Abstract
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is associated with a number of extraintestinal manifestations, which include osteomas, epidermoid cysts, and desmoid tumors, often referred to as “Gardner syndrome.” Recent studies have suggested that some of the phenotypic features of FAP are dependent on the position of the mutation within the APC gene. In particular, the correlation between congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium (CHRPE) and APC genotype indicates that affected families may be divided into distinct groups. We have investigated the association between the dento-osseous features of GS on dental panoramic radiographs (DPRs) and APC genotype in a regional cohort of FAP families. DPRs were performed on 84 affected individuals from 36 families, and the dento-osseous features of FAP were quantified by a weighted scoring system. Significant DPR abnormalities were present in 69% of affected individuals. The APC gene mutation was identified in 27 of these families, and for statistical analysis these were subdivided into three groups. Group 1 comprised 18 affected individuals from seven families with mutations 5' of exon 9; these families (except one) did not express CHRPE. Groups 2 comprised 38 individuals from 16 families with mutations between exon 9 and codon 1444, all of whom expressed CHRPE. Group 3 comprised 11 individuals from four families with mutations 3' of codon 1444, none of whom expressed CHRPE. Families with mutations 3' of codon 1444 had significantly more lesions on DPRs (P < .001) and appeared to have a higher incidence of desmoid tumors. These results suggest that the severity of some of the features of Gardner syndrome may correlate with genotype in FAP.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burn J., Chapman P., Delhanty J., Wood C., Lalloo F., Cachon-Gonzalez M. B., Tsioupra K., Church W., Rhodes M., Gunn A. The UK Northern region genetic register for familial adenomatous polyposis coli: use of age of onset, congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium, and DNA markers in risk calculations. J Med Genet. 1991 May;28(5):289–296. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.5.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspari R., Friedl W., Mandl M., Möslein G., Kadmon M., Knapp M., Jacobasch K. H., Ecker K. W., Kreissler-Haag D., Timmermanns G. Familial adenomatous polyposis: mutation at codon 1309 and early onset of colon cancer. Lancet. 1994 Mar 12;343(8898):629–632. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)92634-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspari R., Olschwang S., Friedl W., Mandl M., Boisson C., Böker T., Augustin A., Kadmon M., Möslein G., Thomas G. Familial adenomatous polyposis: desmoid tumours and lack of ophthalmic lesions (CHRPE) associated with APC mutations beyond codon 1444. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Mar;4(3):337–340. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.3.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich W. F., Lander E. S., Smith J. S., Moser A. R., Gould K. A., Luongo C., Borenstein N., Dove W. Genetic identification of Mom-1, a major modifier locus affecting Min-induced intestinal neoplasia in the mouse. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):631–639. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90484-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDNER E. J. Follow-up study of a family group exhibiting dominant inheritance for a syndrome including intestinal polyps, osteomas, fibromas and epidermal cysts. Am J Hum Genet. 1962 Dec;14:376–390. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDNER E. J., PLENK H. P. Hereditary pattern for multiple osteomas in a family group. Am J Hum Genet. 1952 Mar;4(1):31–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDNER E. J., RICHARDS R. C. Multiple cutaneous and subcutaneous lesions occurring simultaneously with hereditary polyposis and osteomatosis. Am J Hum Genet. 1953 Jun;5(2):139–147. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giardiello F. M., Offerhaus G. J., Traboulsi E. I., Graybeal J. C., Maumenee I. H., Krush A. J., Levin L. S., Booker S. V., Hamilton S. R. Value of combined phenotypic markers in identifying inheritance of familial adenomatous polyposis. Gut. 1991 Oct;32(10):1170–1174. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.10.1170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groden J., Thliveris A., Samowitz W., Carlson M., Gelbert L., Albertsen H., Joslyn G., Stevens J., Spirio L., Robertson M. Identification and characterization of the familial adenomatous polyposis coli gene. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):589–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurbuz A. K., Giardiello F. M., Petersen G. M., Krush A. J., Offerhaus G. J., Booker S. V., Kerr M. C., Hamilton S. R. Desmoid tumours in familial adenomatous polyposis. Gut. 1994 Mar;35(3):377–381. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.3.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson S. V., Bishop D. T., Jay B. Genetic heterogeneity of congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium (CHRPE) in families with familial adenomatous polyposis. J Med Genet. 1994 Jan;31(1):55–58. doi: 10.1136/jmg.31.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagelman D. G., DeCosse J. J., Bussey H. J. Upper gastrointestinal cancer in familial adenomatous polyposis. Lancet. 1988 May 21;1(8595):1149–1151. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91962-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joslyn G., Carlson M., Thliveris A., Albertsen H., Gelbert L., Samowitz W., Groden J., Stevens J., Spirio L., Robertson M. Identification of deletion mutations and three new genes at the familial polyposis locus. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):601–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Nilbert M. C., Su L. K., Vogelstein B., Bryan T. M., Levy D. B., Smith K. J., Preisinger A. C., Hedge P., McKechnie D. Identification of FAP locus genes from chromosome 5q21. Science. 1991 Aug 9;253(5020):661–665. doi: 10.1126/science.1651562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyaki M., Konishi M., Kikuchi-Yanoshita R., Enomoto M., Tanaka K., Takahashi H., Muraoka M., Mori T., Konishi F., Iwama T. Coexistence of somatic and germ-line mutations of APC gene in desmoid tumors from patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Cancer Res. 1993 Nov 1;53(21):5079–5082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagase H., Nakamura Y. Mutations of the APC (adenomatous polyposis coli) gene. Hum Mutat. 1993;2(6):425–434. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380020602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishisho I., Nakamura Y., Miyoshi Y., Miki Y., Ando H., Horii A., Koyama K., Utsunomiya J., Baba S., Hedge P. Mutations of chromosome 5q21 genes in FAP and colorectal cancer patients. Science. 1991 Aug 9;253(5020):665–669. doi: 10.1126/science.1651563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nugent K. P., Phillips R. K., Hodgson S. V., Cottrell S., Smith-Ravin J., Pack K., Bodmer W. F. Phenotypic expression in familial adenomatous polyposis: partial prediction by mutation analysis. Gut. 1994 Nov;35(11):1622–1623. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.11.1622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olschwang S., Tiret A., Laurent-Puig P., Muleris M., Parc R., Thomas G. Restriction of ocular fundus lesions to a specific subgroup of APC mutations in adenomatous polyposis coli patients. Cell. 1993 Dec 3;75(5):959–968. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90539-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul P., Letteboer T., Gelbert L., Groden J., White R., Coppes M. J. Identical APC exon 15 mutations result in a variable phenotype in familial adenomatous polyposis. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jul;2(7):925–931. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.7.925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell S. M., Petersen G. M., Krush A. J., Booker S., Jen J., Giardiello F. M., Hamilton S. R., Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. Molecular diagnosis of familial adenomatous polyposis. N Engl J Med. 1993 Dec 30;329(27):1982–1987. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199312303292702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. J., van der Luijt R., Spycher M., Mary J. L., Müller A., Hoppeler T., Haner M., Müller H., Martinoli S., Brazzola P. L. Novel germline APC gene mutation in a large familial adenomatous polyposis kindred displaying variable phenotypes. Gut. 1995 May;36(5):731–736. doi: 10.1136/gut.36.5.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen-Gupta S., Van der Luijt R. B., Bowles L. V., Meera Khan P., Delhanty J. D. Somatic mutation of APC gene in desmoid tumour in familial adenomatous polyposis. Lancet. 1993 Aug 28;342(8870):552–553. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91677-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield V. C., Beck J. S., Kwitek A. E., Sandstrom D. W., Stone E. M. The sensitivity of single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis for the detection of single base substitutions. Genomics. 1993 May;16(2):325–332. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spirio L., Olschwang S., Groden J., Robertson M., Samowitz W., Joslyn G., Gelbert L., Thliveris A., Carlson M., Otterud B. Alleles of the APC gene: an attenuated form of familial polyposis. Cell. 1993 Dec 3;75(5):951–957. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90538-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
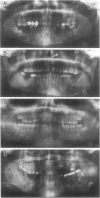
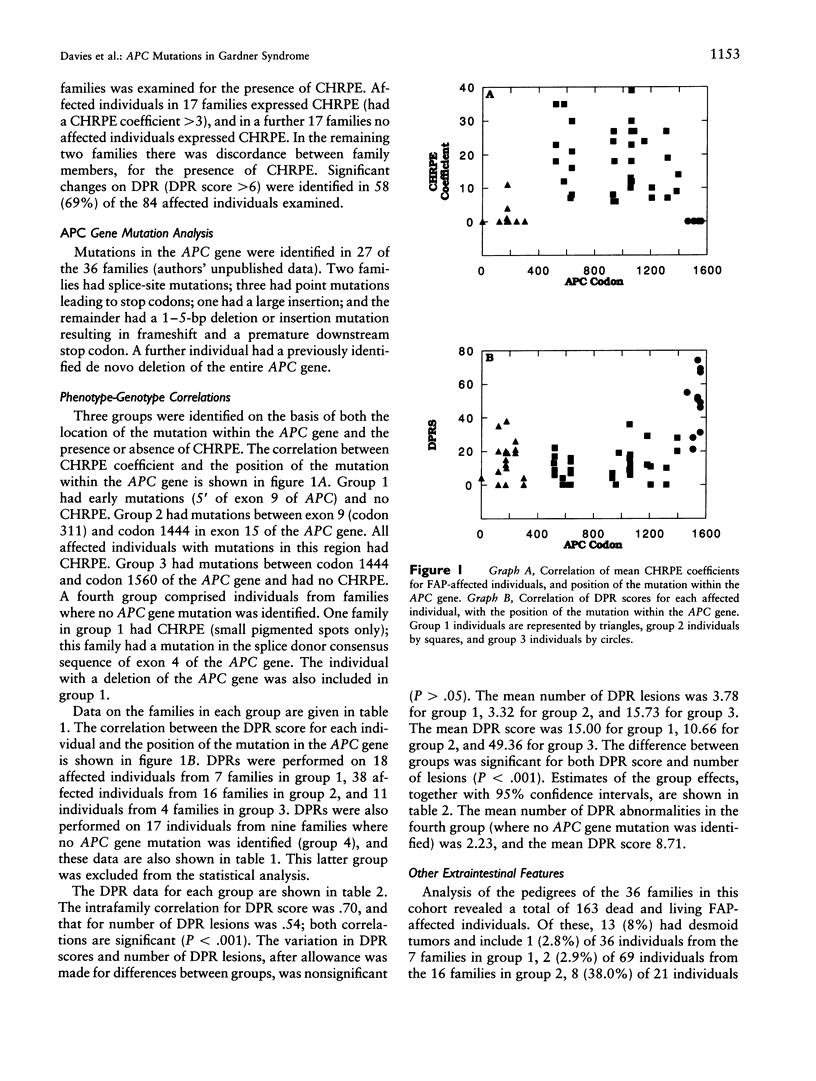
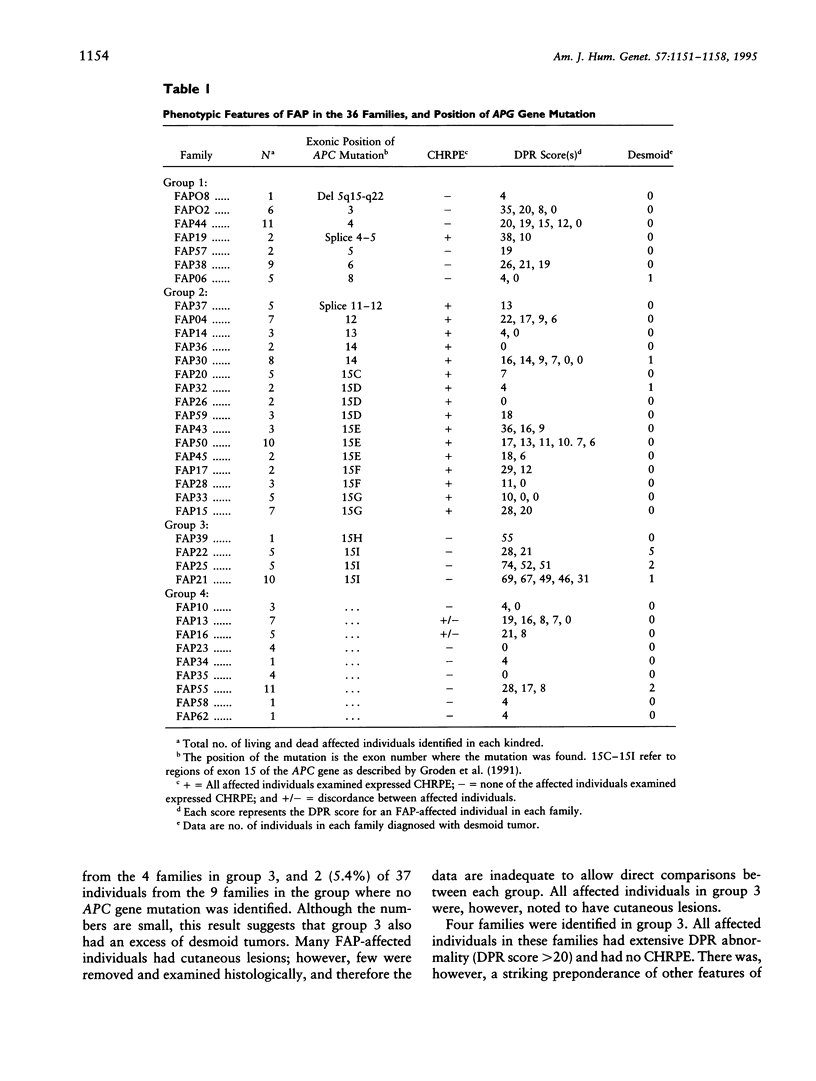
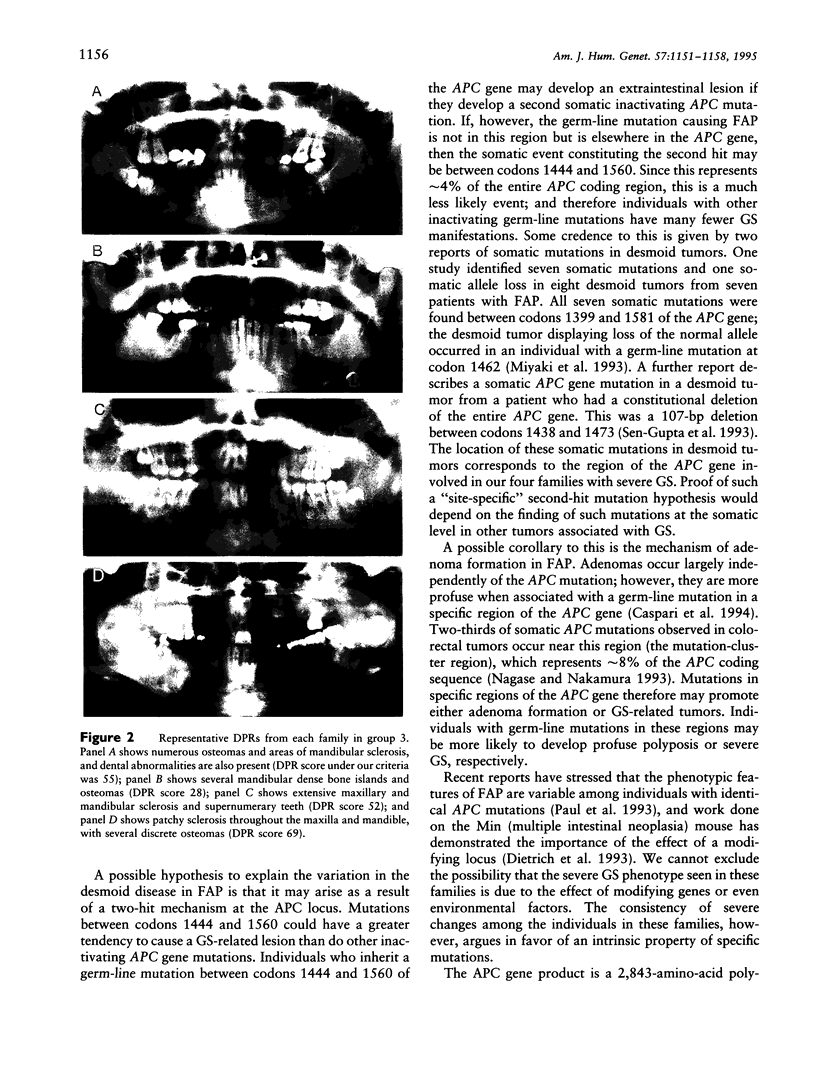
- Thakker N., Davies R., Horner K., Armstrong J., Clancy T., Guy S., Harris R., Sloan P., Evans G. The dental phenotype in familial adenomatous polyposis: diagnostic application of a weighted scoring system for changes on dental panoramic radiographs. J Med Genet. 1995 Jun;32(6):458–464. doi: 10.1136/jmg.32.6.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traboulsi E. I., Krush A. J., Gardner E. J., Booker S. V., Offerhaus G. J., Yardley J. H., Hamilton S. R., Luk G. D., Giardiello F. M., Welsh S. B. Prevalence and importance of pigmented ocular fundus lesions in Gardner's syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1987 Mar 12;316(11):661–667. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198703123161104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsunomiya J., Nakamura T. The occult osteomatous changes in the mandible in patients with familial polyposis coli. Br J Surg. 1975 Jan;62(1):45–51. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800620111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf J., Järvinen H. J., Hietanen J. Gardner's dento-maxillary stigmas in patients with familial adenomatosis coli. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1986 Dec;24(6):410–416. doi: 10.1016/0266-4356(86)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Heyningen V. Genetics. One gene--four syndromes. Nature. 1994 Jan 27;367(6461):319–320. doi: 10.1038/367319a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]