Abstract
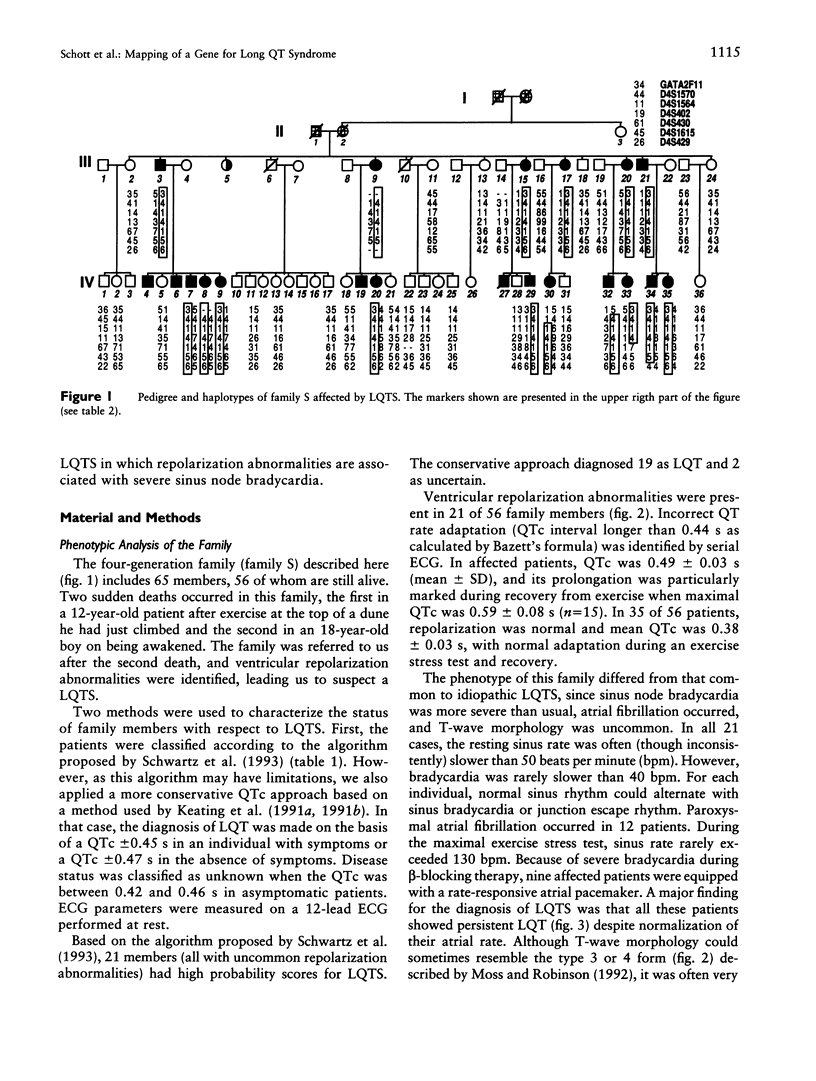
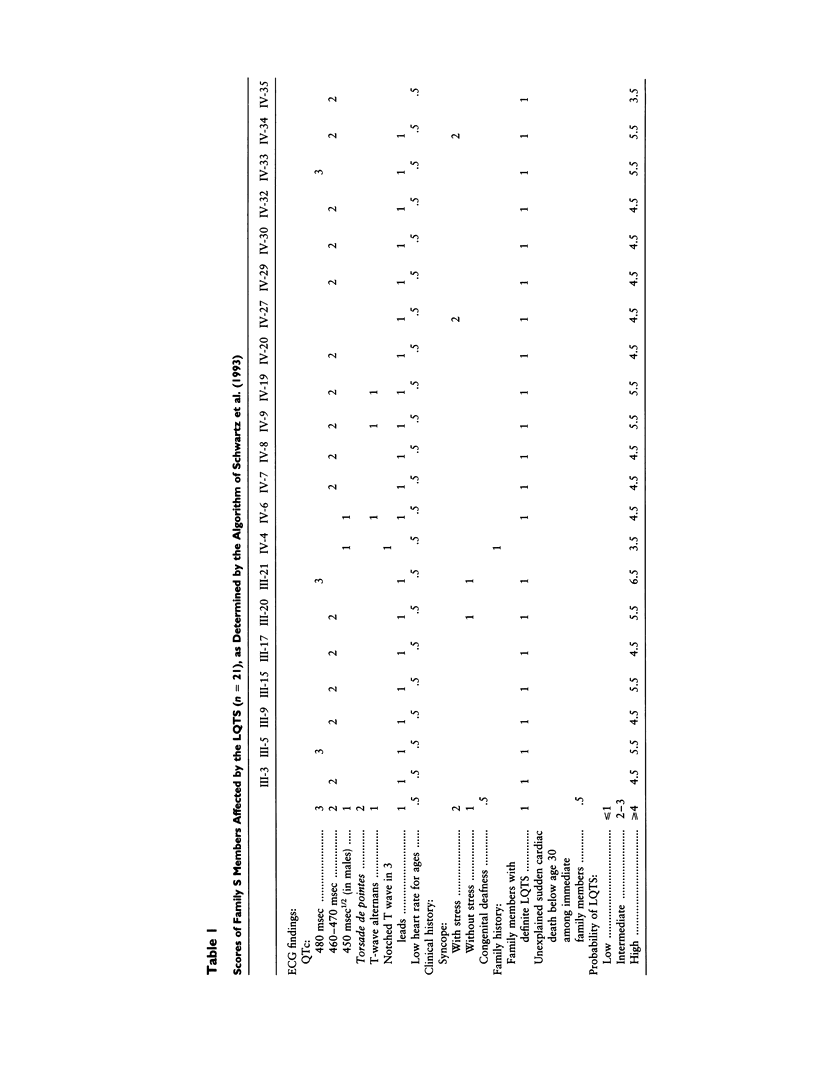
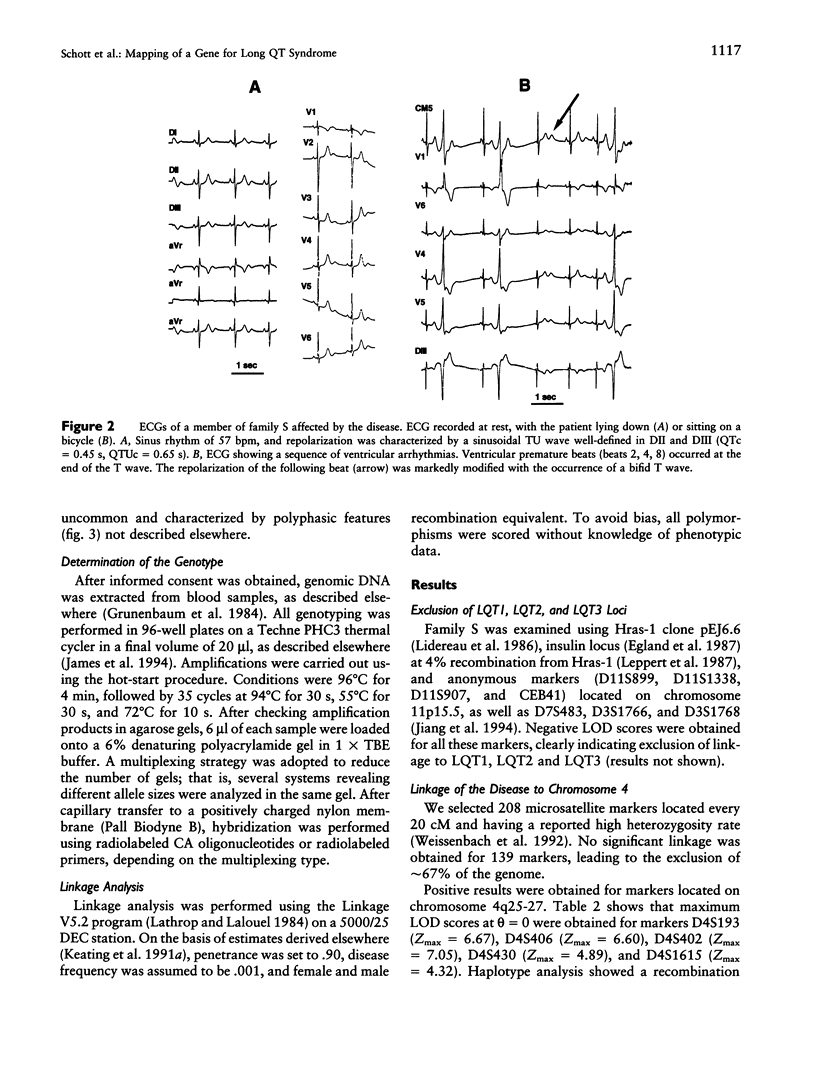
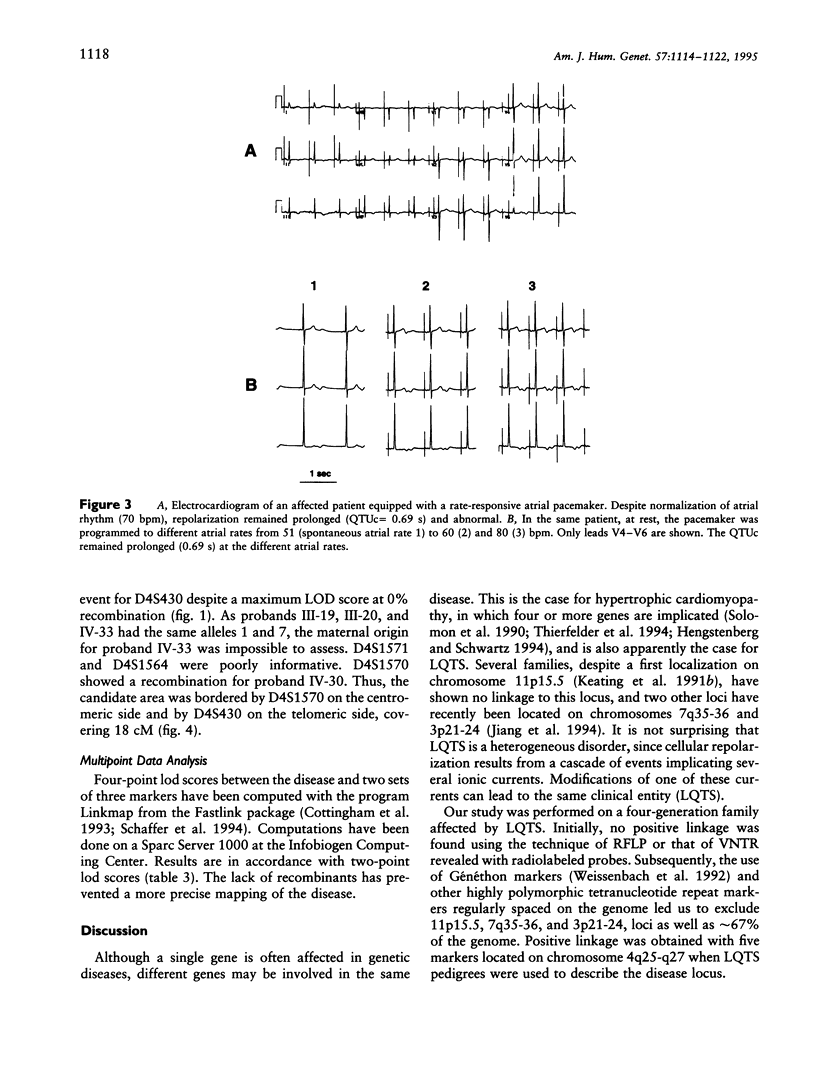
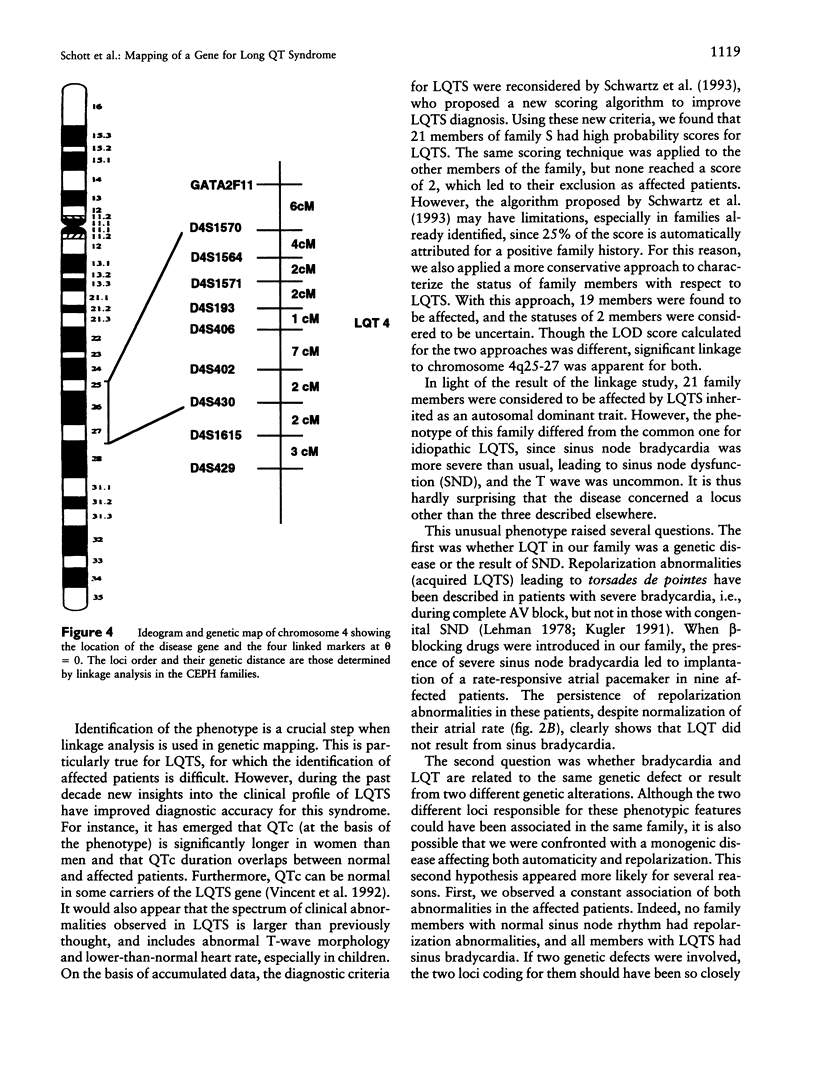
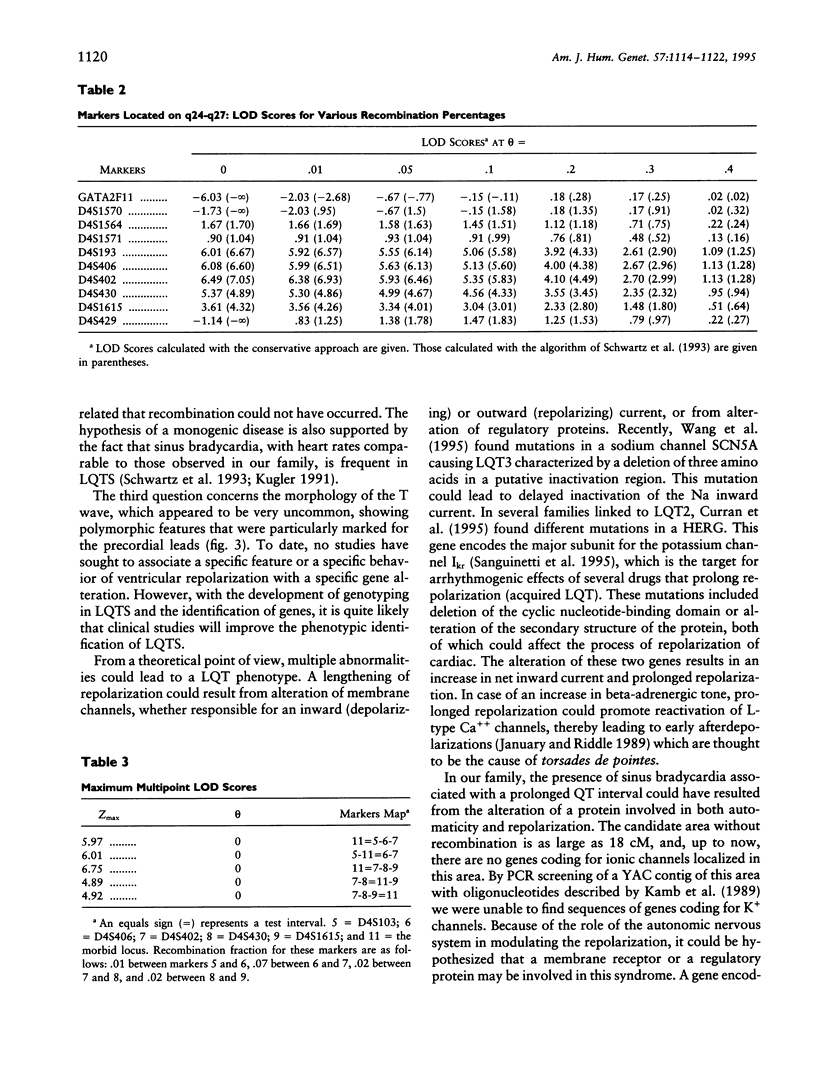
Long QT syndrome (LQTS) is a heterogeneous inherited disorder causing syncope and sudden death from ventricular arrhythmias. A first locus for this disorder was mapped to chromosome 11p15.5. However, locus heterogeneity has been demonstrated in several families, and two other loci have recently been located on chromosomes 7q35-36 and 3p21-24. We used linkage analysis to map the locus in a 65-member family in which LQTS was associated with more marked sinus bradycardia than usual, leading to sinus node dysfunction. Linkage to chromosome 11p15.5, 7q35-36, or 3p21-24 was excluded. Positive linkage was obtained for markers located on chromosome 4q25-27. A maximal LOD score of 7.05 was found for marker D4S402. The identification of a fourth locus for LQTS confirms its genetic heterogeneity. Locus 4q25-27 is associated with a peculiar phenotype within the LQTS entity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barr C. S., Naas A., Freeman M., Lang C. C., Struthers A. D. QT dispersion and sudden unexpected death in chronic heart failure. Lancet. 1994 Feb 5;343(8893):327–329. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91164-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benhorin J., Kalman Y. M., Medina A., Towbin J., Rave-Harel N., Dyer T. D., Blangero J., MacCluer J. W., Kerem B. S. Evidence of genetic heterogeneity in the long QT syndrome. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1960–1962. doi: 10.1126/science.8316839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottingham R. W., Jr, Idury R. M., Schäffer A. A. Faster sequential genetic linkage computations. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jul;53(1):252–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran M. E., Splawski I., Timothy K. W., Vincent G. M., Green E. D., Keating M. T. A molecular basis for cardiac arrhythmia: HERG mutations cause long QT syndrome. Cell. 1995 Mar 10;80(5):795–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90358-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran M., Atkinson D., Timothy K., Vincent G. M., Moss A. J., Leppert M., Keating M. Locus heterogeneity of autosomal dominant long QT syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1993 Aug;92(2):799–803. doi: 10.1172/JCI116653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day C. P., McComb J. M., Campbell R. W. QT dispersion: an indication of arrhythmia risk in patients with long QT intervals. Br Heart J. 1990 Jun;63(6):342–344. doi: 10.1136/hrt.63.6.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean J. C., Cross S., Jennings K. Evidence of genetic and phenotypic heterogeneity in the Romano-Ward syndrome. J Med Genet. 1993 Nov;30(11):947–950. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.11.947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egeland J. A., Gerhard D. S., Pauls D. L., Sussex J. N., Kidd K. K., Allen C. R., Hostetter A. M., Housman D. E. Bipolar affective disorders linked to DNA markers on chromosome 11. 1987 Feb 26-Mar 4Nature. 325(6107):783–787. doi: 10.1038/325783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller C. M., Ismailov I. I., Keeton D. A., Benos D. J. Phosphorylation and activation of a bovine tracheal anion channel by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 28;269(43):26642–26650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunebaum L., Cazenave J. P., Camerino G., Kloepfer C., Mandel J. L., Tolstoshev P., Jaye M., De la Salle H., Lecocq J. P. Carrier detection of Hemophilia B by using a restriction site polymorphism associated with the coagulation Factor IX gene. J Clin Invest. 1984 May;73(5):1491–1495. doi: 10.1172/JCI111354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengstenberg C., Schwartz K. Molecular genetics of familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1994 Jan;26(1):3–10. doi: 10.1006/jmcc.1994.1002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosoda K., Nakao K., Tamura N., Arai H., Ogawa Y., Suga S., Nakanishi S., Imura H. Organization, structure, chromosomal assignment, and expression of the gene encoding the human endothelin-A receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18797–18804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James M. R., Richard C. W., 3rd, Schott J. J., Yousry C., Clark K., Bell J., Terwilliger J. D., Hazan J., Dubay C., Vignal A. A radiation hybrid map of 506 STS markers spanning human chromosome 11. Nat Genet. 1994 Sep;8(1):70–76. doi: 10.1038/ng0994-70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- January C. T., Riddle J. M. Early afterdepolarizations: mechanism of induction and block. A role for L-type Ca2+ current. Circ Res. 1989 May;64(5):977–990. doi: 10.1161/01.res.64.5.977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang C., Atkinson D., Towbin J. A., Splawski I., Lehmann M. H., Li H., Timothy K., Taggart R. T., Schwartz P. J., Vincent G. M. Two long QT syndrome loci map to chromosomes 3 and 7 with evidence for further heterogeneity. Nat Genet. 1994 Oct;8(2):141–147. doi: 10.1038/ng1094-141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keating M., Atkinson D., Dunn C., Timothy K., Vincent G. M., Leppert M. Linkage of a cardiac arrhythmia, the long QT syndrome, and the Harvey ras-1 gene. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):704–706. doi: 10.1126/science.1673802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keating M., Dunn C., Atkinson D., Timothy K., Vincent G. M., Leppert M. Consistent linkage of the long-QT syndrome to the Harvey ras-1 locus on chromosome 11. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Dec;49(6):1335–1339. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kugler J. D. Sinus nodal dysfunction in young patients with long QT syndrome. Am Heart J. 1991 Apr;121(4 Pt 1):1132–1136. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(91)90673-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidereau R., Escot C., Theillet C., Champeme M. H., Brunet M., Gest J., Callahan R. High frequency of rare alleles of the human c-Ha-ras-1 proto-oncogene in breast cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Sep;77(3):697–701. doi: 10.1093/jnci/77.3.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss A. J., Schwartz P. J., Crampton R. S., Tzivoni D., Locati E. H., MacCluer J., Hall W. J., Weitkamp L., Vincent G. M., Garson A., Jr The long QT syndrome. Prospective longitudinal study of 328 families. Circulation. 1991 Sep;84(3):1136–1144. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.3.1136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono K., Tsujimoto G., Sakamoto A., Eto K., Masaki T., Ozaki Y., Satake M. Endothelin-A receptor mediates cardiac inhibition by regulating calcium and potassium currents. Nature. 1994 Jul 28;370(6487):301–304. doi: 10.1038/370301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onozuka M., Furuichi H., Imai S., Fukami Y. Evidence that Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein phosphorylation is involved in the opening process of potassium channels in identified snail neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Mar 11;124(1):35–38. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90816-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanguinetti M. C., Jiang C., Curran M. E., Keating M. T. A mechanistic link between an inherited and an acquired cardiac arrhythmia: HERG encodes the IKr potassium channel. Cell. 1995 Apr 21;81(2):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90340-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz P. J., Moss A. J., Vincent G. M., Crampton R. S. Diagnostic criteria for the long QT syndrome. An update. Circulation. 1993 Aug;88(2):782–784. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.88.2.782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz P. J., Wolf S. QT interval prolongation as predictor of sudden death in patients with myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1978 Jun;57(6):1074–1077. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.57.6.1074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäffer A. A., Gupta S. K., Shriram K., Cottingham R. W., Jr Avoiding recomputation in linkage analysis. Hum Hered. 1994 Jul-Aug;44(4):225–237. doi: 10.1159/000154222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon S. D., Jarcho J. A., McKenna W., Geisterfer-Lowrance A., Germain R., Salerni R., Seidman J. G., Seidman C. E. Familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a genetically heterogeneous disease. J Clin Invest. 1990 Sep;86(3):993–999. doi: 10.1172/JCI114802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierfelder L., Watkins H., MacRae C., Lamas R., McKenna W., Vosberg H. P., Seidman J. G., Seidman C. E. Alpha-tropomyosin and cardiac troponin T mutations cause familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a disease of the sarcomere. Cell. 1994 Jun 3;77(5):701–712. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin J. A., Li H., Taggart R. T., Lehmann M. H., Schwartz P. J., Satler C. A., Ayyagari R., Robinson J. L., Moss A., Hejtmancik J. F. Evidence of genetic heterogeneity in Romano-Ward long QT syndrome. Analysis of 23 families. Circulation. 1994 Dec;90(6):2635–2644. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.90.6.2635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent G. M., Timothy K. W., Leppert M., Keating M. The spectrum of symptoms and QT intervals in carriers of the gene for the long-QT syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1992 Sep 17;327(12):846–852. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199209173271204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Q., Shen J., Splawski I., Atkinson D., Li Z., Robinson J. L., Moss A. J., Towbin J. A., Keating M. T. SCN5A mutations associated with an inherited cardiac arrhythmia, long QT syndrome. Cell. 1995 Mar 10;80(5):805–811. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90359-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Gyapay G., Dib C., Vignal A., Morissette J., Millasseau P., Vaysseix G., Lathrop M. A second-generation linkage map of the human genome. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):794–801. doi: 10.1038/359794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



