Abstract
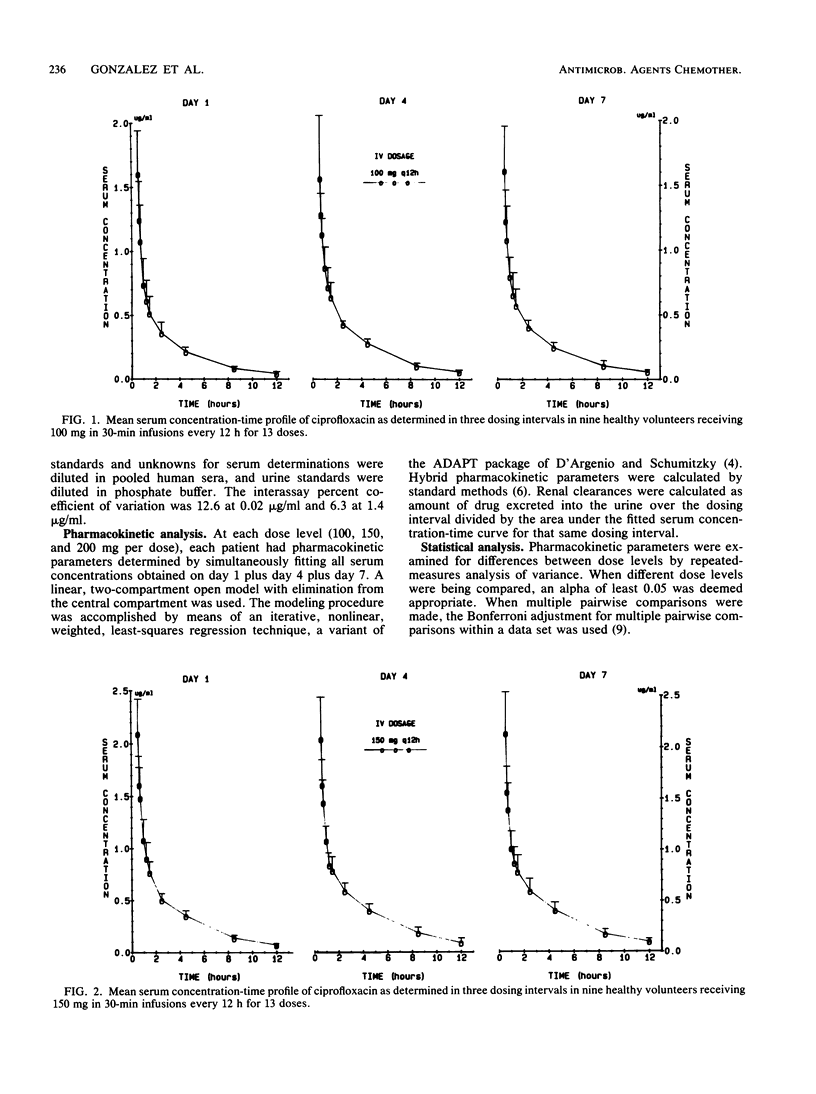
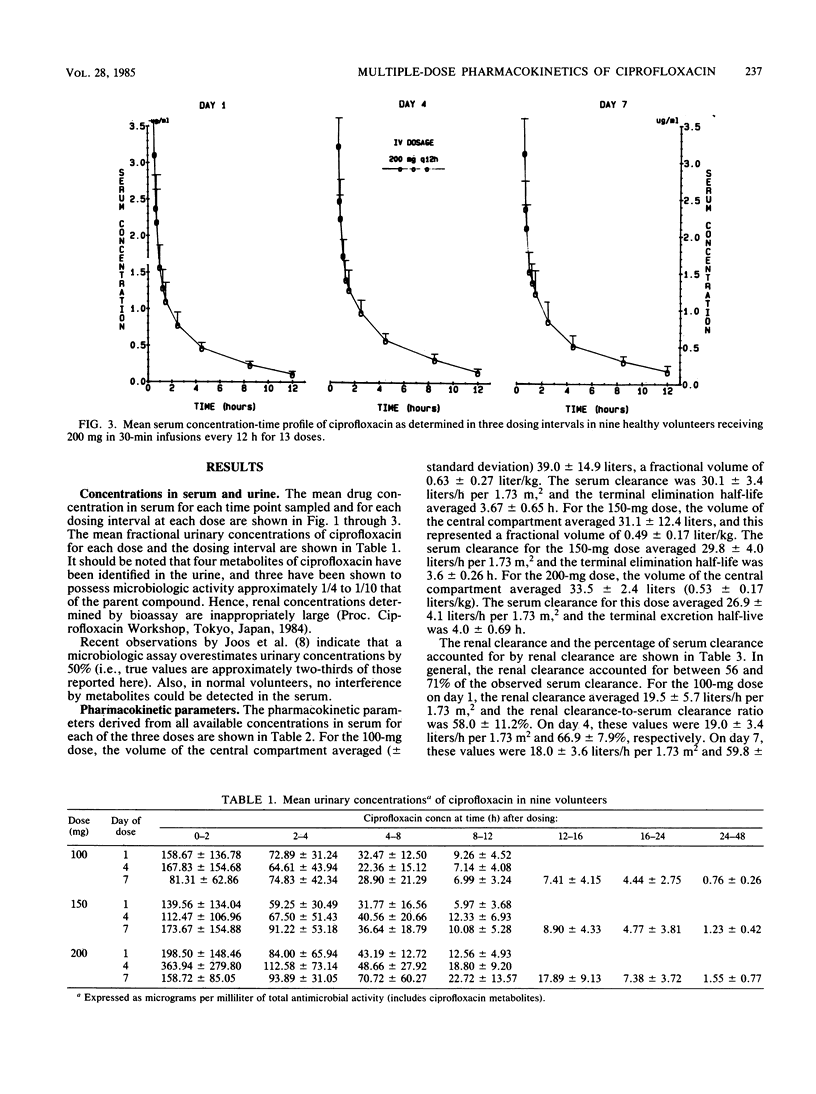
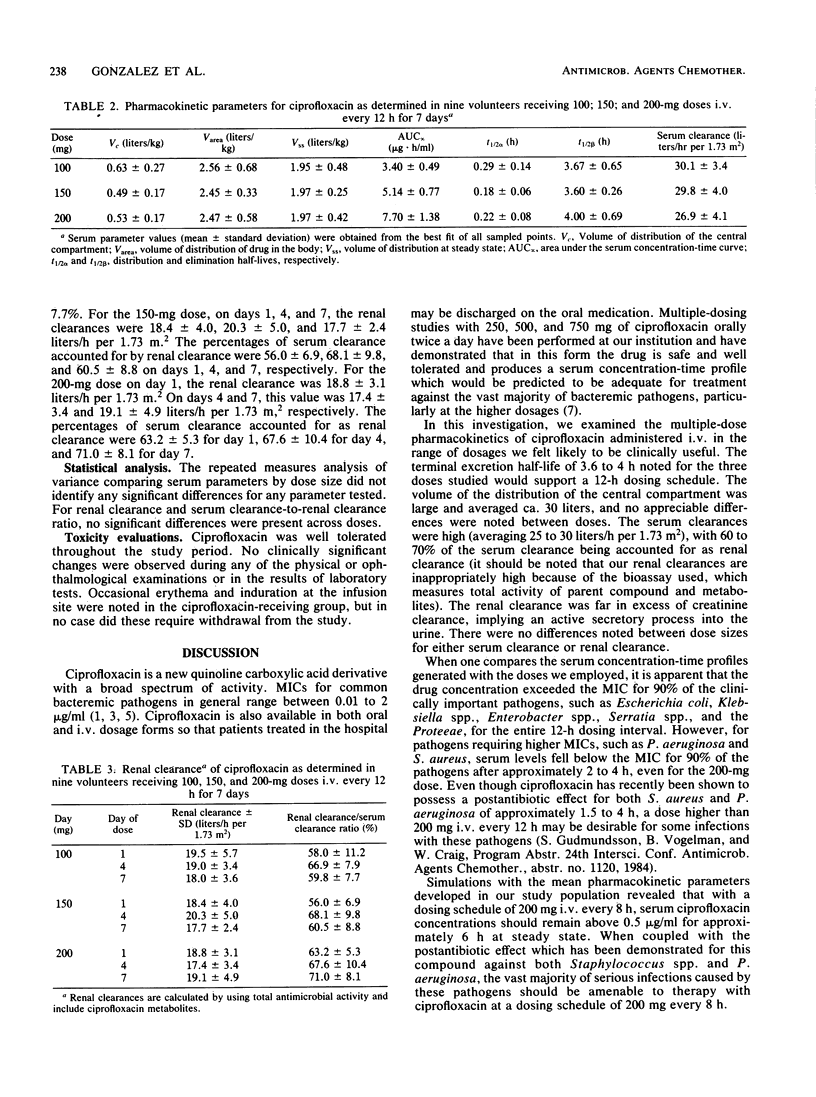
We administered multiple doses of ciprofloxacin intravenously over 30 min every 12 h for 1 week to nine healthy volunteers. Three volunteers received a placebo (vehicle) intravenously. Doses of 100, 150, and 200 mg were evaluated with a 1-week wash-out period intervening between each dose level. Terminal excretion half-lives averaged 3.67 +/- 0.65, 3.60 +/- 0.26, and 4.00 +/- 0.69 h for the 100-, 150-, and 200-mg doses, respectively. Serum clearances were 30.1 +/- 3.4, 29.8 +/- 4.0, and 26.9 +/- 4.1 liters/h per 1.73 m2 for these doses. Urine concentrations remained in excess of the MIC for 90% of the relevant urinary tract pathogens for the full 12-h dosing interval at each dose. Renal clearance accounted for 56 to 71% of the serum clearance. However, because a microbiologic assay was used and biologically active, renally excreted metabolites were identified, the renal clearance determinations are likely to be in excess of the true values. The doses of ciprofloxacin administered intravenously were well tolerated, and the drug concentrations appeared adequate for the treatment of the vast majority of cases of nosocomially acquired sepsis and urinary tract infections. For patients with serious Pseudomonas infections and perhaps staphylococcal infections, either an 8-h dosing schedule or larger doses on a 12-h schedule should be considered.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry A. L., Jones R. N., Thornsberry C., Ayers L. W., Gerlach E. H., Sommers H. M. Antibacterial activities of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, oxolinic acid, cinoxacin, and nalidixic acid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 May;25(5):633–637. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.5.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. V., Brodie J. L., Benner E. J., Kirby W. M. Simplified, accurate method for antibiotic assay of clinical specimens. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Mar;14(2):170–177. doi: 10.1128/am.14.2.170-177.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin N. X., Neu H. C. Ciprofloxacin, a quinolone carboxylic acid compound active against aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):319–326. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Argenio D. Z., Schumitzky A. A program package for simulation and parameter estimation in pharmacokinetic systems. Comput Programs Biomed. 1979 Mar;9(2):115–134. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(79)90025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliopoulos G. M., Gardella A., Moellering R. C., Jr In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin, a new carboxyquinoline antimicrobial agent. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):331–335. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez M. A., Uribe F., Moisen S. D., Fuster A. P., Selen A., Welling P. G., Painter B. Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics and safety of ciprofloxacin in normal volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Nov;26(5):741–744. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.5.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joos B., Ledergerber B., Flepp M., Bettex J. D., Lüthy R., Siegenthaler W. Comparison of high-pressure liquid chromatography and bioassay for determination of ciprofloxacin in serum and urine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Mar;27(3):353–356. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.3.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



