Abstract
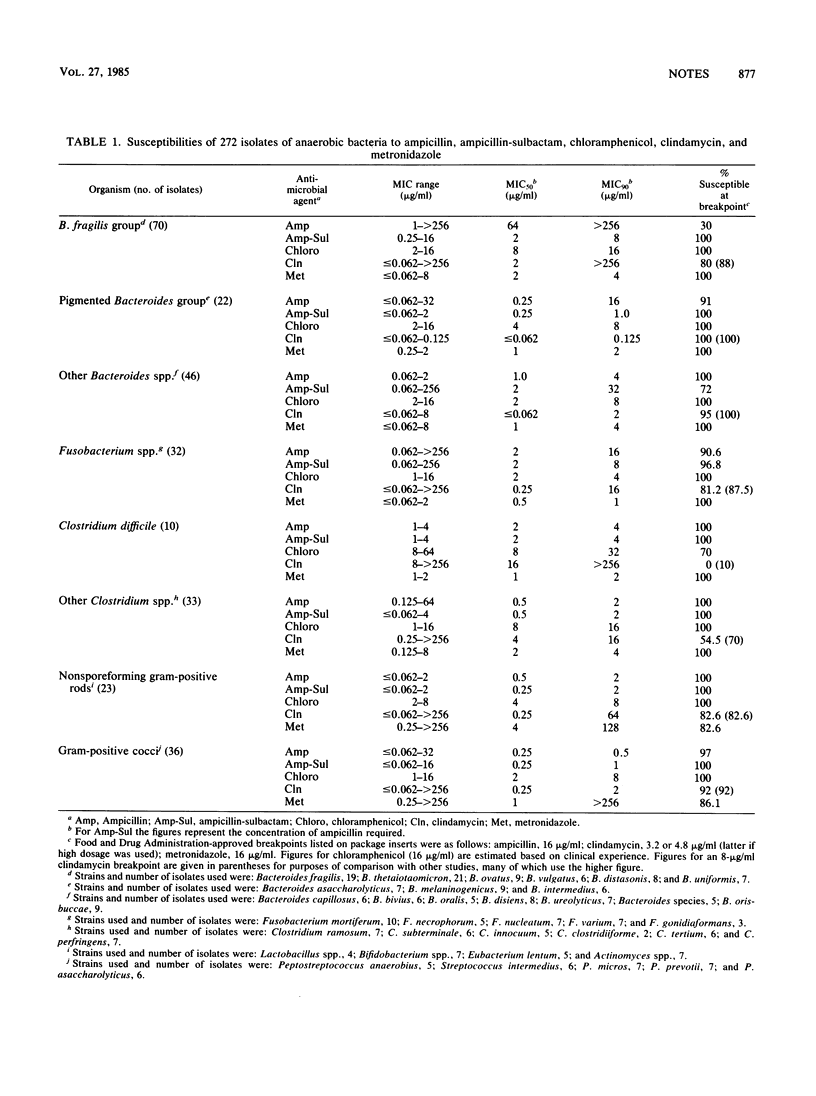
An ampicillin-sulbactam combination was compared with ampicillin alone, chloramphenicol, clindamycin, and metronidazole against 272 strains of anaerobic bacteria. Chloramphenicol and ampicillin-sulbactam were the most effective, inhibiting 98 to 99% of strains tested at breakpoint (16 micrograms/ml). The combination of sulbactam and ampicillin was much more effective than ampicillin alone against Bacteroides fragilis strains but did not differ substantially from ampicillin alone against Fusobacterium spp., gram-positive rods, and gram-positive cocci.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blazevic D. J. Antibiotic susceptibility of the subspecies of Bacteroides fragilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Mar;9(3):481–484. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.3.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosby M. A., Gump D. W. Activity of cefoperazone and two beta-lactamase inhibitors, sulbactam and clavulanic acid, against Bacteroides spp. correlated with beta-lactamase production. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Sep;22(3):398–405. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.3.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English A. R., Retsema J. A., Girard A. E., Lynch J. E., Barth W. E. CP-45,899, a beta-lactamase inhibitor that extends the antibacterial spectrum of beta-lactams: initial bacteriological characterization. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):414–419. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R. J. Inconsistency of synergy between the beta-lactamase inhibitor CP-45,899 and beta-lactam antibiotics against multiply drug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae and pseudomonas species. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Feb;19(2):361–363. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.2.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulds G., Stankewich J. P., Marshall D. C., O'Brien M. M., Hayes S. L., Weidler D. J., McMahon F. G. Pharmacokinetics of sulbactam in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 May;23(5):692–699. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.5.692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood D., Eley A. In-vitro evaluation of sulbactam, a penicillanic acid sulphone with beta-lactamase inhibitory properties. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Aug;10(2):117–123. doi: 10.1093/jac/10.2.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins S. G., Birk R. J., Zabransky R. J. Differences in susceptibilities of species of the Bacteroides fragilis group to several beta-lactam antibiotics: indole production as an indicator of resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Oct;22(4):628–634. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.4.628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Fuchs P. C. Identification and antimicrobial susceptibility of 250 Bacteriodes fragilis subspecies tested by broth microdilution methods. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Apr;9(4):719–721. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.4.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kager L., Liljeqvist L., Malmborg A. S., Nord C. E., Pieper R. Effects of ampicillin plus sulbactam on bowel flora in patients undergoing colorectal surgery. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Aug;22(2):208–212. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.2.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. T., Moosdeen F., Williams J. D. The effect of inhibitors of beta-lactamases on beta-lactamase extracts and on intact cells. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Apr;9(4):287–296. doi: 10.1093/jac/9.4.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plouffe J. F. Treatment of infections caused by ampicillin-resistant pathogens with a combination of ampicillin and CP-45,899. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Mar;21(3):519–520. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.3.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Retsema J. A., English A. R., Girard A. E. CP-45,899 in combination with penicillin or ampicillin against penicillin-resistant Staphylococcus, Haemophilus influenzae, and Bacteroides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Apr;17(4):615–622. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.4.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria to 23 antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):736–752. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



