Abstract
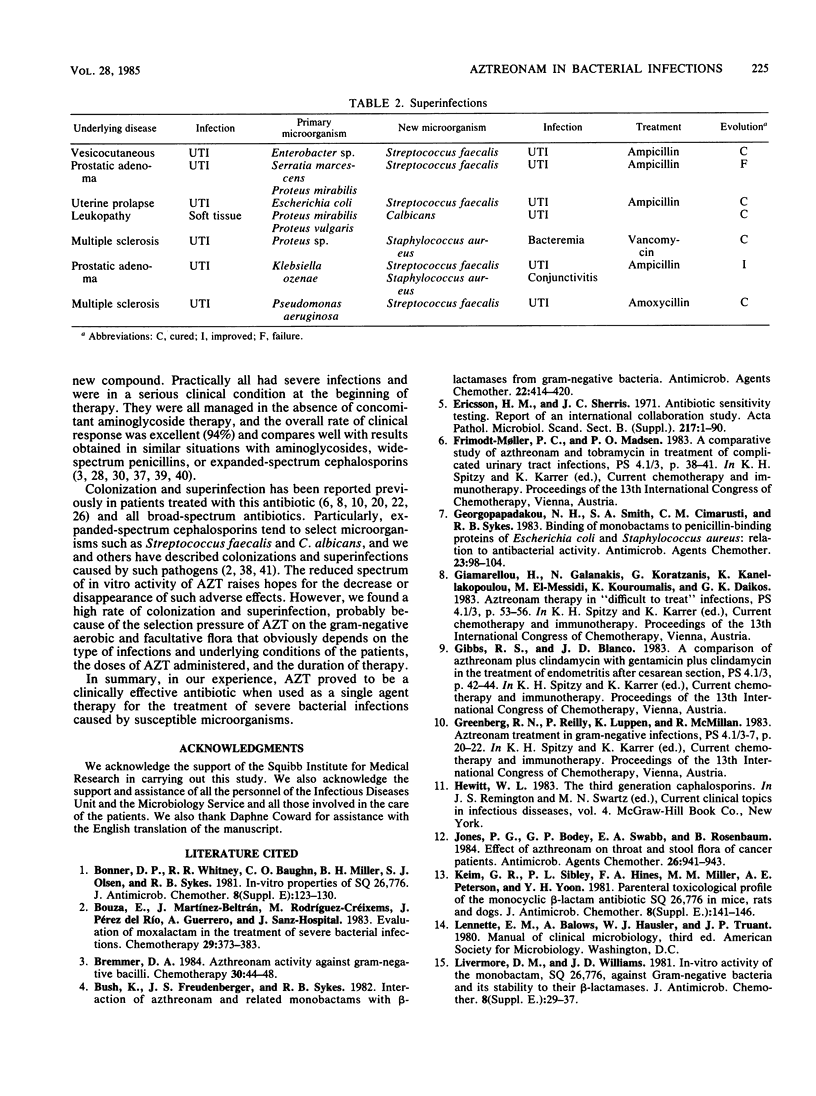
We investigated the clinical efficacy and safety of aztreonam in the treatment of 50 episodes of infection in 46 adult patients. The clinical condition of patients at the beginning of treatment was critical or poor in 28 of the episodes of infection. Episodes treated were 39 urinary tract infections (12 of them with concomitant bacteremia), 2 soft tissue infections, 8 patients with osteomyelitis (1 with concomitant bacteremia), and one episode of pneumonia. Significant isolated microorganisms were aerobic or facultative gram-negative rods and were responsible for the following episodes of infection (number of episodes): members of the family Enterobacteriaceae (49), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (5), and Haemophilus influenzae (1). The overall rate of clinical response to aztreonam was 94% of the treated episodes. Colonization or superinfection or both occurred in 29 episodes, but only 8 episodes required antimicrobial therapy. Aztreonam seems to be an effective single agent therapy for many bacterial infections. Colonization and superinfection by Candida sp., Streptococcus faecalis or Staphylococcus aureus must be monitored.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonner D. P., Whitney R. R., Baughn C. O., Miller B. H., Olsen S. J., Sykes R. B. In-vivo properties of SQ 26,776. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl E):123–130. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_e.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouza E., Martínez-Beltrán J., Rodríguez-Creixems M., Loza E., Pérez del Rio J., Guerrero A., Hospital J. S. Evaluation of lamoxactam in the treatment of severe bacterial infections. Chemotherapy. 1983;29(5):373–383. doi: 10.1159/000238222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush K., Freudenberger J. S., Sykes R. B. Interaction of azthreonam and related monobactams with beta-lactamases from gram-negative bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Sep;22(3):414–420. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.3.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericsson H. M., Sherris J. C. Antibiotic sensitivity testing. Report of an international collaborative study. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;217(Suppl):1+–1+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopapadakou N. H., Smith S. A., Cimarusti C. M., Sykes R. B. Binding of monobactams to penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus: relation to antibacterial activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jan;23(1):98–104. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.1.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBSON M. H., LEVY S. E., KAUFMAN R. M., GALLINEK W. E., DONNELLY O. W. Urine osmolality. A definitive test of renal function. Arch Intern Med. 1962 Jul;110:83–89. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1962.03620190085013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. G., Bodey G. P., Swabb E. A., Rosenbaum B. Effect of aztreonam on throat and stool flora of cancer patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Dec;26(6):941–943. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.6.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keim G. R., Sibley P. L., Hines F. A., Miller M. M., Peterson A. E., Yoon Y. H. Parenteral toxicological profile of the monocyclic beta-lactam antibiotic SQ 26,776 in mice, rats and dogs. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl E):141–146. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_e.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livermore D. M., Williams J. D. In-vitro activity of the monobactam, SQ 26,776, against Gram-negative bacteria and its stability to their beta-lactamases. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl E):29–37. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_e.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCloskey R. V. Results of a clinical trial of cefoxitin, a new cephamycin antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Nov;12(5):636–641. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.5.636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihindu J. C., Scheld W. M., Bolton N. D., Spyker D. A., Swabb E. A., Bolton W. K. Pharmacokinetics of aztreonam in patients with various degrees of renal dysfunction. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Aug;24(2):252–261. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.2.252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Labthavikul P. Antibacterial activity of a monocyclic beta-lactam SQ 26,776. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl E):111–122. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_e.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I., King A., Shannon K., Warren C. SQ 26,776: in-vitro antibacterial activity and susceptibility to beta-lactamases. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl E):103–110. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_e.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scully B. E., Neu H. C. Clinical efficacy of ceftazidime. Treatment of serious infection due to multiresistant Pseudomonas and other gram-negative bacteria. Arch Intern Med. 1984 Jan;144(1):57–62. doi: 10.1001/archinte.144.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scully B. E., Swabb E. A., Neu H. C. Pharmacology of aztreonam after intravenous infusion. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jul;24(1):18–22. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.1.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. R., Baughman K. L., Edwards C. Q., Rogers J. F., Lietman P. S. Controlled comparison of amikacin and gentamicin. N Engl J Med. 1977 Feb 17;296(7):349–353. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197702172960701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutman H. R., Welch D. F., Scribner R. K., Marks M. I. In vitro antimicrobial activity of aztreonam alone and in combination against bacterial isolates from pediatric patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Feb;25(2):212–215. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.2.212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swabb E. A., Leitz M. A., Pilkiewicz F. G., Sugerman A. A. Pharmacokinetics of the monobactam SQ 26,776 after single intravenous doses in healthy subjects. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl E):131–140. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_e.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swabb E. A., Singhvi S. M., Leitz M. A., Frantz M., Sugerman A. Metabolism and pharmacokinetics of aztreonam in healthy subjects. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Sep;24(3):394–400. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.3.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Bonner D. P., Bush K., Georgopapadakou N. H., Wells J. S. Monobactams--monocyclic beta-lactam antibiotics produced by bacteria. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl E):1–16. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_e.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. L. The cephalosporins. Mayo Clin Proc. 1977 Oct;52(10):625–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston D. J., Busuttil R. W., Kurtz T. O., Young L. S. Moxalactam therapy for bacterial infections. Arch Intern Med. 1981 Nov;141(12):1607–1612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston D. J., Murphy W., Young L. S., Hewitt W. L. Piperacillin therapy for serious bacterial infections. Am J Med. 1980 Aug;69(2):255–261. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90386-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Martin W. J., Meyer R. D., Weinstein R. J., Anderson E. T. Gram-negative rod bacteremia: microbiologic, immunologic, and therapeutic considerations. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Apr;86(4):456–471. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-4-456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. L. Enterococcal superinfection and colonization after therapy with moxalactam, a new broad-spectrum antibiotic. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Jun;94(6):784–785. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-6-784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



