Abstract
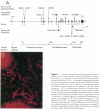
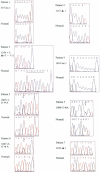
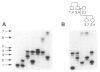
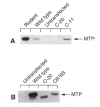
Elevated plasma levels of apolipoprotein B (apoB)–containing lipoproteins constitute a major risk factor for the development of coronary heart disease. In the rare recessively inherited disorder abetalipoproteinemia (ABL) the production of apoB-containing lipoproteins is abolished, despite no abnormality of the apoB gene. In the current study we have characterized the gene encoding a microsomal triglyceride-transfer protein (MTP), localized to chromosome 4q22-24, and have identified a mutation of the MTP gene in both alleles of all individuals in a cohort of eight patients with classical ABL. Each mutant allele is predicted to encode a truncated form of MTP with a variable number of aberrant amino acids at its C-terminal end. Expression of genetically engineered forms of MTP in Cos-1 cells indicates that the C-terminal portion of MTP is necessary for triglyceride-transfer activity. Deletion of 20 amino acids from the carboxyl terminus of the 894-amino-acid protein and a missense mutation of cysteine 878 to serine both abolished activity. These results establish that defects of the MTP gene are the predominant, if not sole, cause of hereditary ABL and that an intact carboxyl terminus is necessary for activity.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews L. G., Markert M. L. Exon skipping in purine nucleoside phosphorylase mRNA processing leading to severe immunodeficiency. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7834–7838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atzel A., Wetterau J. R. Mechanism of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein catalyzed lipid transport. Biochemistry. 1993 Oct 5;32(39):10444–10450. doi: 10.1021/bi00090a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg L. P., Grundy C. B., Thomas F., Millar D. S., Green P. J., Slomski R., Reiss J., Kakkar V. V., Cooper D. N. De novo splice site mutation in the antithrombin III (AT3) gene causing recurrent venous thrombosis: demonstration of exon skipping by ectopic transcript analysis. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):1359–1361. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90070-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borén J., Wettesten M., Sjöberg A., Thorlin T., Bondjers G., Wiklund O., Olofsson S. O. The assembly and secretion of apoB 100 containing lipoproteins in Hep G2 cells. Evidence for different sites for protein synthesis and lipoprotein assembly. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10556–10564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brett D. J., Pease R. J., Scott J., Gibbons G. F. Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein activity remains unchanged in rat livers under conditions of altered very-low-density lipoprotein secretion. Biochem J. 1995 Aug 15;310(Pt 1):11–14. doi: 10.1042/bj3100011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Lipoprotein receptors in the liver. Control signals for plasma cholesterol traffic. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):743–747. doi: 10.1172/JCI111044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher P., Trifonov E. N. Compilation and analysis of eukaryotic POL II promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):10009–10026. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.10009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. A., Thrift R. N., Wu C. C., Howell K. E. Apolipoprotein B is both integrated into and translocated across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Evidence for two functionally distinct pools. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):10005–10011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon J. L., Furukawa S., Ginsberg H. N. Oleate stimulates secretion of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins from Hep G2 cells by inhibiting early intracellular degradation of apolipoprotein B. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):5080–5086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dullaart R. P., Speelberg B., Schuurman H. J., Milne R. W., Havekes L. M., Marcel Y. L., Geuze H. J., Hulshof M. M., Erkelens D. W. Epitopes of apolipoprotein B-100 and B-48 in both liver and intestine. Expression and evidence for local synthesis in recessive abetalipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1397–1404. doi: 10.1172/JCI112727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gharib B., Fox M. F., Bartoli C., Giorgi D., Sansonetti A., Swallow D. M., Dagorn J. C., Berge-lefranc J. L. Human regeneration protein/lithostathine genes map to chromosome 2p12. Ann Hum Genet. 1993 Jan;57(Pt 1):9–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1993.tb00882.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D. A., Jamil H., Sharp D., Mullaney D., Yao Z., Gregg R. E., Wetterau J. Secretion of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins from HeLa cells is dependent on expression of the microsomal triglyceride transfer protein and is regulated by lipid availability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 2;91(16):7628–7632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.16.7628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara Y., Nishio H., Kitoh Y., Takeshima Y., Narita N., Wada H., Yokoyama M., Nakamura H., Matsuo M. A novel point mutation (G-1 to T) in a 5' splice donor site of intron 13 of the dystrophin gene results in exon skipping and is responsible for Becker muscular dystrophy. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Jan;54(1):53–61. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., MacLeod A., Tamaki K., Neil D. L., Monckton D. G. Minisatellite repeat coding as a digital approach to DNA typing. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):204–209. doi: 10.1038/354204a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keohavong P., Thilly W. G. Fidelity of DNA polymerases in DNA amplification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9253–9257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Sitia R. Protein degradation in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):611–614. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90104-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawczak M., Reiss J., Cooper D. N. The mutational spectrum of single base-pair substitutions in mRNA splice junctions of human genes: causes and consequences. Hum Genet. 1992 Sep-Oct;90(1-2):41–54. doi: 10.1007/BF00210743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiper J. M., Bayliss J. D., Pease R. J., Brett D. J., Scott J., Shoulders C. C. Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein, the abetalipoproteinemia gene product, mediates the secretion of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins from heterologous cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 2;269(35):21951–21954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller D. P., Lloyd J. K., Bird A. C. Long-term management of abetalipoproteinaemia. Possible role for vitamin E. Arch Dis Child. 1977 Mar;52(3):209–214. doi: 10.1136/adc.52.3.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller D. P., Lloyd J. K., Wolff O. H. Vitamin E and neurological function. Lancet. 1983 Jan 29;1(8318):225–228. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92598-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohshima T., Sasaki M., Matsuzaka T., Sakuragawa N. A novel splicing abnormality in a Japanese patient with Gaucher's disease. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Sep;2(9):1497–1498. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.9.1497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkel D., Straume T., Gray J. W. Cytogenetic analysis using quantitative, high-sensitivity, fluorescence hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2934–2938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullinger C. R., North J. D., Teng B. B., Rifici V. A., Ronhild de Brito A. E., Scott J. The apolipoprotein B gene is constitutively expressed in HepG2 cells: regulation of secretion by oleic acid, albumin, and insulin, and measurement of the mRNA half-life. J Lipid Res. 1989 Jul;30(7):1065–1077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raag R., Appelt K., Xuong N. H., Banaszak L. Structure of the lamprey yolk lipid-protein complex lipovitellin-phosvitin at 2.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1988 Apr 5;200(3):553–569. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90542-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricci B., Sharp D., O'Rourke E., Kienzle B., Blinderman L., Gordon D., Smith-Monroy C., Robinson G., Gregg R. E., Rader D. J. A 30-amino acid truncation of the microsomal triglyceride transfer protein large subunit disrupts its interaction with protein disulfide-isomerase and causes abetalipoproteinemia. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 16;270(24):14281–14285. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.24.14281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata N., Wu X., Dixon J. L., Ginsberg H. N. Proteolysis and lipid-facilitated translocation are distinct but competitive processes that regulate secretion of apolipoprotein B in Hep G2 cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 5;268(31):22967–22970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlötterer C., Tautz D. Slippage synthesis of simple sequence DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):211–215. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. B., Senapathy P. RNA splice junctions of different classes of eukaryotes: sequence statistics and functional implications in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7155–7174. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp D., Blinderman L., Combs K. A., Kienzle B., Ricci B., Wager-Smith K., Gil C. M., Turck C. W., Bouma M. E., Rader D. J. Cloning and gene defects in microsomal triglyceride transfer protein associated with abetalipoproteinaemia. Nature. 1993 Sep 2;365(6441):65–69. doi: 10.1038/365065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp D., Ricci B., Kienzle B., Lin M. C., Wetterau J. R. Human microsomal triglyceride transfer protein large subunit gene structure. Biochemistry. 1994 Aug 9;33(31):9057–9061. doi: 10.1021/bi00197a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoulders C. C., Brett D. J., Bayliss J. D., Narcisi T. M., Jarmuz A., Grantham T. T., Leoni P. R., Bhattacharya S., Pease R. J., Cullen P. M. Abetalipoproteinemia is caused by defects of the gene encoding the 97 kDa subunit of a microsomal triglyceride transfer protein. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Dec;2(12):2109–2116. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.12.2109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoulders C. C., Narcisi T. M., Read J., Chester A., Brett D. J., Scott J., Anderson T. A., Levitt D. G., Banaszak L. J. The abetalipoproteinemia gene is a member of the vitellogenin family and encodes an alpha-helical domain. Nat Struct Biol. 1994 May;1(5):285–286. doi: 10.1038/nsb0594-285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tall A. R. Plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein. J Lipid Res. 1993 Aug;34(8):1255–1274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmud P. J., Lloyd J. K., Muller D. P., Collins D. R., Scott J., Humphries S. Genetic evidence from two families that the apolipoprotein B gene is not involved in abetalipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1988 Nov;82(5):1803–1806. doi: 10.1172/JCI113795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thrift R. N., Drisko J., Dueland S., Trawick J. D., Davis R. A. Translocation of apolipoprotein B across the endoplasmic reticulum is blocked in a nonhepatic cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9161–9165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmins P. A., Poliks B., Banaszak L. The location of bound lipid in the lipovitellin complex. Science. 1992 Jul 31;257(5070):652–655. doi: 10.1126/science.1496377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan S., Cullen P., Pacy P., Halliday D., Scott J. Stable isotopes show a direct relation between VLDL apoB overproduction and serum triglyceride levels and indicate a metabolically and biochemically coherent basis for familial combined hyperlipidemia. Arterioscler Thromb. 1993 Jul;13(7):1110–1118. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.13.7.1110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W. Evolution and expression of vitellogenin genes. Trends Genet. 1988 Aug;4(8):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90155-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetterau J. R., Aggerbeck L. P., Bouma M. E., Eisenberg C., Munck A., Hermier M., Schmitz J., Gay G., Rader D. J., Gregg R. E. Absence of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein in individuals with abetalipoproteinemia. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):999–1001. doi: 10.1126/science.1439810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetterau J. R., Combs K. A., Spinner S. N., Joiner B. J. Protein disulfide isomerase is a component of the microsomal triglyceride transfer protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9800–9807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetterau J. R., Combs K. A., Spinner S. N., Joiner B. J. Protein disulfide isomerase is a component of the microsomal triglyceride transfer protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9800–9807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White A. L., Graham D. L., LeGros J., Pease R. J., Scott J. Oleate-mediated stimulation of apolipoprotein B secretion from rat hepatoma cells. A function of the ability of apolipoprotein B to direct lipoprotein assembly and escape presecretory degradation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15657–15664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong Z., Wilson V., Patel I., Povey S., Jeffreys A. J. Characterization of a panel of highly variable minisatellites cloned from human DNA. Ann Hum Genet. 1987 Oct;51(Pt 4):269–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1987.tb01062.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]