Abstract
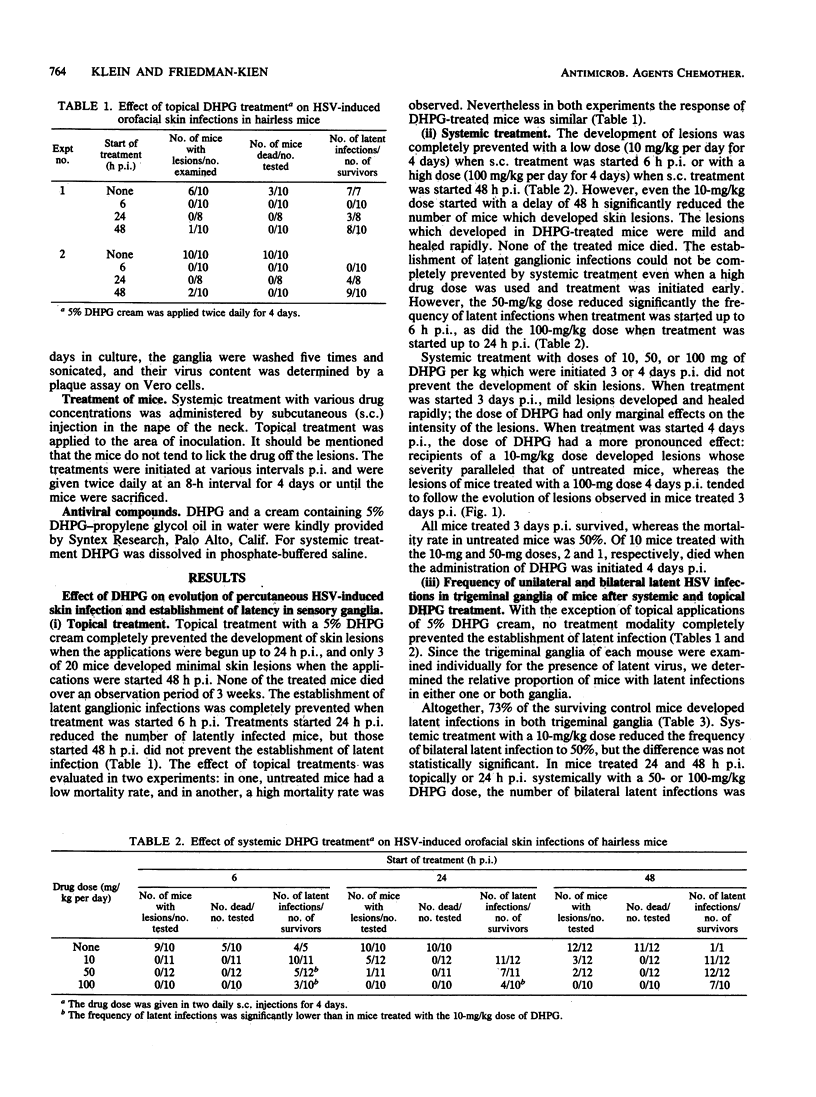
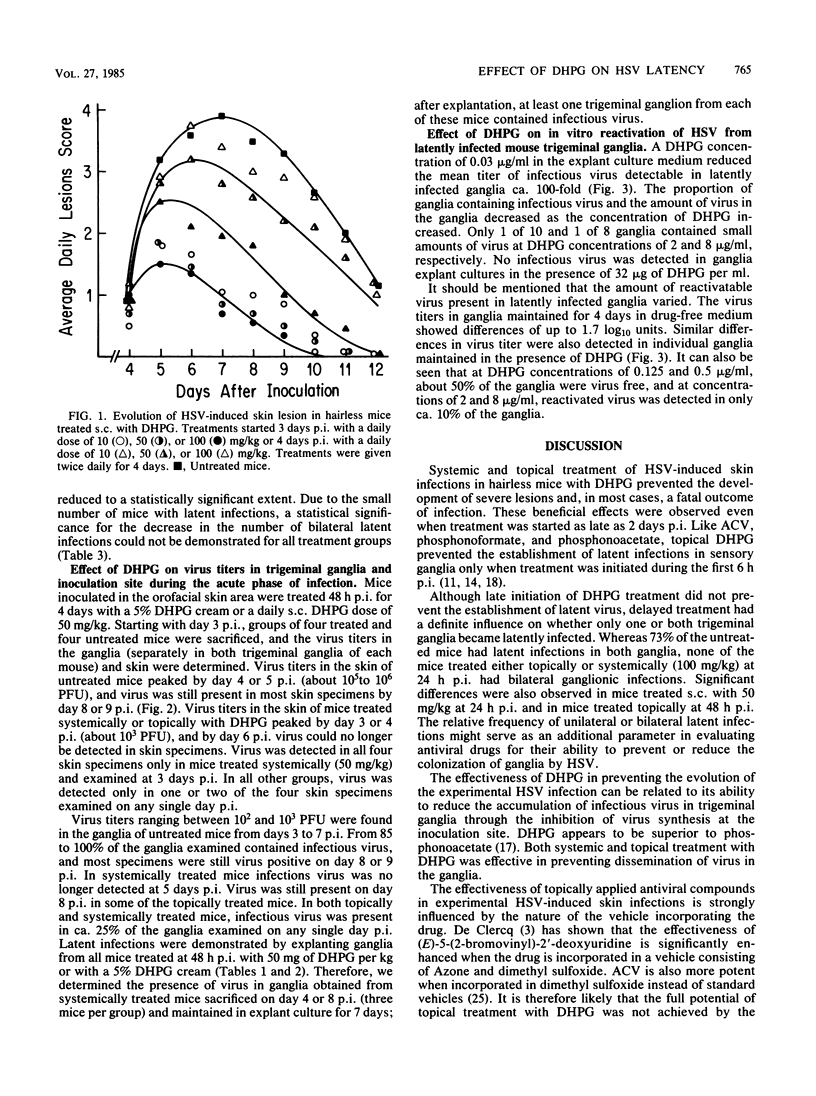
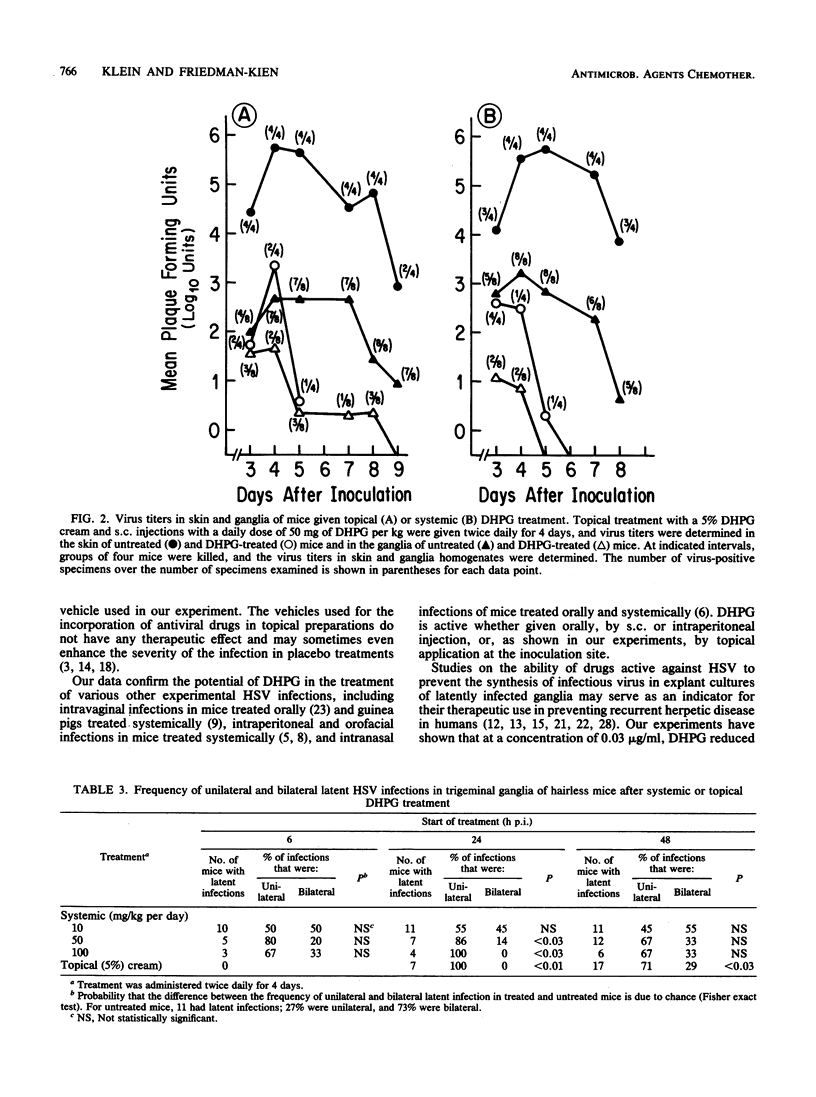
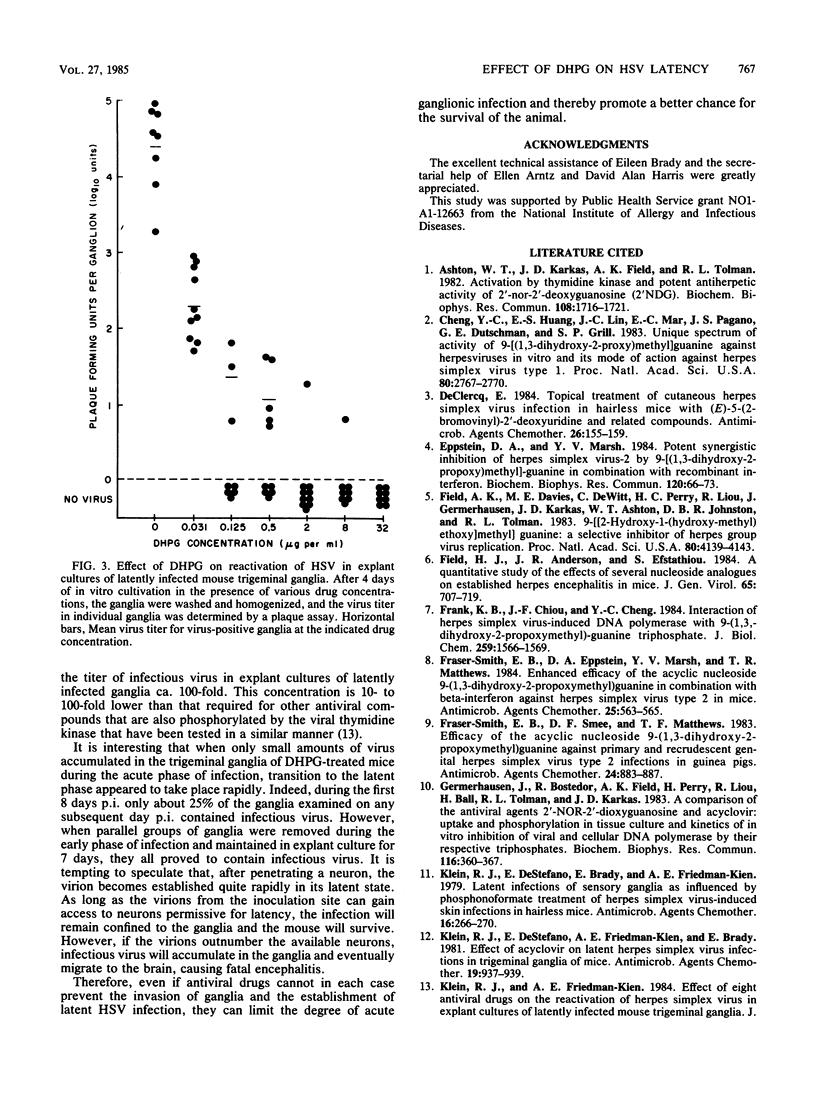
The effect of topical and systemic treatment with 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine on the evolution of herpes simplex virus-induced skin infection in hairless mice was investigated. Systemic (subcutaneous) treatment with a 10-mg/kg dose and topical applications with a 5% cream started up to 48 h after infection prevented the development of severe skin lesions and a fatal outcome. However, the establishment of latent infections was prevented only by topical treatment started at 6 h after infection. Systemic (50 mg/kg) and topical treatments started 48 h after infection reduced virus titers in the skin and ganglia and promoted rapid clearance of virus from these sites. The clearance of infectious virus from ganglia during the acute phase of infection was followed by early establishment of latency. 9-(1,3-Dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine (0.03 microgram/ml) significantly inhibited the synthesis of infectious virus in explant cultures of latently infected ganglia, and at concentrations higher than 8 micrograms/ml no infectious virus was detectable in ganglia explant cultures.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashton W. T., Karkas J. D., Field A. K., Tolman R. L. Activation by thymidine kinase and potent antiherpetic activity of 2'-nor-2'-deoxyguanosine (2'NDG). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Oct 29;108(4):1716–1721. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(82)80109-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. C., Huang E. S., Lin J. C., Mar E. C., Pagano J. S., Dutschman G. E., Grill S. P. Unique spectrum of activity of 9-[(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxy)methyl]-guanine against herpesviruses in vitro and its mode of action against herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2767–2770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eppstein D. A., Marsh Y. V. Potent synergistic inhibition of herpes simplex virus-2 by 9-[(1, 3-dihydroxy-2-propoxy)methyl]guanine in combination with recombinant interferons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Apr 16;120(1):66–73. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91414-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field A. K., Davies M. E., DeWitt C., Perry H. C., Liou R., Germershausen J., Karkas J. D., Ashton W. T., Johnston D. B., Tolman R. L. 9-([2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethoxy]methyl)guanine: a selective inhibitor of herpes group virus replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4139–4143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank K. B., Chiou J. F., Cheng Y. C. Interaction of herpes simplex virus-induced DNA polymerase with 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1566–1569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser-Smith E. B., Eppstein D. A., Marsh Y. V., Matthews T. R. Enhanced efficacy of the acyclic nucleoside 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine in combination with beta-interferon against herpes simplex virus type 2 in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 May;25(5):563–565. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.5.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser-Smith E. B., Smee D. F., Matthews T. R. Efficacy of the acyclic nucleoside 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine against primary and recrudescent genital herpes simplex virus type 2 infections in guinea pigs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Dec;24(6):883–887. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.6.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germershausen J., Bostedor R., Field A. K., Perry H., Liou R., Bull H., Tolman R. L., Karkas J. D. A comparison of the antiviral agents 2'-nor-2'-deoxyguanosine and acyclovir: uptake and phosphorylation in tissue culture and kinetics of in vitro inhibition of viral and cellular DNA polymerases by their respective triphosphates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Oct 31;116(2):360–367. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90530-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. J., DeStefano E., Brady E., Friedman-Kien A. E. Latent infections of sensory ganglia as influenced by phosphonoformate treatment of herpes simplex virus-induced skin infections in hairless mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Sep;16(3):266–270. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.3.266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. J., DeStefano E., Friedman-Kien A. E., Brady E. Effect of acyclovir on latent herpes simplex virus infections in trigeminal ganglia of mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):937–939. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. J., Friedman-Kien A. E., DeStefano E. Effect of discontinuous acyclovir treatment on in vitro reactivation of herpes simplex virus from latently infected trigeminal ganglia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jul;24(1):129–131. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. J., Friedman-Kien A. E., DeStefano E. Latent herpes simplex virus infections in sensory ganglia of hairless mice prevented by acycloguanosine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 May;15(5):723–729. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.5.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. J., Friedman-Kien A. E., Fondak A. A., Buimovici-Klein E. Immune response and latent infection after topical treatment of herpes simplex virus infection in hairless mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):842–848. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.842-848.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. J., Friedman-Kien A. E., Kaley L., Brady E. Effects of topical applications of phosphonoacetate on colonization of mouse trigeminal ganglia with herpes simplex virus type 1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jul;26(1):65–68. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. J., Friedman-Kien A. E., Yellin P. B. Orofacial herpes simplex virus infection in hairless mice: latent virus in trigeminal ganglia after topical antiviral treatment. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):130–135. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.130-135.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mar E. C., Cheng Y. C., Huang E. S. Effect of 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine on human cytomegalovirus replication in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Oct;24(4):518–521. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.4.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. C., Dvorak C. A., Smee D. F., Matthews T. R., Verheyden J. P. 9-[(1,3-Dihydroxy-2-propoxy)methyl]guanine: a new potent and selective antiherpes agent. J Med Chem. 1983 May;26(5):759–761. doi: 10.1021/jm00359a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park N. H., Pavan-Langston D., Declercq E. Effect of acyclovir, bromovinyldeoxyuridine, vidarabine, and L-lysine on latent ganglionic herpes simplex virus in vitro. Am J Med. 1982 Jul 20;73(1A):151–154. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavan-Langston D., Park N. H., De Clercq E. In vitro effect of (E)-5-(2-bromovinyl)-2'-deoxyuridine, 5'-amino-5-iodo-2',5'-dideoxyuridine and 2-deoxy-D-glucose on latent ganglionic herpes simplex virus infection. Antiviral Res. 1984 Apr;4(1-2):53–61. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(84)90025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smee D. F., Martin J. C., Verheyden J. P., Matthews T. R. Anti-herpesvirus activity of the acyclic nucleoside 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 May;23(5):676–682. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.5.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. O., Galloway K. S., Kennell W. L., Ogilvie K. K., Radatus B. K. A new nucleoside analog, 9-[[2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethoxyl]methyl]guanine, highly active in vitro against herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jul;22(1):55–61. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spruance S. L., McKeough M. B., Cardinal J. R. Penetration of guinea pig skin by acyclovir in different vehicles and correlation with the efficacy of topical therapy of experimental cutaneous herpes simplex virus infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jan;25(1):10–15. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.1.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair M. H., Miller W. H., Miller R. L., Lambe C. U., Furman P. A. Inhibition of cellular alpha DNA polymerase and herpes simplex virus-induced DNA polymerases by the triphosphate of BW759U. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Feb;25(2):191–194. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.2.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trousdale M. D., Nesburn A. B., Willey D. E., Taaid H. Efficacy of BW759 (9-[[2-hydroxy-1(hydroxymethyl)ethoxy]methyl]guanine) against herpes simplex virus type 1 keratitis in rabbits. Curr Eye Res. 1984 Aug;3(8):1007–1015. doi: 10.3109/02713688409011747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohlenberg C., Openshaw H., Notkins A. L. In vitro system for studying the efficacy of antiviral agents in preventing the reactivation of latent herpes simplex virus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Apr;15(4):625–627. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.4.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Clercq E. Topical treatment of cutaneous herpes simplex virus infection in hairless mice with (E)-5-(2-bromovinyl)-2'-deoxyuridine and related compounds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):155–159. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



