Jinno Y., Hashimoto K., Imaizumi K., Kuroki Y., Fukushima Y., Sugimoto T., Renedo M., Wagstaff J. Molecular and clinical study of 61 Angelman syndrome patients. Am J Med Genet. 1994 Aug 15;52(2):158–163. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320520207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh S., Kubota T., Ohta T., Jinno Y., Niikawa N., Sugimoto T., Wagstaff J., Lalande M. Familial Angelman syndrome caused by imprinted submicroscopic deletion encompassing GABAA receptor beta 3-subunit gene. Lancet. 1992 Feb 8;339(8789):366–367. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91686-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinzel A. A., Brecevic L., Bernasconi F., Binkert F., Berthet F., Wuilloud A., Robinson W. P. Intrachromosomal triplication of 15q11-q13. J Med Genet. 1994 Oct;31(10):798–803. doi: 10.1136/jmg.31.10.798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr N. K., Bryant S. P., Attwood J., Nyberg K., Cox S. A., Mills A., Bains R., Warne D., Cullin L., Povey S. European Gene Mapping Project (EUROGEM): genetic maps based on the CEPH reference families. Eur J Hum Genet. 1994;2(3):193–203. doi: 10.1159/000472364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surti U., Hoffner L., Chakravarti A., Ferrell R. E. Genetics and biology of human ovarian teratomas. I. Cytogenetic analysis and mechanism of origin. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Oct;47(4):635–643. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. S., Nakao M., Christian S., Orstavik K. H., Tommerup N., Ledbetter D. H., Beaudet A. L. Deletions of a differentially methylated CpG island at the SNRPN gene define a putative imprinting control region. Nat Genet. 1994 Sep;8(1):52–58. doi: 10.1038/ng0994-52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson I. M., Cook G. P., Carter N. P., Elaswarapu R., Smith S., Walter G., Buluwela L., Rabbitts T. H., Winter G. Human immunoglobulin VH and D segments on chromosomes 15q11.2 and 16p11.2. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jun;3(6):853–860. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.6.853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb T. Inv dup(15) supernumerary marker chromosomes. J Med Genet. 1994 Aug;31(8):585–594. doi: 10.1136/jmg.31.8.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen P. H., Li X. M., Tsai S. P., Johnson C., Mohandas T., Shapiro L. J. Frequent deletions of the human X chromosome distal short arm result from recombination between low copy repetitive elements. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90472-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zackowski J. L., Nicholls R. D., Gray B. A., Bent-Williams A., Gottlieb W., Harris P. J., Waters M. F., Driscoll D. J., Zori R. T., Williams C. A. Cytogenetic and molecular analysis in Angelman syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Apr 1;46(1):7–11. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320460104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




