Abstract
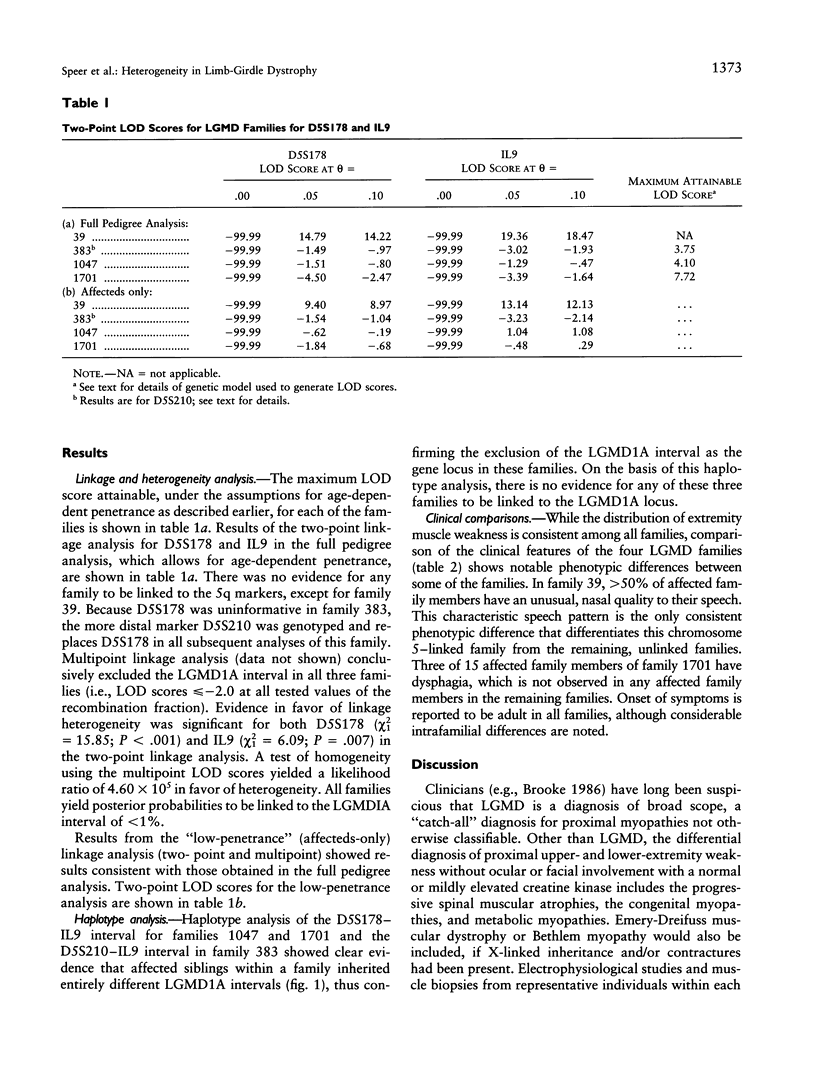
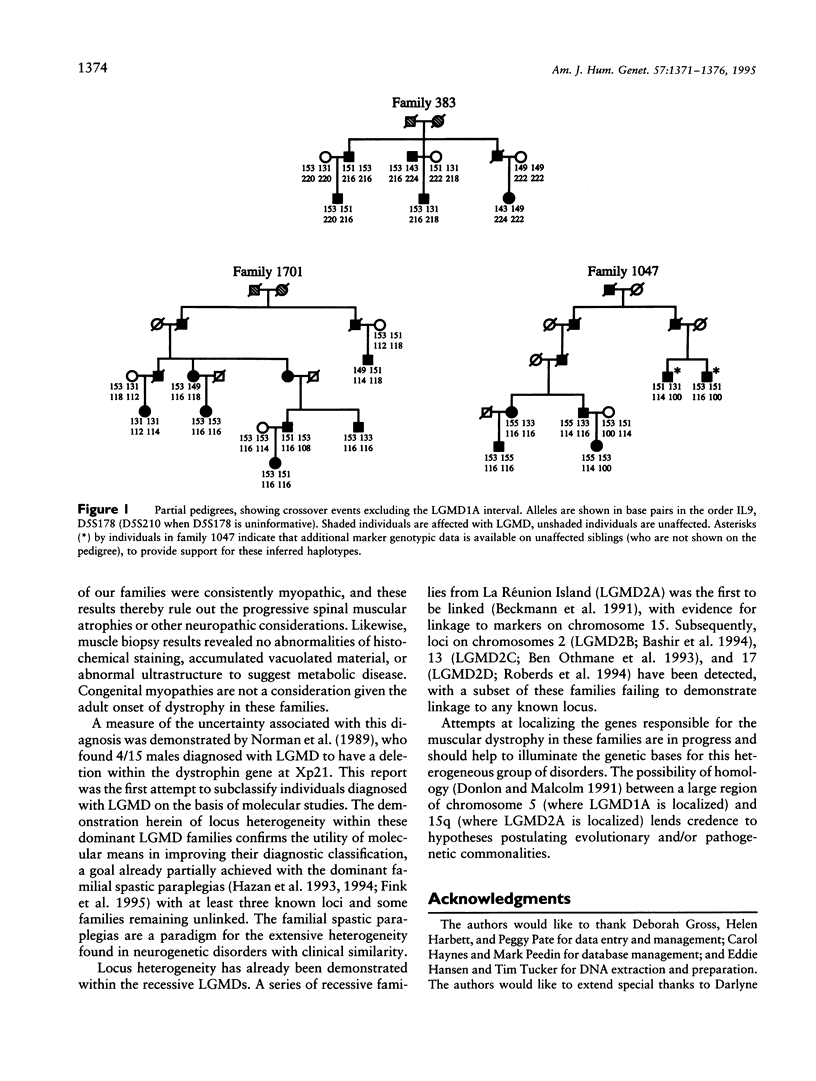
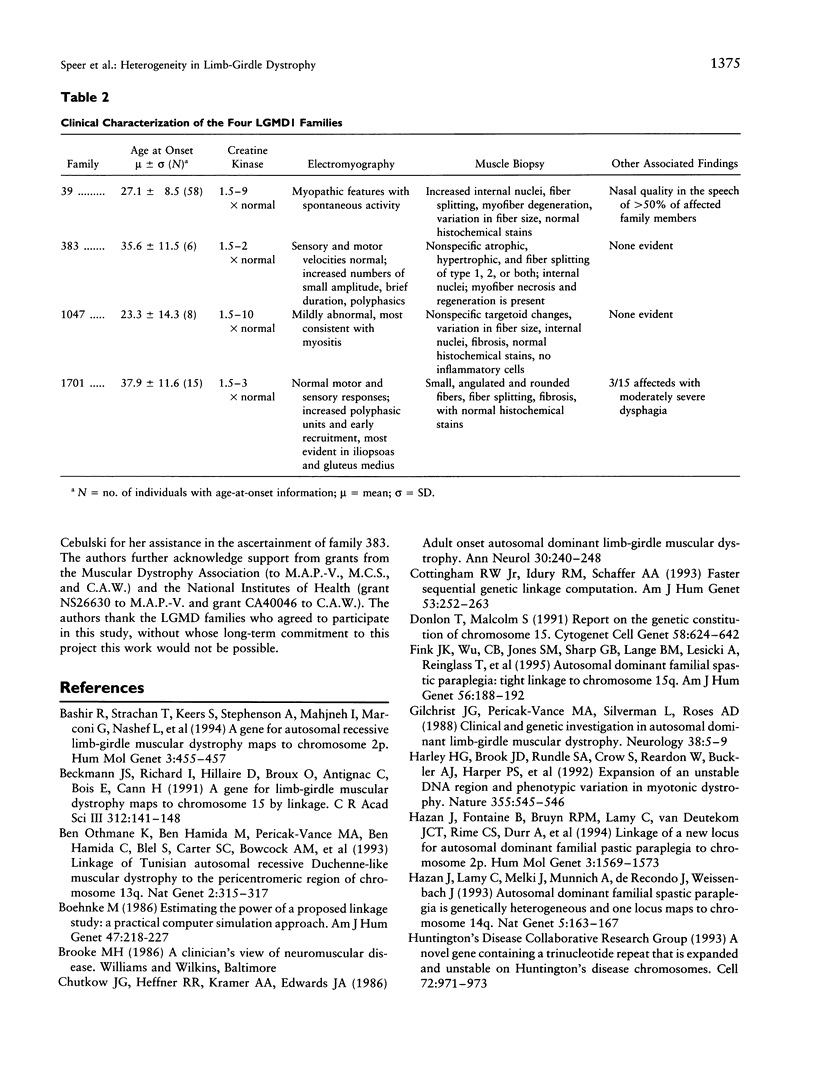
Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD) is a diagnostic classification encompassing a broad group of proximal myopathies. A gene for the dominant form of LGMD (LGMD1A) has recently been localized to a 7-cM region of chromosome 5q between D5S178 and IL9. We studied three additional dominant LGMD families for linkage to these two markers and excluded all from localization to this region, providing evidence for locus heterogeneity within the dominant form of LGMD. Although the patterns of muscle weakness were similar in all families studied, the majority of affected family members in the chromosome 5–linked pedigree have a dysarthric speech pattern, which is not present in any of the five unlinked families. The demonstration of heterogeneity within autosomal dominant LGMD is the first step in attempting to subclassify these families with similar clinical phenotypes on a molecular level.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bashir R., Strachan T., Keers S., Stephenson A., Mahjneh I., Marconi G., Nashef L., Bushby K. M. A gene for autosomal recessive limb-girdle muscular dystrophy maps to chromosome 2p. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Mar;3(3):455–457. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.3.455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann J. S., Richard I., Hillaire D., Broux O., Antignac C., Bois E., Cann H., Cottingham R. W., Jr, Feingold N., Feingold J. A gene for limb-girdle muscular dystrophy maps to chromosome 15 by linkage. C R Acad Sci III. 1991;312(4):141–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben Othmane K., Ben Hamida M., Pericak-Vance M. A., Ben Hamida C., Blel S., Carter S. C., Bowcock A. M., Petruhkin K., Gilliam T. C., Roses A. D. Linkage of Tunisian autosomal recessive Duchenne-like muscular dystrophy to the pericentromeric region of chromosome 13q. Nat Genet. 1992 Dec;2(4):315–317. doi: 10.1038/ng1292-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehnke M. Sample-size guidelines for linkage analysis of a dominant locus for a quantitative trait by the method of lod scores. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Aug;47(2):218–227. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottingham R. W., Jr, Idury R. M., Schäffer A. A. Faster sequential genetic linkage computations. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jul;53(1):252–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink J. K., Wu C. T., Jones S. M., Sharp G. B., Lange B. M., Lesicki A., Reinglass T., Varvil T., Otterud B., Leppert M. Autosomal dominant familial spastic paraplegia: tight linkage to chromosome 15q. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jan;56(1):188–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilchrist J. M., Pericak-Vance M., Silverman L., Roses A. D. Clinical and genetic investigation in autosomal dominant limb-girdle muscular dystrophy. Neurology. 1988 Jan;38(1):5–9. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley H. G., Brook J. D., Rundle S. A., Crow S., Reardon W., Buckler A. J., Harper P. S., Housman D. E., Shaw D. J. Expansion of an unstable DNA region and phenotypic variation in myotonic dystrophy. Nature. 1992 Feb 6;355(6360):545–546. doi: 10.1038/355545a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazan J., Fontaine B., Bruyn R. P., Lamy C., van Deutekom J. C., Rime C. S., Dürr A., Melki J., Lyon-Caen O., Agid Y. Linkage of a new locus for autosomal dominant familial spastic paraplegia to chromosome 2p. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Sep;3(9):1569–1573. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.9.1569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazan J., Lamy C., Melki J., Munnich A., de Recondo J., Weissenbach J. Autosomal dominant familial spastic paraplegia is genetically heterogeneous and one locus maps to chromosome 14q. Nat Genet. 1993 Oct;5(2):163–167. doi: 10.1038/ng1093-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabs E. W., Li X., Lovett M., Yamaoka L. H., Taylor E., Speer M. C., Coss C., Cadle R., Hall B., Brown K. Genetic and physical mapping of the Treacher Collins syndrome locus with respect to loci in the chromosome 5q3 region. Genomics. 1993 Oct;18(1):7–13. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. E., Strehler D. A. Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy: clinical manifestations and detection of preclinical disease. Pediatrics. 1968 Feb;41(2):495–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON N. E., CHUNG C. S. Formal genetics of muscular dystrophy. Am J Hum Genet. 1959 Dec;11:360–379. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan M., Tsilfidis C., Sabourin L., Shutler G., Amemiya C., Jansen G., Neville C., Narang M., Barceló J., O'Hoy K. Myotonic dystrophy mutation: an unstable CTG repeat in the 3' untranslated region of the gene. Science. 1992 Mar 6;255(5049):1253–1255. doi: 10.1126/science.1546325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman A., Thomas N., Coakley J., Harper P. Distinction of Becker from limb-girdle muscular dystrophy by means of dystrophin cDNA probes. Lancet. 1989 Mar 4;1(8636):466–468. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91367-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploughman L. M., Boehnke M. Estimating the power of a proposed linkage study for a complex genetic trait. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;44(4):543–551. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberds S. L., Leturcq F., Allamand V., Piccolo F., Jeanpierre M., Anderson R. D., Lim L. E., Lee J. C., Tomé F. M., Romero N. B. Missense mutations in the adhalin gene linked to autosomal recessive muscular dystrophy. Cell. 1994 Aug 26;78(4):625–633. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90527-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneiderman L. J., Sampson W. I., Schoene W. C., Haydon G. B. Genetic studies of a family with two unusual autosomal dominant conditions: muscular dystrophy and Pelger-Huet anomaly. Clinical, pathologic and linkage considerations. Am J Med. 1969 Mar;46(3):380–393. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäffer A. A., Gupta S. K., Shriram K., Cottingham R. W., Jr Avoiding recomputation in linkage analysis. Hum Hered. 1994 Jul-Aug;44(4):225–237. doi: 10.1159/000154222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shokeir M. H., Kobrinsky N. L. Autosomal recessive muscular dystrophy in Manitoba Hutterites. Clin Genet. 1976 Feb;9(2):197–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1976.tb01568.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speer M. C., Yamaoka L. H., Gilchrist J. H., Gaskell C. P., Stajich J. M., Vance J. M., Kazantsev A., Lastra A. A., Haynes C. S., Beckmann J. S. Confirmation of genetic heterogeneity in limb-girdle muscular dystrophy: linkage of an autosomal dominant form to chromosome 5q. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Jun;50(6):1211–1217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szubryt S. R., Neuman W. L., Westbrook C. A. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the D5S178 locus. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jan;2(1):90–90. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.1.90-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., Polymeropoulos M. H., May P. E., Kwitek A. E., Xiao H., McPherson J. D., Wasmuth J. J. Mapping of human chromosome 5 microsatellite DNA polymorphisms. Genomics. 1991 Nov;11(3):695–700. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90077-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaoka L. H., Pericak-Vance M. A., Speer M. C., Gaskell P. C., Jr, Stajich J., Haynes C., Hung W. Y., Laberge C., Thibault M. C., Mathieu J. Tight linkage of creatine kinase (CKMM) to myotonic dystrophy on chromosome 19. Neurology. 1990 Feb;40(2):222–226. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.2.222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaoka L. H., Westbrook C. A., Speer M. C., Gilchrist J. M., Jabs E. W., Schweins E. G., Stajich J. M., Gaskell P. C., Roses A. D., Pericak-Vance M. A. Development of a microsatellite genetic map spanning 5q31-q33 and subsequent placement of the LGMD1A locus between D5S178 and IL9. Neuromuscul Disord. 1994 Sep-Nov;4(5-6):471–475. doi: 10.1016/0960-8966(94)90086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. R., Emery A. E. A population study of adult onset limb-girdle muscular dystrophy. J Med Genet. 1985 Aug;22(4):250–257. doi: 10.1136/jmg.22.4.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



