Abstract
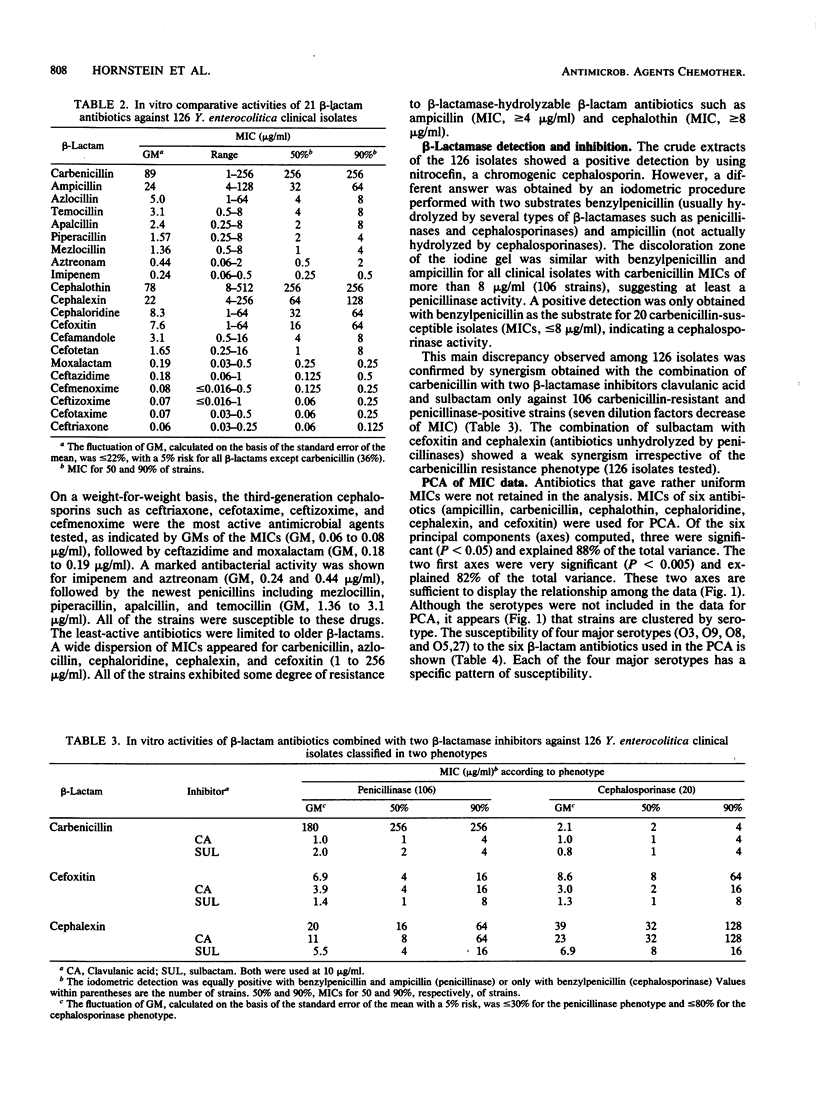
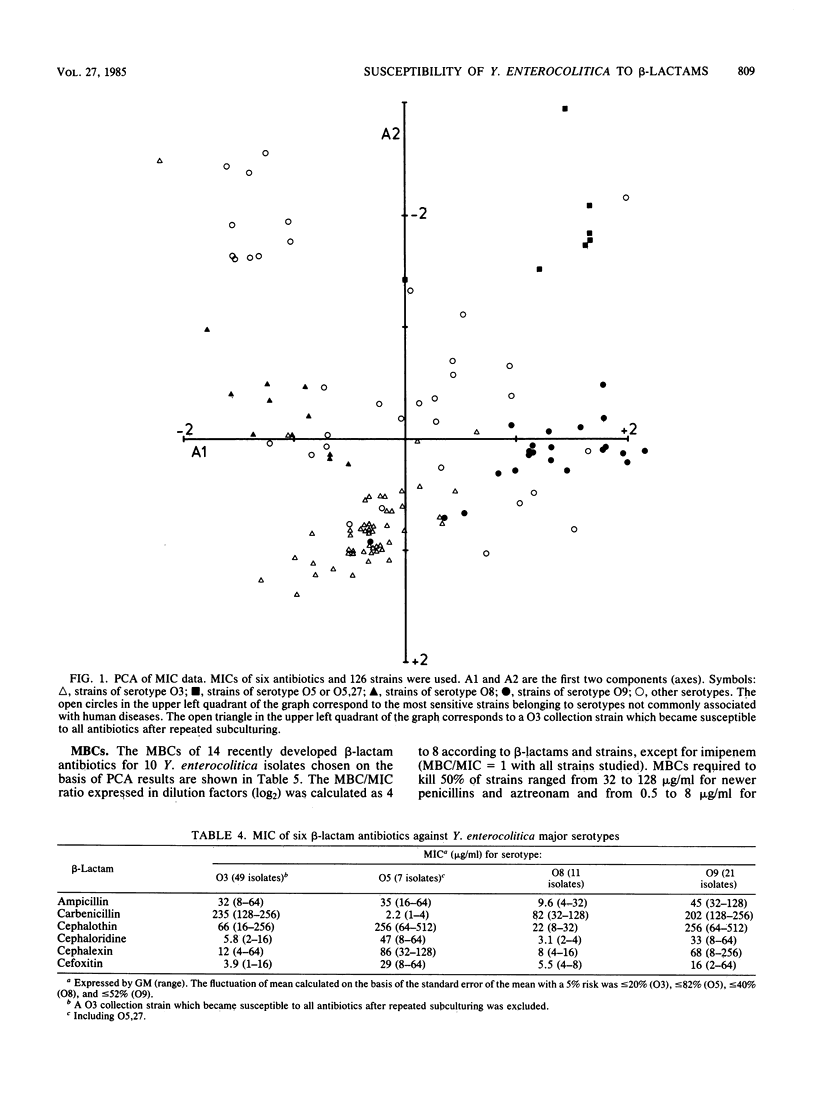
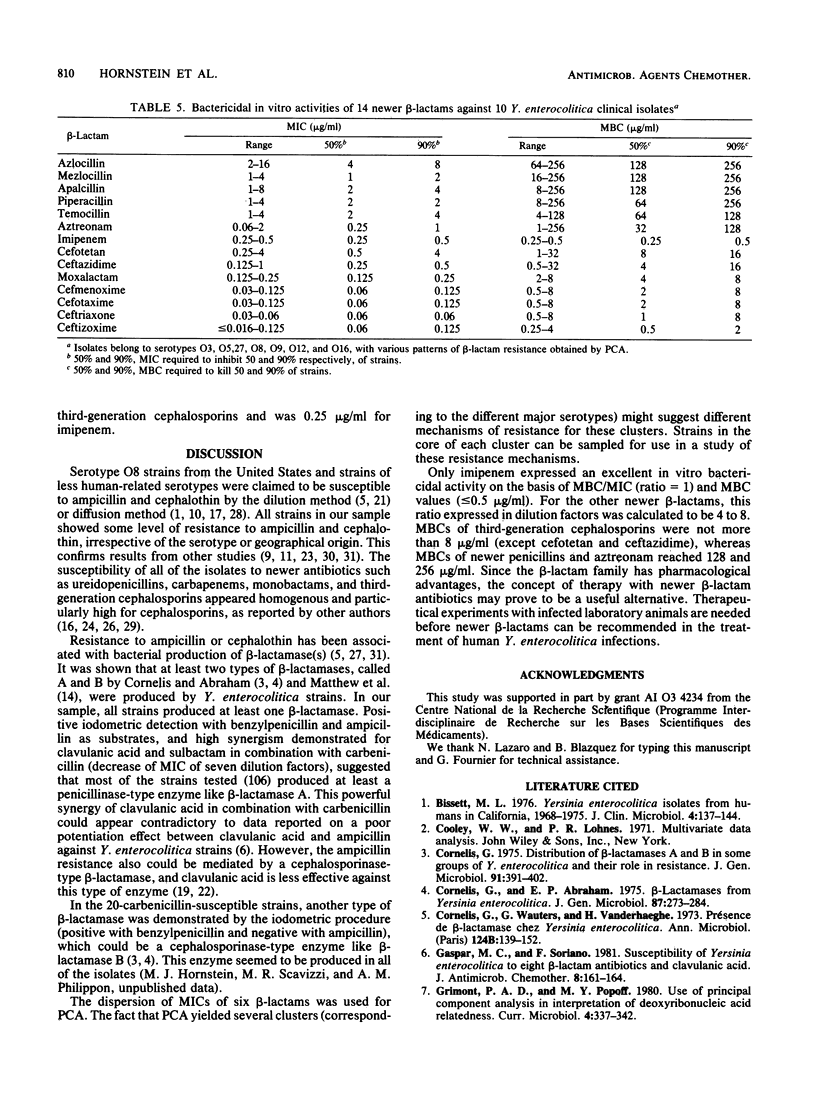
The MICs of 21 beta-lactam antibiotics were measured against 126 clinically significant and epidemiologically unrelated Yersinia enterocolitica isolates. The most active antimicrobial agents tested (geometric means of MICs) were ceftriaxone, cefotaxime, ceftizoxime, and cefmenoxime (0.06 to 0.08 micrograms/ml). Mezlocillin (1.36 micrograms/ml) and piperacillin (1.57 micrograms/ml) were the most active penicillins. Aztreonam and imipenem had MICs of 0.44 and 0.24 micrograms/ml. All isolates exhibited some degree of resistance against ampicillin (MICs, greater than or equal to 4 micrograms/ml) and cephalothin (MICs, greater than or equal to 8 micrograms/ml). Cephalosporinase or penicillinase activities were expressed by all isolates. A principal component analysis of MIC data separated the major serotypes (O3, O9, O8, and O5,27). The MCBs of 14 newer beta-lactams were measured against 10 clinical isolates. On the basis of the ratio of MBC to MIC (expressed in dilution factors), a real bactericidal activity was only observed for imipenem (MBC/MIC = 1). For the other newer beta-lactams, the ratios ranged from 4 to 8.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bissett M. L. Yersinia enterocolitica isolates from humans in California, 1968-1975. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Aug;4(2):137–144. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.2.137-144.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G., Abraham E. P. Beta-lactamases from Yersinia enterocolitica. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Apr;87(2):273–284. doi: 10.1099/00221287-87-2-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaspar M. C., Soriano F. Susceptibility of Yersinia enterocolitica to eight beta-lactam antibiotics and clavulanic acid. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Aug;8(2):161–164. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.2.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerberg S., Sorger S., Marks M. I. Antimicrobial susceptibilities of Yersinia enterocolitica biotype 4, serotype O:3. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Mar;11(3):566–568. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.3.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhlin I., Winblad S. Susceptibility to mecillinam and other antibiotics of 28 O-serotypes of Yersinia enterocolitica. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Oct;8(4):291–297. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.4.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa Y., Ikemura K. Isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis from human specimens and their drug-resistance in the Niigata District of Japan. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1979;5:106–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labia R., Barthélémy M. L'enzymogramme des beta-lactamases: adaptation en cel de la méthode iodométrique. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1979 Oct;130B(3):295–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labia R., Barthélémy M., Masson J. M. Multiplicité des beta lactamases: un probléme d'isoenzymes. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1976 Nov 29;283(14):1597–1600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew M., Cornelis G., Wauters G. Correlation of serological and biochemical groupings of Yersinia enterocolitica with the beta-lactamases of the strains. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Sep;102(1):55–59. doi: 10.1099/00221287-102-1-55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollaret H. H., Omland T., Henriksen S. D., Baeroe P. R., Rykner G., Scavizzi M. Les septicémies humaines a "Yersinia enterocolitica". A propos de dix-sept cas récents. Presse Med. 1971 Feb 13;79(8):345–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muytjens H. L., van der Ros-van de Repe J. Comparative activities of 13 beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jun;21(6):925–934. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.6.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabson A. R., Hallett A. F., Koornhof H. J. Generalized Yersinia enterocolitica infection. J Infect Dis. 1975 Apr;131(4):447–451. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.4.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raevuori M., Harvey S. M., Pickett M. J., Martin W. J. Yersinia enterocolitica: in vitro antimicrobial susceptibility. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 May;13(5):888–890. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.5.888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reading C., Cole M. Clavulanic acid: a beta-lactamase-inhiting beta-lactam from Streptomyces clavuligerus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 May;11(5):852–857. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.5.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scribner R. K., Marks M. I., Weber A., Pai C. H. Yersinia enterocolitica: comparative in vitro activities of seven new beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jul;22(1):140–141. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.1.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenwirth A. C. Bacteremia with and without meningitis due to Yersinia enterocolitica, Edwardsiella tarda, Comamonas terrigena, and Pseudomonas maltophilia. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1970 Oct 30;174(2):488–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1970.tb45575.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano F., Vega J. The susceptibility of Yersinia to eleven antimicrobials. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Dec;10(6):543–547. doi: 10.1093/jac/10.6.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Matthew M. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their role in resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1976 Jun;2(2):115–157. doi: 10.1093/jac/2.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toma S., Lafleur L. Survey on the incidence of Yersinia enterocolitica infection in Canada. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Sep;28(3):469–473. doi: 10.1128/am.28.3.469-473.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbist L. Comparison of in vitro activities of eight beta-lactamase-stable cephalosporins against beta-lactamase-producing gram-negative bacilli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Mar;19(3):407–413. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.3.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



