Abstract
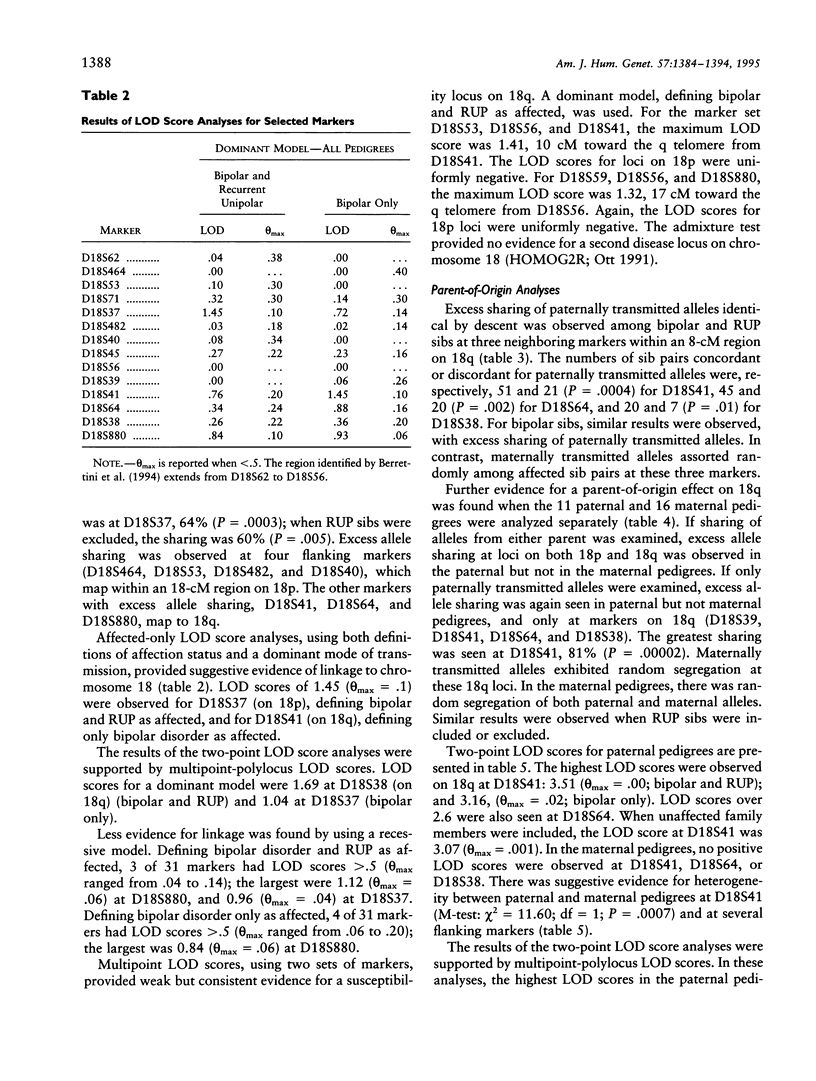
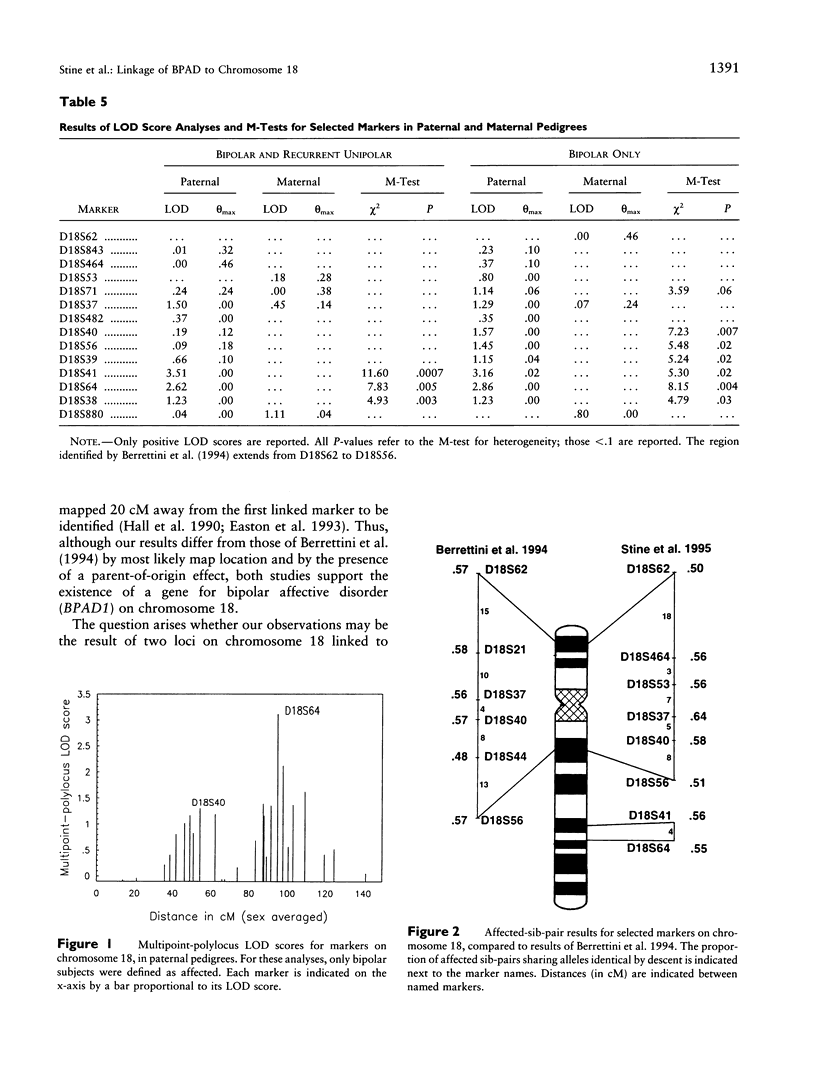
A susceptibility gene on chromosome 18 and a parent-of-origin effect have been suggested for bipolar affective disorder (BPAD). We have studied 28 nuclear families selected for apparent unilineal transmission of the BPAD phenotype, by using 31 polymorphic markers spanning chromosome 18. Evidence for linkage was tested with affected-sib-pair and LOD score methods under two definitions of the affected phenotype. The affected-sib-pair analyses indicated excess allele sharing for markers on 18p within the region reported previously. The greatest sharing was at D18S37: 64% in bipolar and recurrent unipolar (RUP) sib pairs (P = .0006). In addition, excess sharing of the paternally, but not maternally, transmitted alleles was observed at three markers on 18q: at D18S41, 51 bipolar and RUP sib pairs were concordant for paternally transmitted alleles, and 21 pairs were discordant (P = .0004). The evidence for linkage to loci on both 18p and 18q was strongest in the 11 paternal pedigrees, i.e., those in which the father or one of the father's sibs is affected. In these pedigrees, the greatest allele sharing (81%; P = .00002) and the highest LOD score (3.51; θ = 0.0) were observed at D18S41. Our results provide further support for linkage of BPAD to chromosome 18 and the first molecular evidence for a parent-of-origin effect operating in this disorder. The number of loci involved, and their precise location, require further study.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron M., Freimer N. F., Risch N., Lerer B., Alexander J. R., Straub R. E., Asokan S., Das K., Peterson A., Amos J. Diminished support for linkage between manic depressive illness and X-chromosome markers in three Israeli pedigrees. Nat Genet. 1993 Jan;3(1):49–55. doi: 10.1038/ng0193-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. Linkage between an X-chromosome marker (deutan color blindness) and bipolar affective illness. Occurrence in the family of a lithium carbonate-responsive schizo-affective proband. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1977 Jun;34(6):721–725. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1977.01770180107010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berrettini W. H., Ferraro T. N., Goldin L. R., Weeks D. E., Detera-Wadleigh S., Nurnberger J. I., Jr, Gershon E. S. Chromosome 18 DNA markers and manic-depressive illness: evidence for a susceptibility gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):5918–5921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.5918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coryell W., Endicott J., Andreasen N., Keller M. Bipolar I, bipolar II, and nonbipolar major depression among the relatives of affectively ill probands. Am J Psychiatry. 1985 Jul;142(7):817–821. doi: 10.1176/ajp.142.7.817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe R. R., Smouse P. E. The genetic implications of age-dependent penetrance in manic-depressive illness. J Psychiatr Res. 1977;13(4):273–285. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(77)90015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easton D. F., Bishop D. T., Ford D., Crockford G. P. Genetic linkage analysis in familial breast and ovarian cancer: results from 214 families. The Breast Cancer Linkage Consortium. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Apr;52(4):678–701. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egeland J. A., Gerhard D. S., Pauls D. L., Sussex J. N., Kidd K. K., Allen C. R., Hostetter A. M., Housman D. E. Bipolar affective disorders linked to DNA markers on chromosome 11. 1987 Feb 26-Mar 4Nature. 325(6107):783–787. doi: 10.1038/325783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endicott J., Nee J., Andreasen N., Clayton P., Keller M., Coryell W. Bipolar II. Combine or keep separate? J Affect Disord. 1985 Jan-Feb;8(1):17–28. doi: 10.1016/0165-0327(85)90068-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endicott J., Spitzer R. L. A diagnostic interview: the schedule for affective disorders and schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1978 Jul;35(7):837–844. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1978.01770310043002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gantz I., Tashiro T., Barcroft C., Konda Y., Shimoto Y., Miwa H., Glover T., Munzert G., Yamada T. Localization of the genes encoding the melanocortin-2 (adrenocorticotropic hormone) and melanocortin-3 receptors to chromosomes 18p11.2 and 20q13.2-q13.3 by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Genomics. 1993 Oct;18(1):166–167. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon E. S., Targum S. D., Matthysse S., Bunney W. E., Jr Color blindness not closely linked to bipolar illness. Report of a new pedigree series. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1979 Dec;36(13):1423–1430. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1979.01780130041005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin L. R., Gershon E. S., Targum S. D., Sparkes R. S., McGinniss M. Segregation and linkage analyses in families of patients with bipolar, unipolar, and schizoaffective mood disorders. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Mar;35(2):274–287. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyapay G., Morissette J., Vignal A., Dib C., Fizames C., Millasseau P., Marc S., Bernardi G., Lathrop M., Weissenbach J. The 1993-94 Généthon human genetic linkage map. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2 Spec No):246–339. doi: 10.1038/ng0694supp-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. M., Lee M. K., Newman B., Morrow J. E., Anderson L. A., Huey B., King M. C. Linkage of early-onset familial breast cancer to chromosome 17q21. Science. 1990 Dec 21;250(4988):1684–1689. doi: 10.1126/science.2270482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. T., Reed R. R. Golf: an olfactory neuron specific-G protein involved in odorant signal transduction. Science. 1989 May 19;244(4906):790–795. doi: 10.1126/science.2499043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelsoe J. R., Ginns E. I., Egeland J. A., Gerhard D. S., Goldstein A. M., Bale S. J., Pauls D. L., Long R. T., Kidd K. K., Conte G. Re-evaluation of the linkage relationship between chromosome 11p loci and the gene for bipolar affective disorder in the Old Order Amish. Nature. 1989 Nov 16;342(6247):238–243. doi: 10.1038/342238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruglyak L., Lander E. S. High-resolution genetic mapping of complex traits. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 May;56(5):1212–1223. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Green P. Construction of multilocus genetic linkage maps in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2363–2367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Schork N. J. Genetic dissection of complex traits. Science. 1994 Sep 30;265(5181):2037–2048. doi: 10.1126/science.8091226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON N. E. The detection and estimation of linkage between the genes for elliptocytosis and the Rh blood type. Am J Hum Genet. 1956 Jun;8(2):80–96. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McInnis M. G., McMahon F. J., Chase G. A., Simpson S. G., Ross C. A., DePaulo J. R., Jr Anticipation in bipolar affective disorder. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Aug;53(2):385–390. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon F. J., Stine O. C., Chase G. A., Meyers D. A., Simpson S. G., DePaulo J. R., Jr Influence of clinical subtype, sex, and lineality on age at onset of major affective disorder in a family sample. Am J Psychiatry. 1994 Feb;151(2):210–215. doi: 10.1176/ajp.151.2.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon F. J., Stine O. C., Meyers D. A., Simpson S. G., DePaulo J. R. Patterns of maternal transmission in bipolar affective disorder. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jun;56(6):1277–1286. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendlewicz J., Fleiss J. L., Fieve R. R. Evidence for X-linkage in the transmission of manic-depressive illness. JAMA. 1972 Dec 25;222(13):1624–1627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendlewicz J., Rainer J. D. Morbidity risk and genetic transmission in manic-depressive illness. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Nov;26(6):692–701. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rourke D. H., McGuffin P., Reich T. Genetic analysis of manic-depressive illness. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1983 Sep;62(1):51–59. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330620108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich T., Clayton P. J., Winokur G. Family history studies: V. The genetics of mania. Am J Psychiatry. 1969 Apr;125(10):1358–1369. doi: 10.1176/ajp.125.10.1358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice J., Reich T., Andreasen N. C., Endicott J., Van Eerdewegh M., Fishman R., Hirschfeld R. M., Klerman G. L. The familial transmission of bipolar illness. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1987 May;44(5):441–447. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1987.01800170063009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins L. N., Helzer J. E., Weissman M. M., Orvaschel H., Gruenberg E., Burke J. D., Jr, Regier D. A. Lifetime prevalence of specific psychiatric disorders in three sites. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1984 Oct;41(10):949–958. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1984.01790210031005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalling M., Hudson T. J., Buetow K. H., Housman D. E. Direct detection of novel expanded trinucleotide repeats in the human genome. Nat Genet. 1993 Jun;4(2):135–139. doi: 10.1038/ng0693-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson S. G., Folstein S. E., Meyers D. A., DePaulo J. R. Assessment of lineality in bipolar I linkage studies. Am J Psychiatry. 1992 Dec;149(12):1660–1665. doi: 10.1176/ajp.149.12.1660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straub R. E., Speer M. C., Luo Y., Rojas K., Overhauser J., Ott J., Gilliam T. C. A microsatellite genetic linkage map of human chromosome 18. Genomics. 1993 Jan;15(1):48–56. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suarez B. K., Van Eerdewegh P. A comparison of three affected-sib-pair scoring methods to detect HLA-linked disease susceptibility genes. Am J Med Genet. 1984 May;18(1):135–146. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320180117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger J. D. A powerful likelihood method for the analysis of linkage disequilibrium between trait loci and one or more polymorphic marker loci. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Mar;56(3):777–787. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger J. D., Ott J. A novel polylocus method for linkage analysis using the lod-score or affected sib-pair method. Genet Epidemiol. 1993;10(6):477–482. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370100625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh F. S., Barton C. H., Putt W., Moore S. E., Kelsell D., Spurr N., Goodfellow P. N. N-cadherin gene maps to human chromosome 18 and is not linked to the E-cadherin gene. J Neurochem. 1990 Sep;55(3):805–812. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. E., Lehner T., Squires-Wheeler E., Kaufmann C., Ott J. Measuring the inflation of the lod score due to its maximization over model parameter values in human linkage analysis. Genet Epidemiol. 1990;7(4):237–243. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370070402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



