Abstract
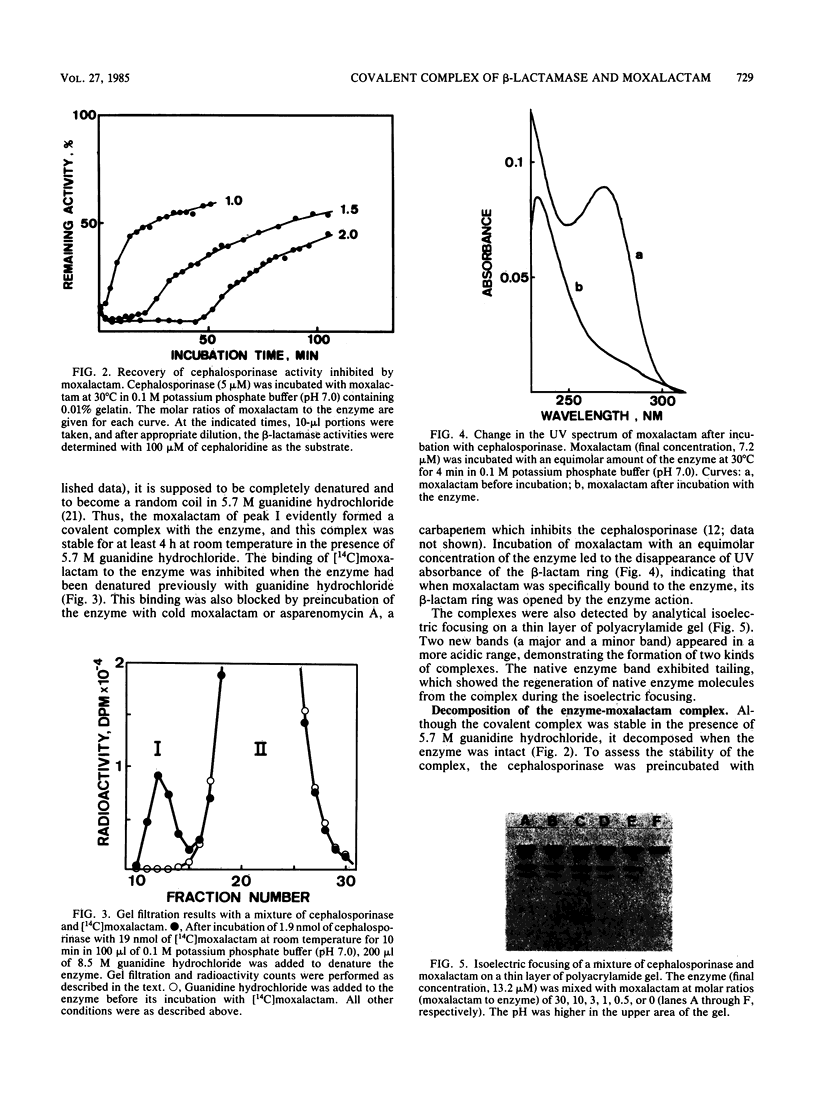
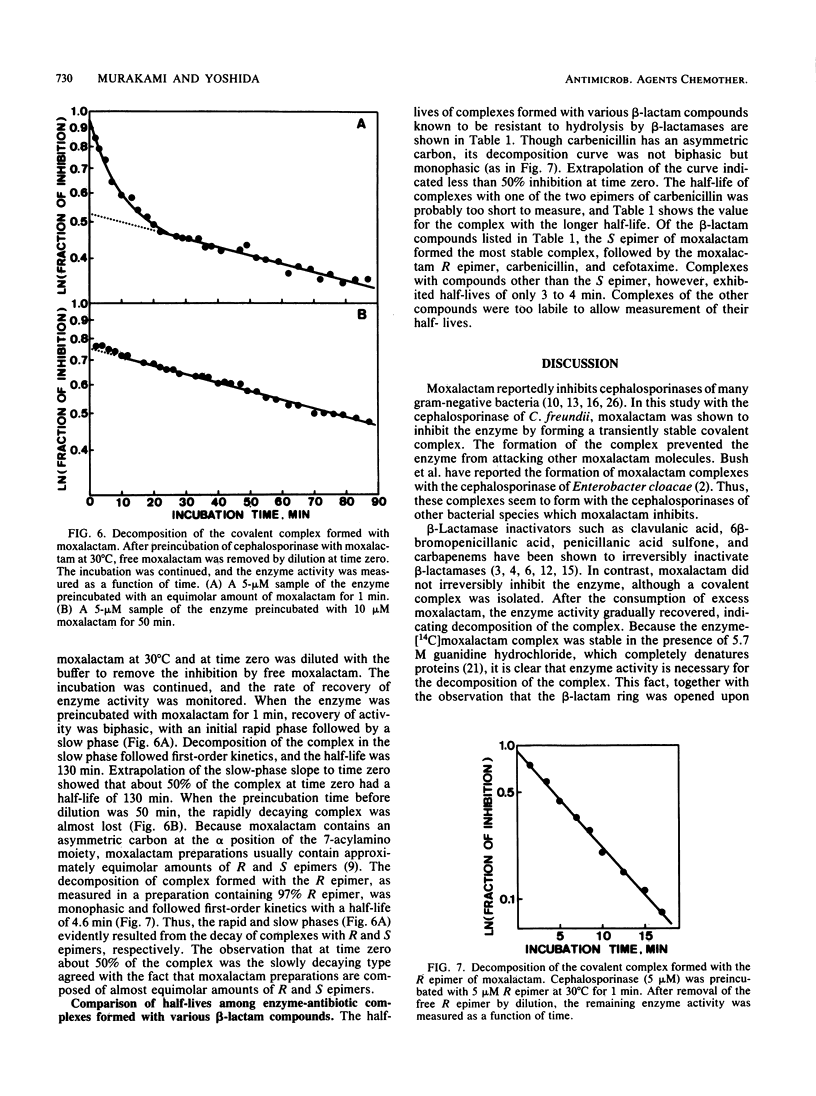
The inhibition of Citrobacter freundii cephalosporinase activity by moxalactam is shown to be due to the formation of a transiently stable covalent complex, probably acyl enzyme. The covalent complex formed was identified by coelution of [14C] moxalactam with the enzyme by using Sephadex G-25 gel filtration in the presence of 5.7 M guanidine hydrochloride and by analytical isoelectric focusing. Both the side-chain carboxyl group and the 7 alpha-methoxy group of moxalactam were necessary to stabilize the complex. Moxalactam is racemic with respect to the alpha carbon of the 7 beta-acylamino side chain, and the complex with the R epimer (half-life, 4.6 min) decomposed much more rapidly than that formed with the S epimer (half-life, 130 min). For other beta-lactam antibiotics that were stable to beta-lactamase, the half-lives of enzyme-antibiotic complexes were less than 4 min.
Full text
PDF



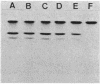
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson E. G., Pratt R. F. Pre-steady state beta-lactamase kinetics. Observation of a covalent intermediate during turnover of a fluorescent cephalosporin by the beta-lactamase of STaphylococcus aureus PC1. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11401–11404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush K., Freudenberger J. S., Sykes R. B. Interaction of azthreonam and related monobactams with beta-lactamases from gram-negative bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Sep;22(3):414–420. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.3.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnas R. L., Fisher J., Knowles J. R. Chemical studies on the inactivation of Escherichia coli RTEM beta-lactamase by clavulanic acid. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2185–2189. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnas R. L., Knowles J. R. Inhibition of the RTEM beta-lactamase from Escherichia coli. Interaction of enzyme with derivatives of olivanic acid. Biochemistry. 1981 May 12;20(10):2732–2737. doi: 10.1021/bi00513a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citri N., Pollock M. R. The biochemistry and function of beta-lactamase (penicillinase). Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1966;28:237–323. doi: 10.1002/9780470122730.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English A. R., Retsema J. A., Girard A. E., Lynch J. E., Barth W. E. CP-45,899, a beta-lactamase inhibitor that extends the antibacterial spectrum of beta-lactams: initial bacteriological characterization. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):414–419. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher J., Belasco J. G., Khosla S., Knowles J. R. beta-Lactamase proceeds via an acyl-enzyme intermediate. Interaction of the Escherichia coli RTEM enzyme with cefoxitin. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 24;19(13):2895–2901. doi: 10.1021/bi00554a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konaka R., Kuruma K., Nishimura R., Kimura Y., Yoshida T. High-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of a new beta-lactam antibiotic, 6059-S (moxalactam). J Chromatogr. 1981 Sep 11;225(1):169–178. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)80256-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami K., Doi M., Yoshida T. Asparenomycins A, B and C, new carbapenem antibiotics. V. Inhibition of beta-lactamases. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1982 Jan;35(1):39–45. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.35.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami K., Yoshida T. Role of the 7 alpha-methoxy and side-chain carboxyl of moxalactam in beta-lactamase stability and antibacterial activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jan;19(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt R. F., Loosemore M. J. 6-beta-bromopenicillanic acid, a potent beta-lactamase inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4145–4149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Sykes R. B. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their possible physiological role. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;9:31–88. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H. The beta-lactamase stability of a novel beta-lactam antibiotic containing a 7 alpha-methoxyoxacephem nucleus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Jul;6(4):445–453. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.4.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C. Inducible beta-lactamases and non-hydrolytic resistance mechanisms. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Jan;13(1):1–3. doi: 10.1093/jac/13.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeberg A. H., Tolxdorff-Neutzling R. M., Wiedemann B. Chromosomal beta-lactamases of Enterobacter cloacae are responsible for resistance to third-generation cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):918–925. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji J., Hinoo H., Sakazaki R., Tsuji N., Nagashima K., Matsumoto K., Takahashi Y., Kozuki S., Hattori T., Kondo E. Asparenomycins A, B and C, new carbapenem antibiotics. II. Isolation and chemical characterization. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1982 Jan;35(1):15–23. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.35.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C. Protein denaturation. Adv Protein Chem. 1968;23:121–282. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60401-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Then R. L., Angehrn P. Trapping of nonhydrolyzable cephalosporins by cephalosporinases in Enterobacter cloacae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a possible resistance mechanism. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 May;21(5):711–717. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.5.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Wills P. J., Bedford K. A. Epimers of moxalactam: in vitro comparison of activity and stability. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jul;20(1):30–32. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Yokota T. Beta-lactamase-directed barrier for penicillins of Escherichia coli carrying R plasmids. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jun;11(6):936–940. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.6.936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T., Matsuura S., Mayama M., Kameda Y., Kuwahara S. Moxalactam (6059-S), a novel 1-oxa-beta-lactam with an expanded antibacterial spectrum: laboratory evaluation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Mar;17(3):302–312. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.3.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T. Structural requirements for antibacterial activity and beta-lactamase stability of 7 beta-arylmalonylamino-7 alpha-methoxy-1-oxacephems. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 May 16;289(1036):231–237. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1980.0041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]