Abstract
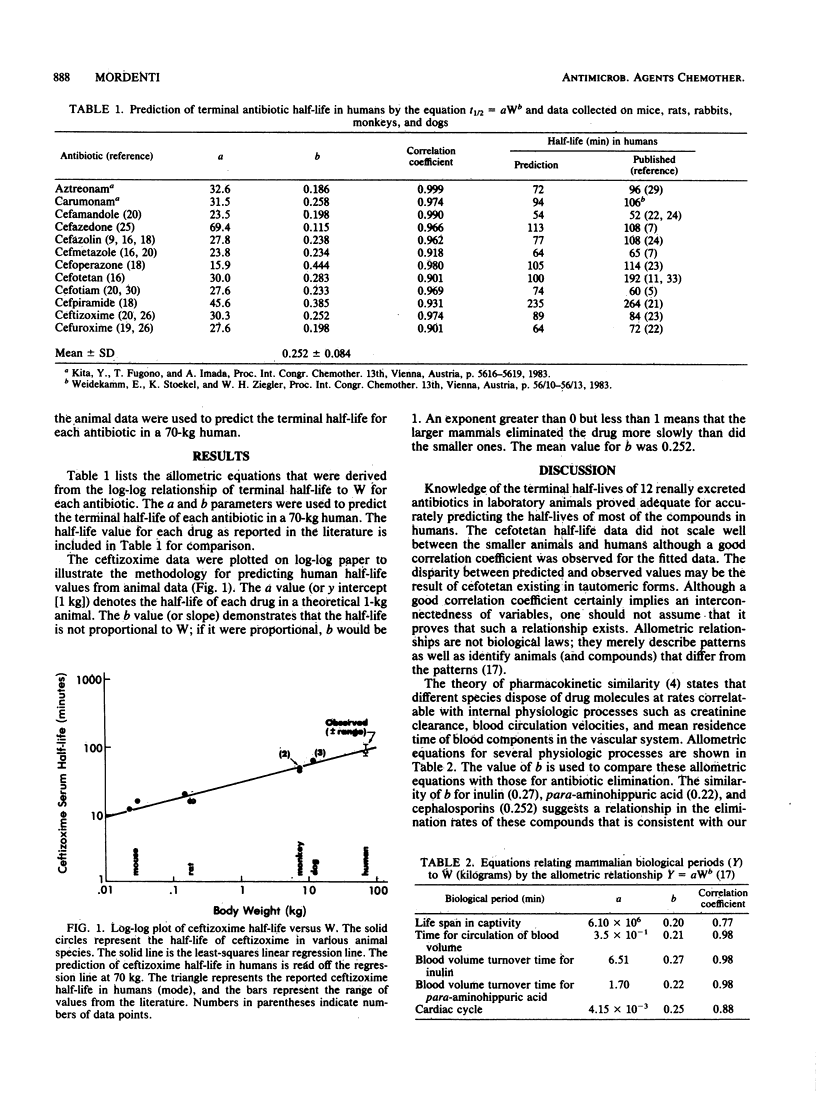
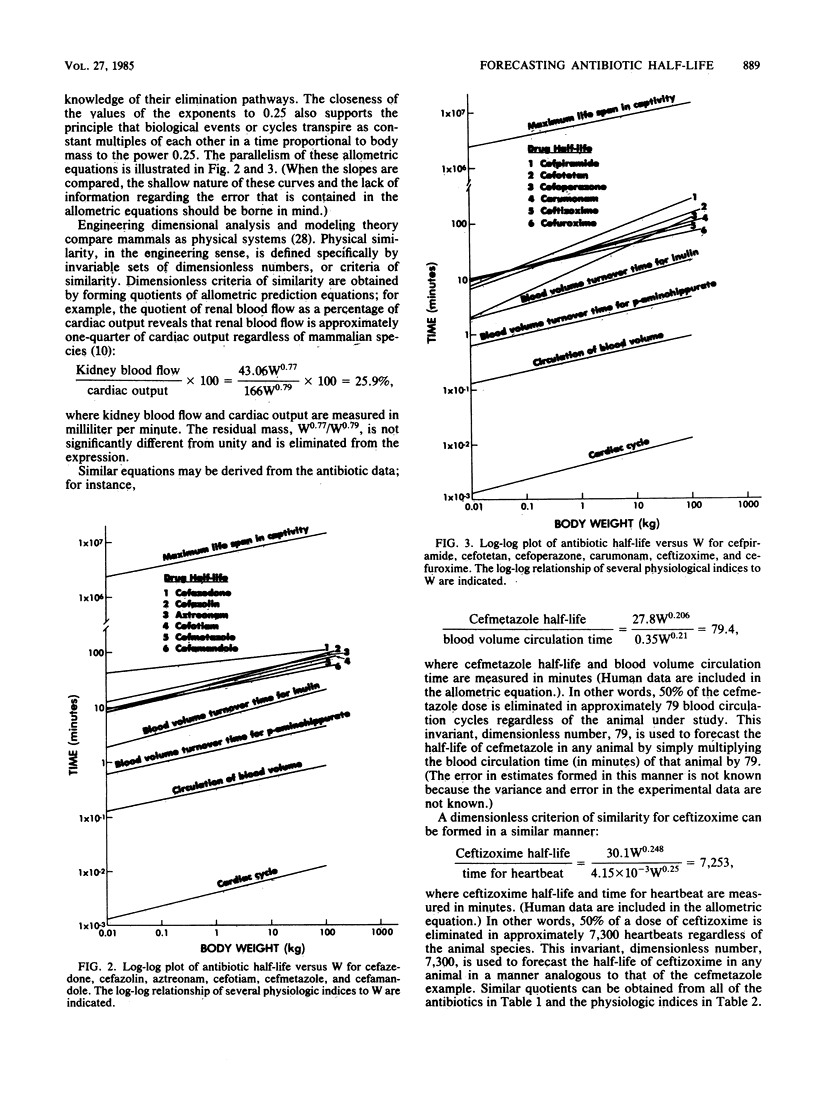
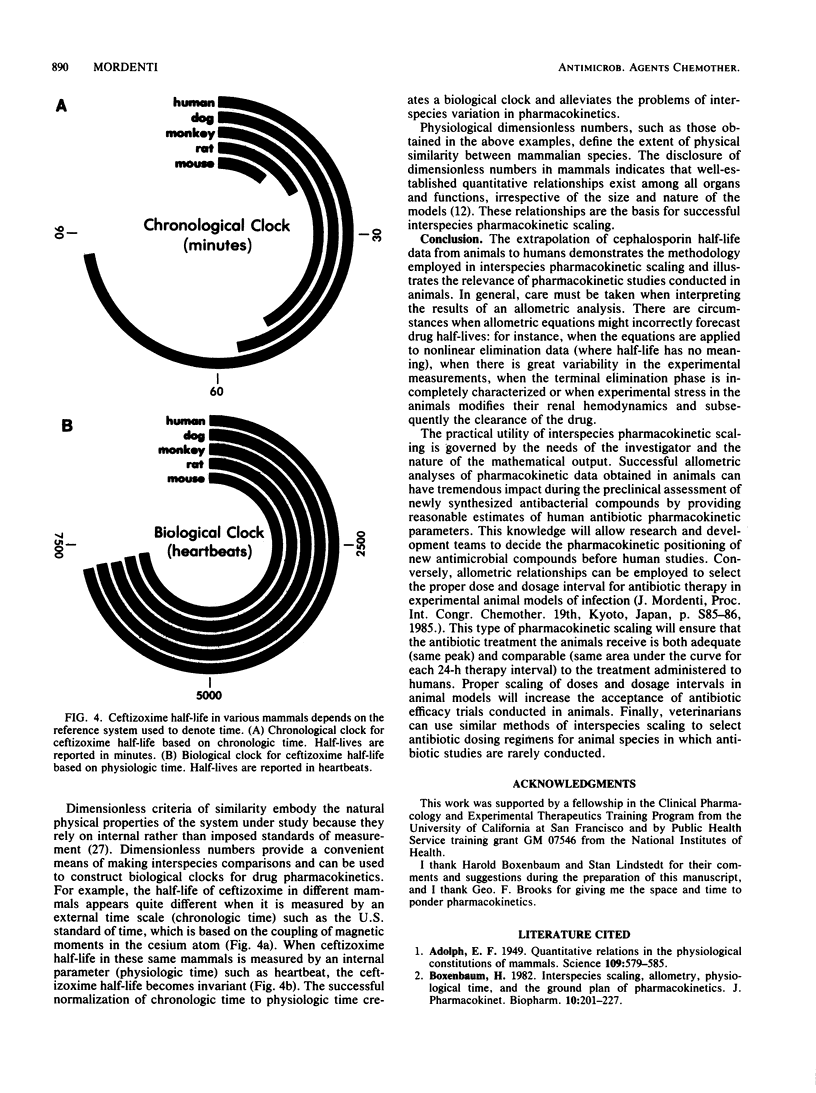
The postdistribution half-lives of 10 cephalosporin and 2 monobactam antibiotics in humans were predicted from data obtained in other mammals. This forecasting was accomplished with the allometric equation t1/2 = aWb, where a is the y intercept and b is the slope obtained from the log-log plot of antibiotic half-life (t1/2) versus body weight (W). Dimensionless similarity criteria were used to produce a biological clock for ceftizoxime elimination. The creation of the biological clock, which measured physiologic time (heartbeats) rather than chronologic time (minutes), demonstrated that ceftizoxime half-life was identical in five mammals. This methodology will contribute to infectious disease research through a greater understanding of pharmacokinetic scaling in mammals.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adolph E. F. Quantitative Relations in the Physiological Constitutions of Mammals. Science. 1949 Jun 10;109(2841):579–585. doi: 10.1126/science.109.2841.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxenbaum H. Interspecies pharmacokinetic scaling and the evolutionary-comparative paradigm. Drug Metab Rev. 1984;15(5-6):1071–1121. doi: 10.3109/03602538409033558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxenbaum H. Interspecies scaling, allometry, physiological time, and the ground plan of pharmacokinetics. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1982 Apr;10(2):201–227. doi: 10.1007/BF01062336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxenbaum H., Ronfeld R. Interspecies pharmacokinetic scaling and the Dedrick plots. Am J Physiol. 1983 Dec;245(6):R768–R775. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1983.245.6.R768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brisson A. M., Bryskier A., Millerioux L., Fourtillan J. B. Pharmacokinetics of cefotiam administered intravenously and intramuscularly to healthy adults. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Oct;26(4):513–518. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.4.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brogard J. M., Comte F. Pharmacokinetics of the new cephalosporins. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1982;31:145–210. doi: 10.1159/000400133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calder W. A., 3rd Scaling of physiological processes in homeothermic animals. Annu Rev Physiol. 1981;43:301–322. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.43.030181.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingeldein E., Wahlig H. Blood levels and tissue concentrations of cefazedone in animals. Arzneimittelforschung. 1979;29(2A):400–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards N. A. Scaling of renal functions in mammals. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1975 Sep 1;52(1):63–66. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9629(75)80128-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUNTHER B., GUERRA E. Biological similarities. Acta Physiol Lat Am. 1955;5(4):169–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guibert J., Kitzis M. D., Yvelin C., Acar J. F. Pharmacokinetics of single intravenous and intramuscular doses of cefotetan in normal human volunteers. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Jan;11 (Suppl):201–206. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.suppl_a.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günther B. Allometric ratios, invariant numbers and the theory of biological similarities. Pflugers Arch. 1972;331(4):283–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00592689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komiya M., Kikuchi Y., Tachibana A., Yano K. Pharmacokinetics of new broad-spectrum cephamycin, YM09330, parenterally administered to various experimental animals. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Aug;20(2):176–183. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.2.176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui H., Yano K., Okuda T. Pharmacokinetics of the cephalosporin SM-1652 in mice, rats, rabbits, dogs, and rhesus monkeys. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Aug;22(2):213–217. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.2.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Jr, Nelson J. D., Grimm L. Pharmacokinetics and bacteriological efficacy of cefoperazone, ceftriaxone, and moxalactam in experimental Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae meningitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):262–267. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakawa T., Sakamoto H., Fukada S., Nakamoto S., Hirose T., Itoh N., Nishida M. Pharmacokinetics of ceftizoxime in animals after parenteral dosing. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Feb;17(2):157–164. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.2.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa K., Koyama M., Matsui H., Ikeda C., Yano K., Nakatsuru N., Yoshinaga K., Noguchi T. Pharmacokinetics of cefpiramide (SM-1652) in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Feb;25(2):221–225. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. Comparison of the pharmacokinetics of cefamandole and other cephalosporin compounds. J Infect Dis. 1978 May;137 (Suppl):S80–S87. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.supplement.s80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. The new beta-lactamase-stable cephalosporins. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Sep;97(3):408–419. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-3-408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAHL W. R. Similarity and dimensional methods in biology. Science. 1962 Jul 20;137(3525):205–212. doi: 10.1126/science.137.3525.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sailer H., Diekmann H. W., Faro H. P., Garbe A. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of cefazedone in Wistar rat, beagle dog and rhesus monkey. Arzneimittelforschung. 1979;29(2A):404–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl W. R. Organ weights in primates and other mammals. Science. 1965 Nov 19;150(3699):1039–1042. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3699.1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swabb E. A., Singhvi S. M., Leitz M. A., Frantz M., Sugerman A. Metabolism and pharmacokinetics of aztreonam in healthy subjects. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Sep;24(3):394–400. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.3.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanayama S., Kondo T., Kanai Y. Metabolic fate of SCE-963, a new broad-spectrum cephalosporin, after parenteral administration in rats and dogs. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1978 Jul;31(7):703–711. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.31.703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON SCHELLING H. Mathematical deductions from empirical relations between metabolism, surface area, and weight. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1954 Apr 2;56(7):1143–1163. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1954.tb30308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates R. A., Adam H. K., Donnelly R. J., Houghton H. L., Charlesworth E. A., Laws E. A. Pharmacokinetics and tolerance of single intravenous doses of cefotetan disodium in male Caucasian volunteers. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Jan;11 (Suppl):185–191. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.suppl_a.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



