Abstract
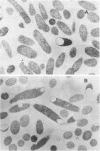
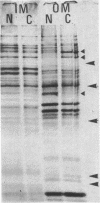
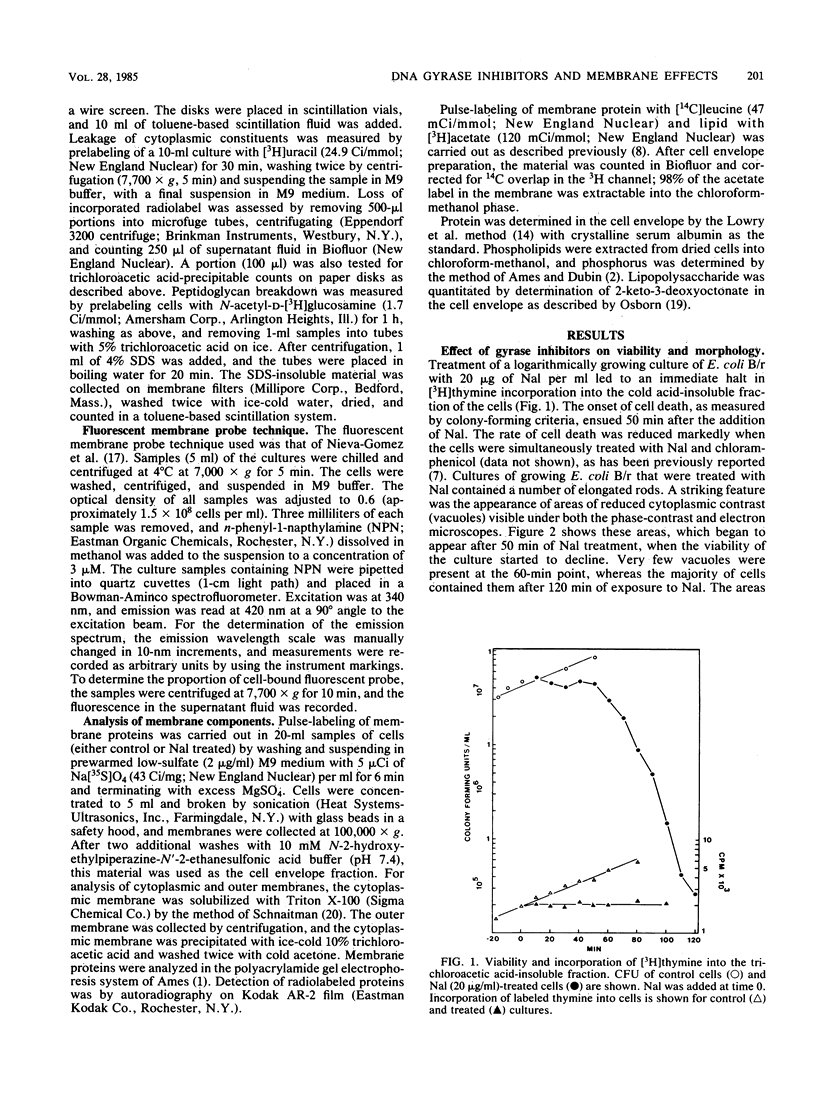
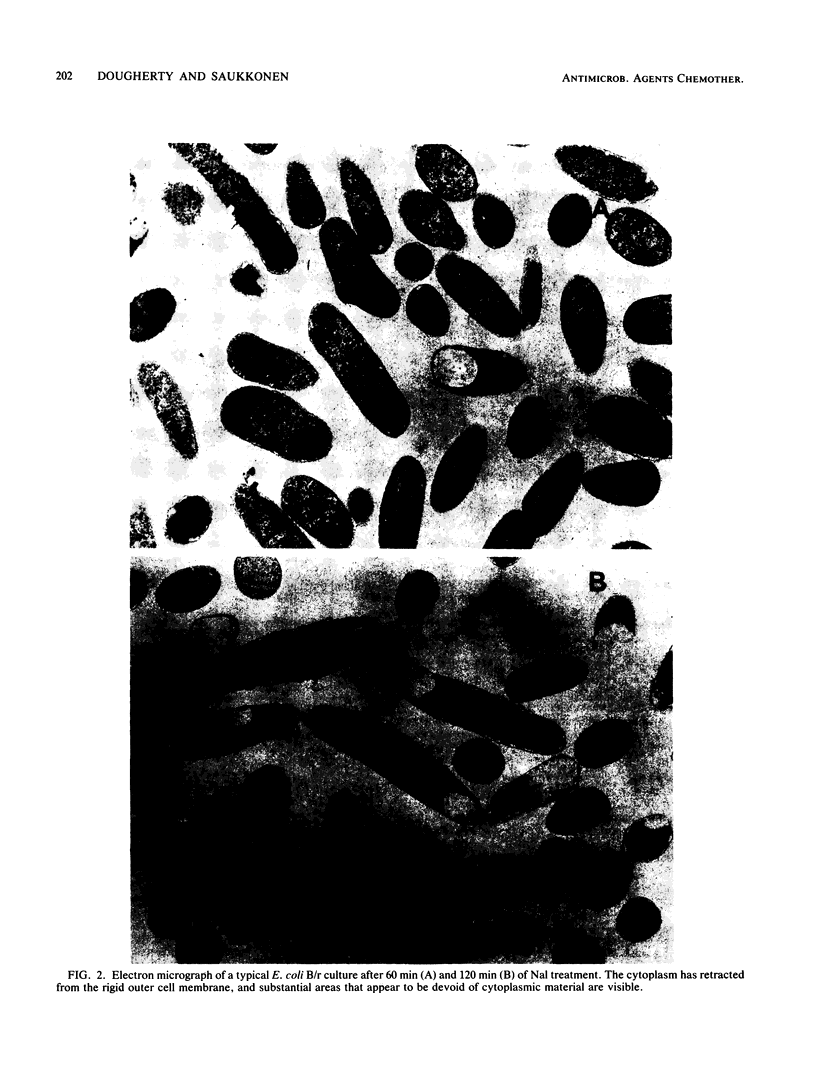
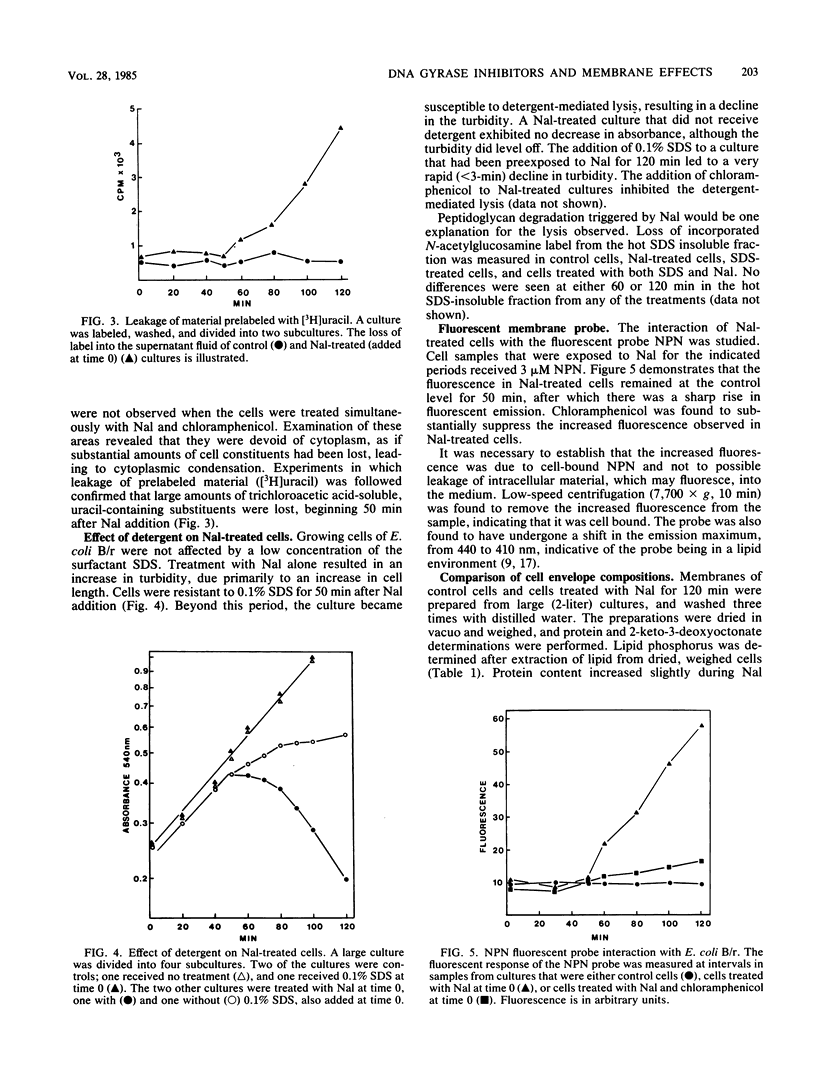
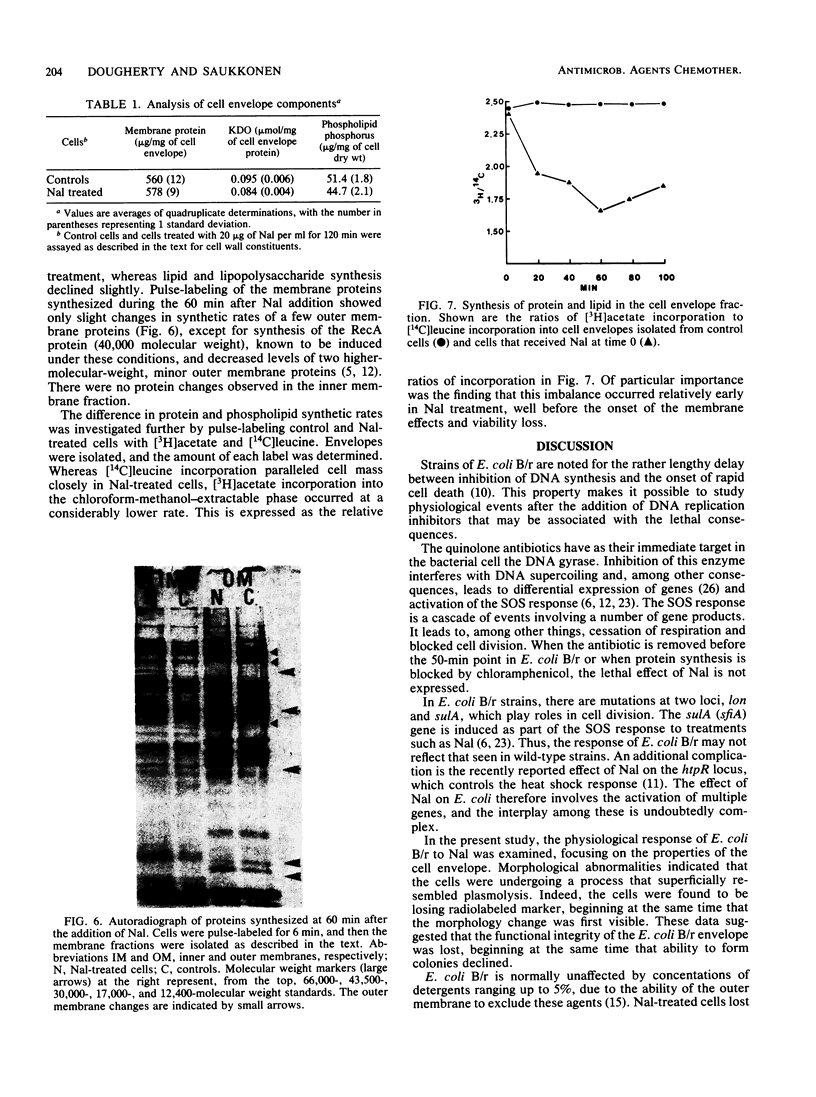
Inhibition of DNA synthesis in Escherichia coli B/r by a DNA gyrase inhibitor results in cell death after a 50-min lag period. Examination of the cells under phase-contrast and electron microscopes revealed that they appeared to undergo plasmolysis coincident with the onset of cell death. The inhibited cells were also found to become susceptible to low levels of detergent at this time. With a fluorescent membrane probe, the level of membrane permeability was assessed and found to increase concurrently with the decrease in culture viability. Analysis of the cell envelope constituents revealed that, other than a shift in the protein/lipid ratio, the compositions of the cell membranes were unperturbed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES B. N., DUBIN D. T. The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F. Resolution of bacterial proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on slabs. Membrane, soluble, and periplasmic fractions. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):634–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauernfeind A., Petermüller C. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and nalidixic acid. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;2(2):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF02001575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caster J. H. Selection of thymine-requiring strains from Escherichia coli on solid medium. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1804–1804. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1804-.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao L. Nalidixic acid-induced protein alterations in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jan;11(1):167–170. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K. Biology of bacterial deoxyribonucleic acid topoisomerases. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Dec;48(4):273–289. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.4.273-289.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakenbeck R., Messer W. Oscillations in the synthesis of cell wall components in synchronized cultures of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1234–1238. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1234-1238.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helgerson S. L., Cramer W. A. Changes in E. coli cell envelope structure caused by uncouplers of active transport and colicin E1. J Supramol Struct. 1976;5(3):291–308. doi: 10.1002/jss.400050304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor G. J., Deering R. A. Effect of nalidixic acid and hydroxyurea on division ability of Escherichia coli fil+ and lon- strains. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):520–530. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.520-530.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. H., Walker G. C. groEL and dnaK genes of Escherichia coli are induced by UV irradiation and nalidixic acid in an htpR+-dependent fashion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1499–1503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Mount D. W. The SOS regulatory system of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh B., Grant C., Hancock R. E. Use of the fluorescent probe 1-N-phenylnaphthylamine to study the interactions of aminoglycoside antibiotics with the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Oct;26(4):546–551. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.4.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Van Alphen L. Molecular architecture and functioning of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli and other gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):51–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieva-Gomez D., Gennis R. B. Affinity of intact Escherichia coli for hydrophobic membrane probes is a function of the physiological state of the cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1811–1815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieva-Gomez D., Konisky J. Membrane changes in Escherichia coli induced by colicin Ia and agents known to disrupt energy transduction. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 29;15(13):2747–2753. doi: 10.1021/bi00658a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J. STUDIES ON THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. I. EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF 2-KETO- 3-DEOXYOCTONATE IN THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:499–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by Triton X-100. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):545–552. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.545-552.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson P. A., Schenley R. L. Evidence relating cessation of respiration, cell envelope changes, and death in ultraviolet-irradiated Escherichia coli B-r cells. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):551–559. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.551-559.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson P. A., Schenley R. L. Respiration, growth and viability of repair-deficient mutants of Escherichia coli after ultraviolet irradiation. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1974 Jan;25(1):51–60. doi: 10.1080/09553007414550051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Ultraviolet mutagenesis and inducible DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):869–907. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.869-907.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woldringh C. L., van Iterson W. Effects of treatment with sodium dodecyl sulfate on the ultrastructure of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Sep;111(3):801–813. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.3.801-813.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M. K., Konisky J. Increased binding of a hydrophobic, photolabile probe to Escherichia coli inversely correlates to membrane potential but not adenosine 5'-triphosphate levels. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):341–347. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.341-347.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. L., Heller K., Gellert M., Zubay G. Differential sensitivity of gene expression in vitro to inhibitors of DNA gyrase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3304–3308. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoda K., Nagai K., Tamura G. Properties of proteins produced after damage to deoxyribonucleic acid of Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1977 May;81(5):1357–1365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]