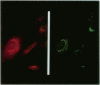Abstract
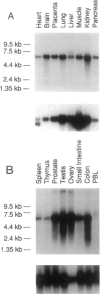
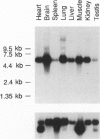
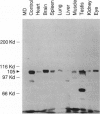
The oculocerebrorenal syndrome of Lowe (OCRL) is a multisystem disorder affecting the lens, kidney, and CNS. The predicted amino acid sequence of the OCRL gene, OCRL-1, was used to develop antibodies against the OCRL-1 protein. Western blot analysis using affinity-purified serum against the amino terminus of the OCRL-1 gene product (ocrl-1) demonstrates a single protein of 105 kD in fibroblasts of a normal individual that is absent in fibroblasts of an OCRL patient who lacks OCRL-1 transcript. A single protein with the same electrophoretic mobility is found by western analysis in various human cultured cell lines, and approximately the same size protein is also found in all mouse tissues tested. Northern analysis of various human and mouse tissues demonstrate that OCRL-1 transcript is expressed in nearly all tissues examined. By immunofluorescence, the ocrl-1 antibody stains a juxtanuclear region in normal fibroblast cells, while no specific staining is evident in the OCRL patient who produces no transcript. Colocalization of the ocrl-1 protein to the Golgi complex was demonstrated using a known monoclonal antibody against a Golgi-specific coat protein, beta-COP (beta coatomer protein).
Full text
PDF


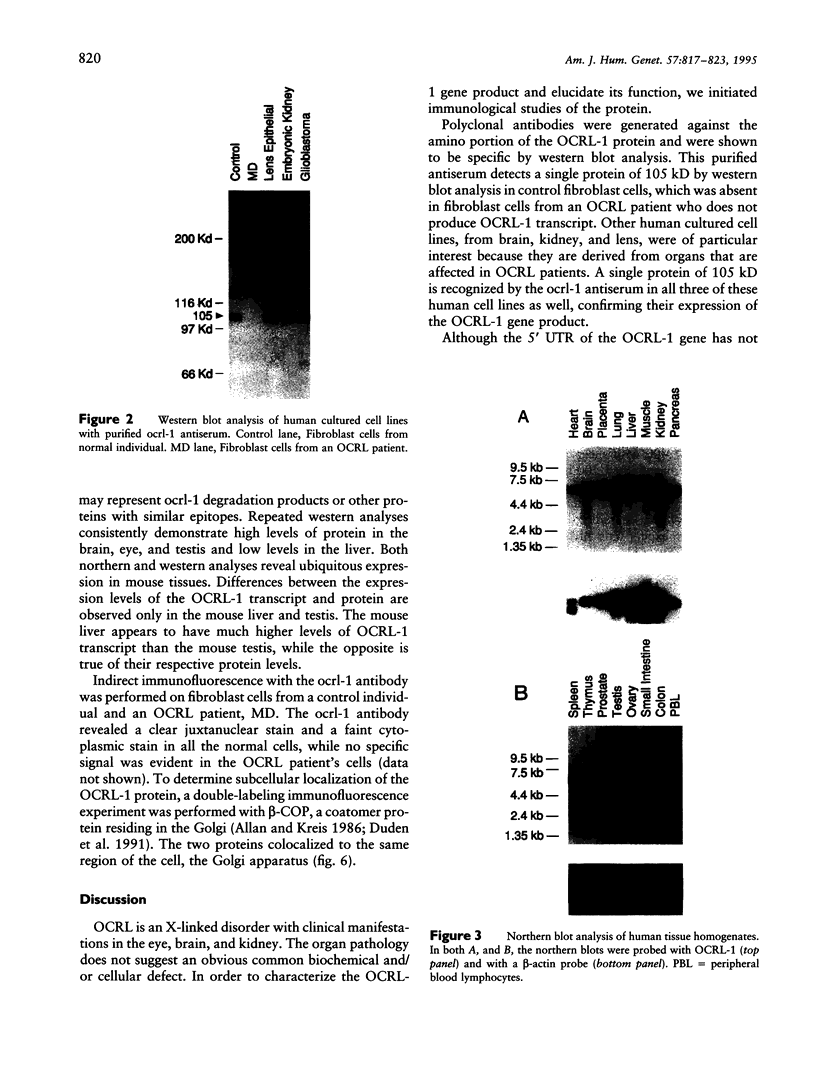
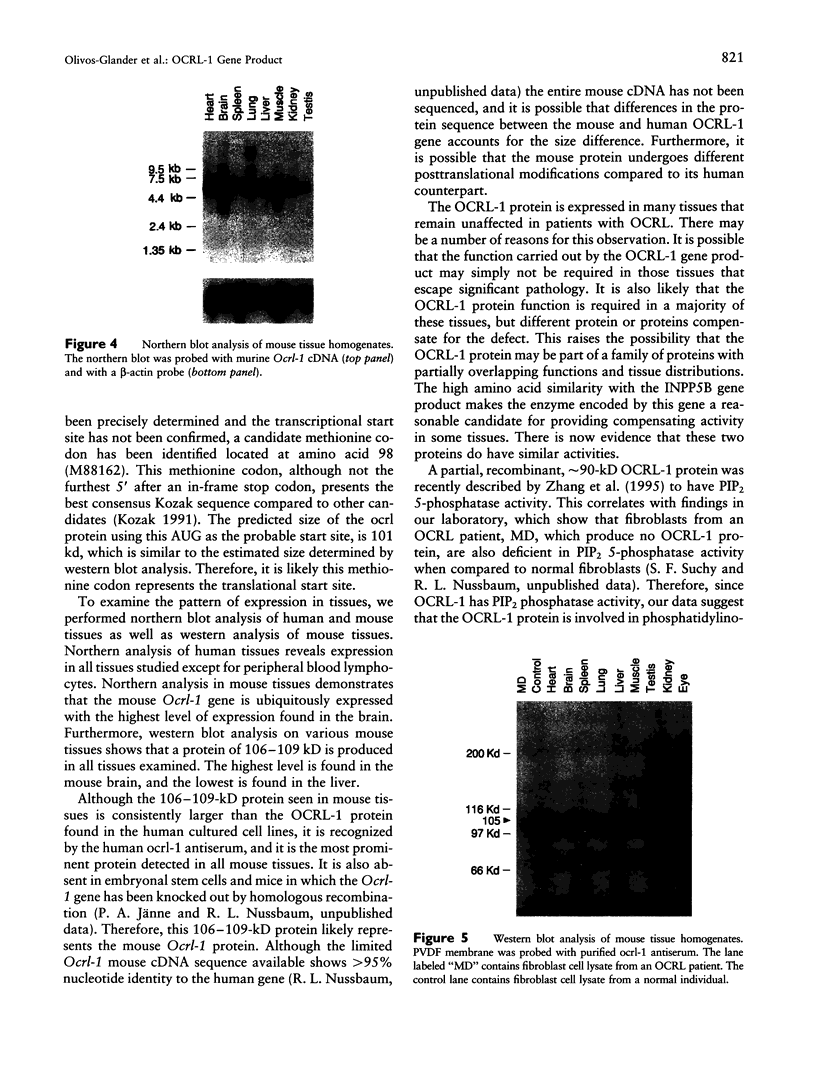
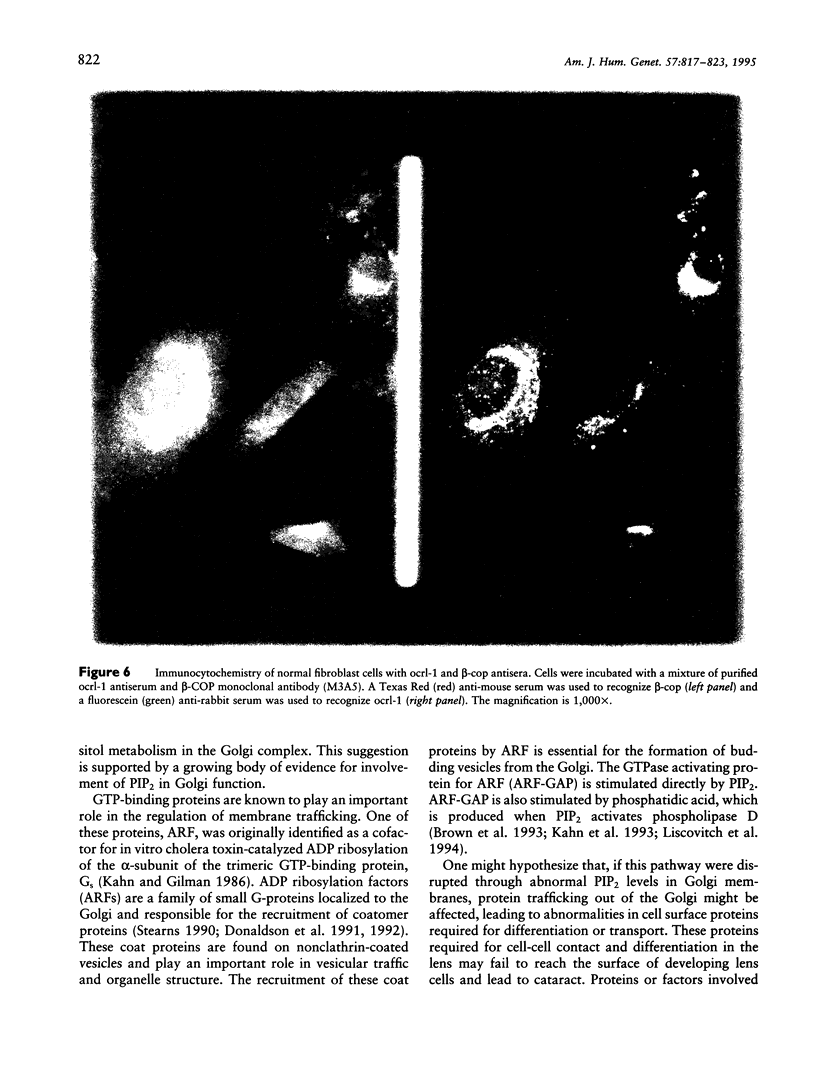

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan V. J., Kreis T. E. A microtubule-binding protein associated with membranes of the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2229–2239. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andley U. P., Rhim J. S., Chylack L. T., Jr, Fleming T. P. Propagation and immortalization of human lens epithelial cells in culture. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1994 Jun;35(7):3094–3102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attree O., Olivos I. M., Okabe I., Bailey L. C., Nelson D. L., Lewis R. A., McInnes R. R., Nussbaum R. L. The Lowe's oculocerebrorenal syndrome gene encodes a protein highly homologous to inositol polyphosphate-5-phosphatase. Nature. 1992 Jul 16;358(6383):239–242. doi: 10.1038/358239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H. A., Gutowski S., Moomaw C. R., Slaughter C., Sternweis P. C. ADP-ribosylation factor, a small GTP-dependent regulatory protein, stimulates phospholipase D activity. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1137–1144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90323-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Cassel D., Kahn R. A., Klausner R. D. ADP-ribosylation factor, a small GTP-binding protein, is required for binding of the coatomer protein beta-COP to Golgi membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6408–6412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Kahn R. A., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Klausner R. D. Binding of ARF and beta-COP to Golgi membranes: possible regulation by a trimeric G protein. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1197–1199. doi: 10.1126/science.1957170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duden R., Griffiths G., Frank R., Argos P., Kreis T. E. Beta-COP, a 110 kd protein associated with non-clathrin-coated vesicles and the Golgi complex, shows homology to beta-adaptin. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):649–665. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90248-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A., Gilman A. G. The protein cofactor necessary for ADP-ribosylation of Gs by cholera toxin is itself a GTP binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7906–7911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A., Yucel J. K., Malhotra V. ARF signaling: a potential role for phospholipase D in membrane traffic. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1045–1048. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90314-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenworthy L., Park T., Charnas L. R. Cognitive and behavioral profile of the oculocerebrorenal syndrome of Lowe. Am J Med Genet. 1993 May 15;46(3):297–303. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320460312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of vertebrate mRNA sequences: intimations of translational control. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(4):887–903. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.4.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWE C. U., TERREY M., MacLACHLAN E. A. Organic-aciduria, decreased renal ammonia production, hydrophthalmos, and mental retardation; a clinical entity. AMA Am J Dis Child. 1952 Feb;83(2):164–184. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1952.02040060030004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leahey A. M., Charnas L. R., Nussbaum R. L. Nonsense mutations in the OCRL-1 gene in patients with the oculocerebrorenal syndrome of Lowe. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Apr;2(4):461–463. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.4.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liscovitch M., Chalifa V., Pertile P., Chen C. S., Cantley L. C. Novel function of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate as a cofactor for brain membrane phospholipase D. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 26;269(34):21403–21406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzaris M., Jackson S. P., Laxminarayan K. M., Speed C. J., Mitchell C. A. Identification and characterization of the phosphatidylinositol-(4, 5)-bisphosphate 5-phosphatase in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3397–3402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross T. S., Jefferson A. B., Mitchell C. A., Majerus P. W. Cloning and expression of human 75-kDa inositol polyphosphate-5-phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20283–20289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stearns T., Willingham M. C., Botstein D., Kahn R. A. ADP-ribosylation factor is functionally and physically associated with the Golgi complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1238–1242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X., Jefferson A. B., Auethavekiat V., Majerus P. W. The protein deficient in Lowe syndrome is a phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 5-phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 23;92(11):4853–4856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.11.4853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]