Abstract
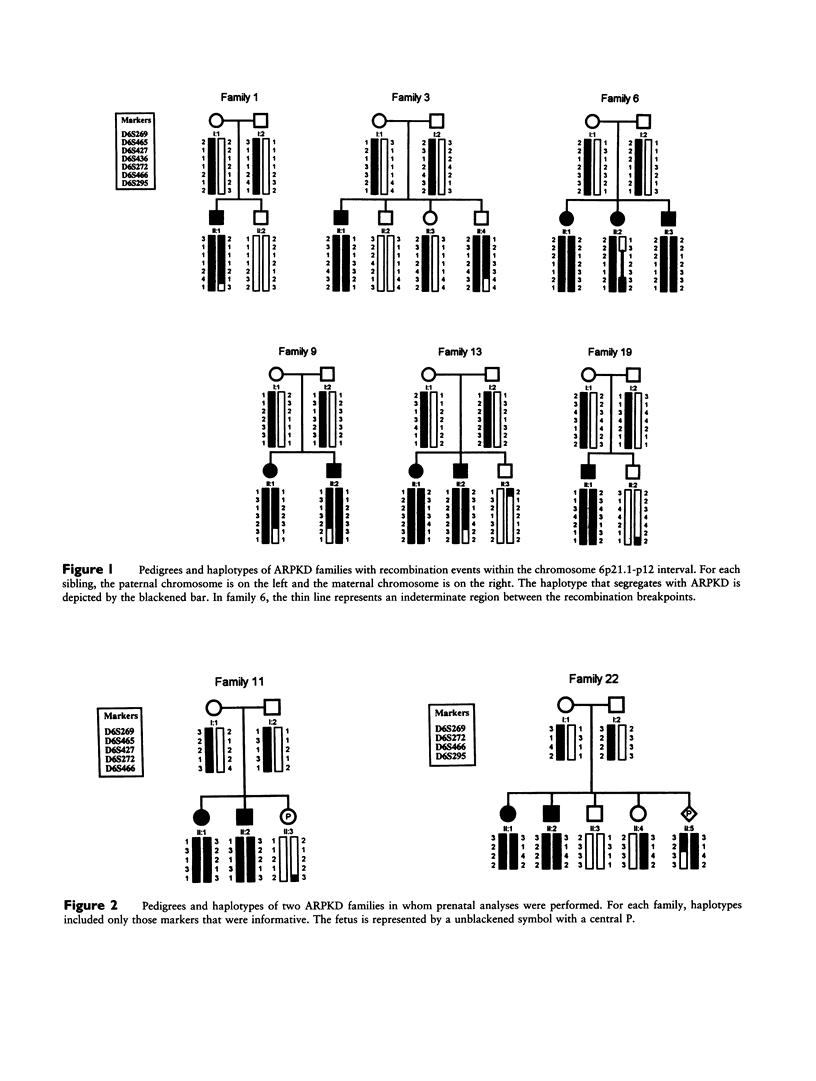
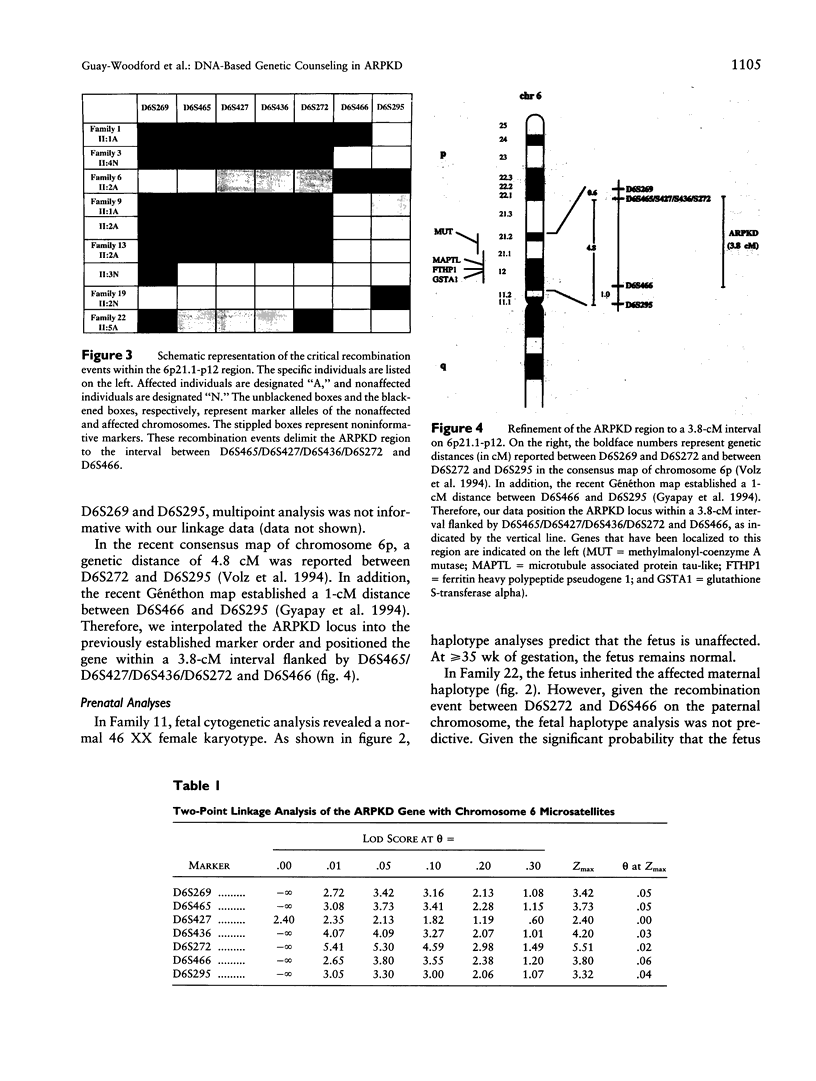
Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) is a one of the most common hereditary renal cystic diseases in children. Its clinical spectrum is widely variable with most cases presenting in infancy. Most affected neonates die within the first few hours of life. At present, prenatal diagnosis relies on fetal sonography, which is often imprecise in detecting even the severe form of the disease. Recently, in a cohort of families with mostly milder ARPKD phenotypes, an ARPKD locus was mapped to a 13-cM region of chromosome 6p21-cen. To determine whether severe perinatal ARPKD also maps to chromosome 6p, we have analyzed the segregation of seven microsatellite markers from the ARPKD interval in 22 families with the severe phenotype. In the majority of the affected infants, ARPKD was documented by histopathology. Our data confirm linkage and refine the ARPKD region to a 3.8-cM interval, delimited by the markers D6S465/D6S427/D6S436/D6S272 and D6S466. Taken together, these results suggest that, despite the wide variability in clinical phenotypes, there is a single ARPKD gene. These linkage data and the absence of genetic heterogeneity in all families tested to date have important implications for DNA-based prenatal diagnoses as well as for the isolation of the ARPKD gene.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blyth H., Ockenden B. G. Polycystic disease of kidney and liver presenting in childhood. J Med Genet. 1971 Sep;8(3):257–284. doi: 10.1136/jmg.8.3.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzustowicz L. M., Lehner T., Castilla L. H., Penchaszadeh G. K., Wilhelmsen K. C., Daniels R., Davies K. E., Leppert M., Ziter F., Wood D. Genetic mapping of chronic childhood-onset spinal muscular atrophy to chromosome 5q11.2-13.3. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):540–541. doi: 10.1038/344540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyapay G., Morissette J., Vignal A., Dib C., Fizames C., Millasseau P., Marc S., Bernardi G., Lathrop M., Weissenbach J. The 1993-94 Généthon human genetic linkage map. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2 Spec No):246–339. doi: 10.1038/ng0694supp-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan B. S., Fay J., Shah V., Dillon M. J., Barratt T. M. Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol. 1989 Jan;3(1):43–49. doi: 10.1007/BF00859625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käriäinen H., Koskimies O., Norio R. Dominant and recessive polycystic kidney disease in children: evaluation of clinical features and laboratory data. Pediatr Nephrol. 1988 Jul;2(3):296–302. doi: 10.1007/BF00858681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Multilocus linkage analysis in humans: detection of linkage and estimation of recombination. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):482–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer J. H., Lee-Tischler M. J., Kwon H. Y., Schrick J. J., Avner E. D., Sweeney W. E., Godfrey V. L., Cacheiro N. L., Wilkinson J. E., Woychik R. P. Candidate gene associated with a mutation causing recessive polycystic kidney disease in mice. Science. 1994 May 27;264(5163):1329–1333. doi: 10.1126/science.8191288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mücher G., Wirth B., Zerres K. Refining the map and defining flanking markers of the gene for autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease on chromosome 6p21.1-p12. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Dec;55(6):1281–1284. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSATHANONDH V., POTTER E. L. PATHOGENESIS OF POLYCYSTIC KIDNEYS. TYPE 1 DUE TO HYPERPLASIA OF INTERSTITIAL PORTIONS OF COLLECTING TUBULES. Arch Pathol. 1964 May;77:466–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preminger G. M., Koch W. E., Fried F. A., McFarland E., Murphy E. D., Mandell J. Murine congenital polycystic kidney disease: a model for studying development of cystic disease. J Urol. 1982 Mar;127(3):556–560. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)53911-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuss A., Wladimiroff J. W., Niermeyer M. F. Sonographic, clinical and genetic aspects of prenatal diagnosis of cystic kidney disease. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1991;17(7):687–694. doi: 10.1016/0301-5629(91)90100-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon E. A., Cook S., Davisson M. T., D'Eustachio P., Guay-Woodford L. M. The mouse congenital polycystic kidney (cpk) locus maps within 1.3 cM of the chromosome 12 marker D12Nyu2. Genomics. 1994 May 15;21(2):415–418. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsui L. C. The spectrum of cystic fibrosis mutations. Trends Genet. 1992 Nov;8(11):392–398. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90301-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volz A., Boyle J. M., Cann H. M., Cottingham R. W., Orr H. T., Ziegler A. Report of the Second International Workshop on Human Chromosome 6. Genomics. 1994 May 15;21(2):464–472. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerres K. Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. Clin Investig. 1992 Sep;70(9):794–801. doi: 10.1007/BF00180750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerres K., Hansmann M., Mallmann R., Gembruch U. Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. Problems of prenatal diagnosis. Prenat Diagn. 1988 Mar;8(3):215–229. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970080308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerres K., Mücher G., Bachner L., Deschennes G., Eggermann T., Käriäinen H., Knapp M., Lennert T., Misselwitz J., von Mühlendahl K. E. Mapping of the gene for autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) to chromosome 6p21-cen. Nat Genet. 1994 Jul;7(3):429–432. doi: 10.1038/ng0794-429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


