Abstract
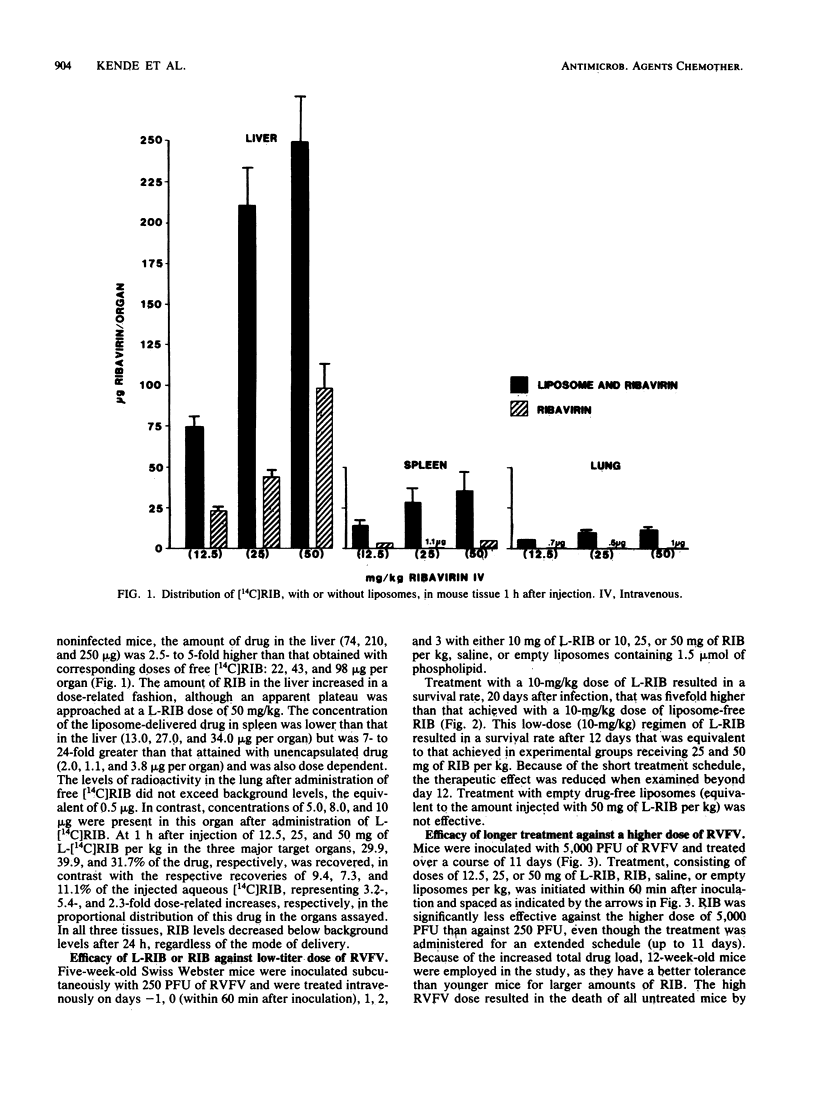
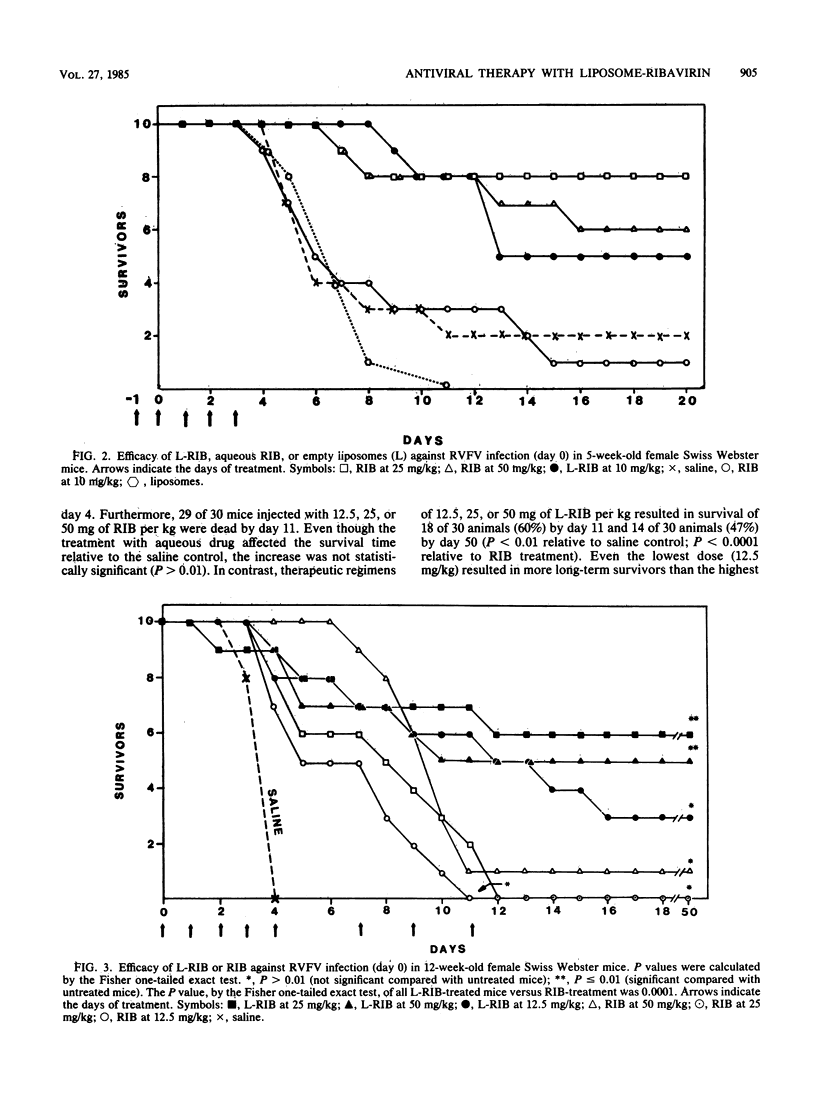
Administration of liposome-encapsulated ribavirin to mice led to ribavirin concentrations in the liver, the primary site of Rift Valley fever virus proliferation, that were fivefold greater than those attained with the same doses of free ribavirin. Liposomal ribavirin given at a dose of either 25 or 50 mg of drug per kg of body weight protected mice against a rapidly lethal high-titer challenge with Rift Valley fever virus, whereas similar doses of free drug or empty liposomes had no detectable benefit. Hence, tissue targeting of ribavirin with liposomes substantially increased the therapeutic index by increasing the efficacy of the treatment. By using liposomes as drug carriers, a nontoxic, low-dose regimen of ribavirin had a therapeutic effect that was comparable to that achieved with higher but potentially more toxic doses of free ribavirin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alving C. R. Delivery of liposome-encapsulated drugs to macrophages. Pharmacol Ther. 1983;22(3):407–424. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(83)90010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alving C. R., Steck E. A., Chapman W. L., Jr, Waits V. B., Hendricks L. D., Swartz G. M., Jr, Hanson W. L. Therapy of leishmaniasis: superior efficacies of liposome-encapsulated drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2959–2963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desiderio J. V., Campbell S. G. Liposome-encapsulated cephalothin in the treatment of experimental murine salmonellosis. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1983 Oct;34(4):279–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easterday B. C. Rift valley fever. Adv Vet Sci. 1965;10:65–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddy G. A., Peters C. J. The extended horizons of Rift Valley fever: current and projected immunogens. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1980;47:179–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara E. A., Oishi J. S., Wannemacher R. W., Jr, Stephen E. L. Plasma disappearance, urine excretion, and tissue distribution of ribavirin in rats and rhesus monkeys. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jun;19(6):1042–1049. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.6.1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser-Smith E. B., Eppstein D. A., Larsen M. A., Matthews T. R. Protective effect of a muramyl dipeptide analog encapsulated in or mixed with liposomes against Candida albicans infection. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):172–178. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.172-178.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybill J. R., Craven P. C., Taylor R. L., Williams D. M., Magee W. E. Treatment of murine cryptococcosis with liposome-associated amphotericin B. J Infect Dis. 1982 May;145(5):748–752. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Berestein G., Mehta R., Hopfer R. L., Mills K., Kasi L., Mehta K., Fainstein V., Luna M., Hersh E. M., Juliano R. Treatment and prophylaxis of disseminated infection due to Candida albicans in mice with liposome-encapsulated amphotericin B. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):939–945. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIMS C. A. Rift Valley Fever virus in mice. I. General features of the infection. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Apr;37(2):99–109. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meegan J. M. The Rift Valley fever epizootic in Egypt 1977-78. 1. Description of the epizzotic and virological studies. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1979;73(6):618–623. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(79)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- New R. R., Chance M. L., Heath S. Antileishmanial activity of amphotericin and other antifungal agents entrapped in liposomes. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Nov;8(5):371–381. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.5.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. G., Barral-Netto M., Inverso J. A. Treatment of experimental visceral leishmaniasis with lymphokine encapsulated in liposomes. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3116–3119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay C., Barza M., Fiore C., Szoka F. Efficacy of liposome-intercalated amphotericin B in the treatment of systemic candidiasis in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):170–173. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell D. A., Heath T. D., Colley C. M., Ryman B. E. New aspects of liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 14;457(3-4):259–302. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



