Abstract
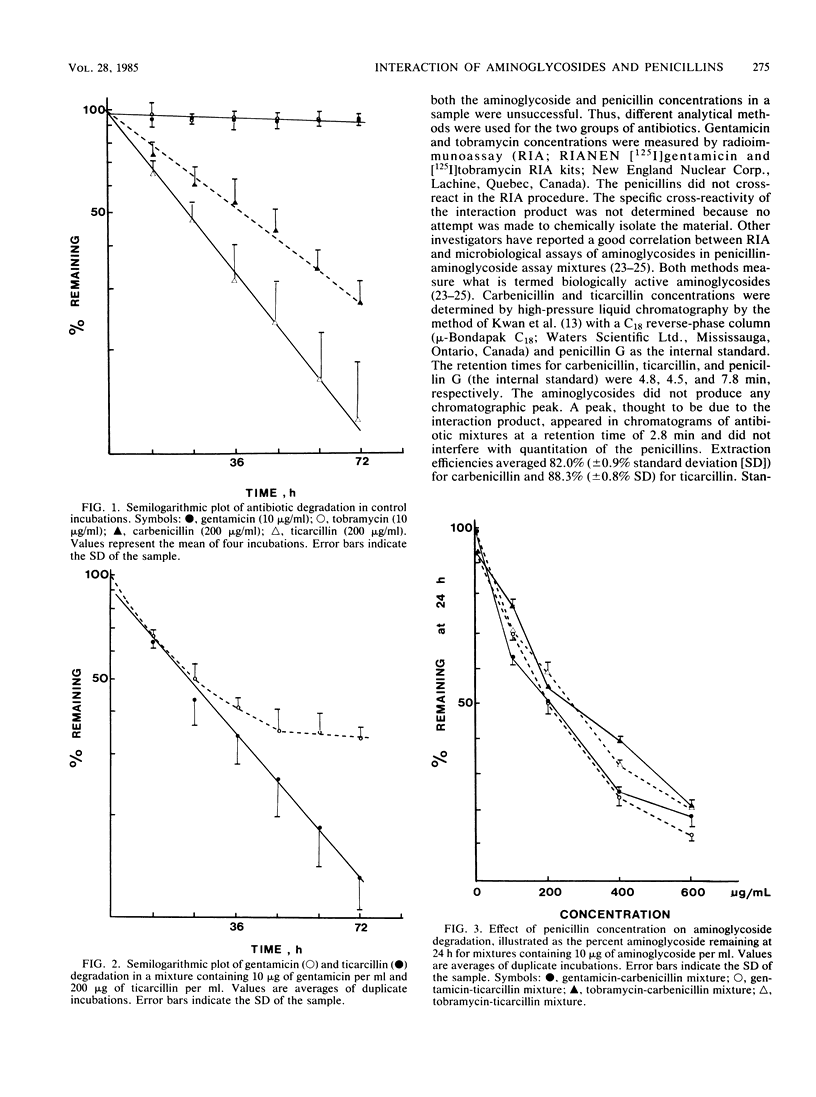
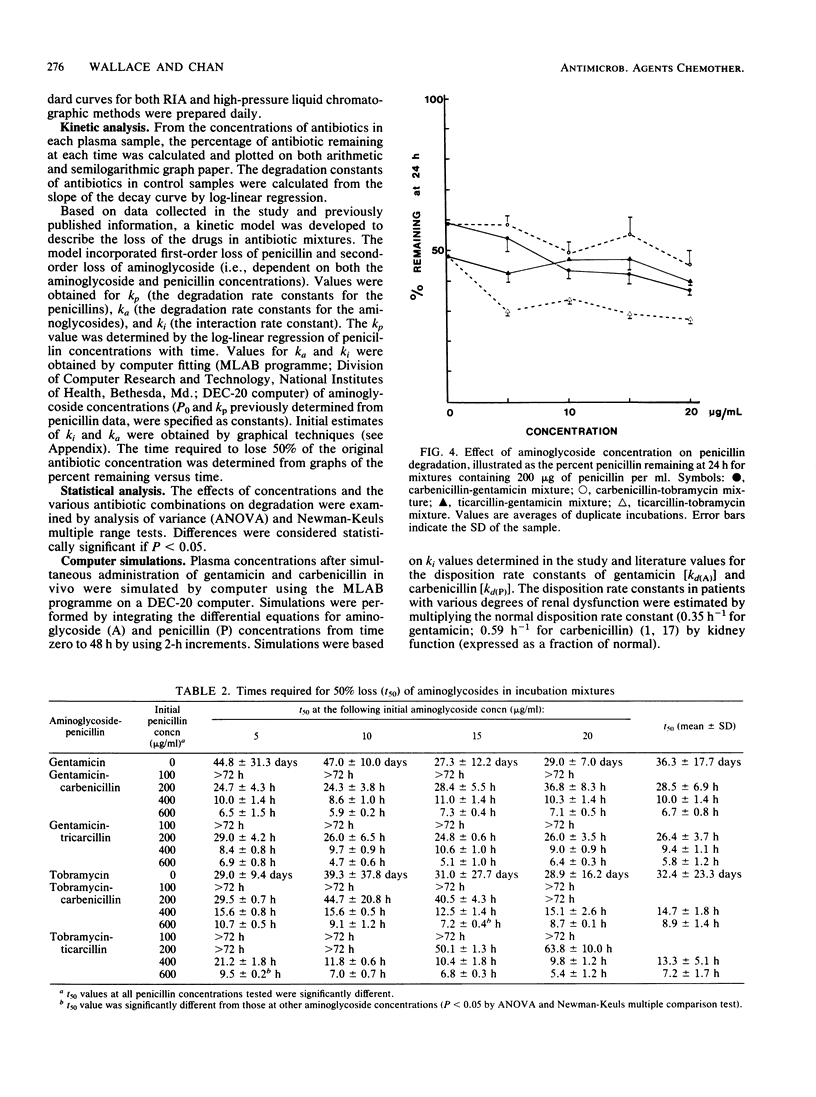
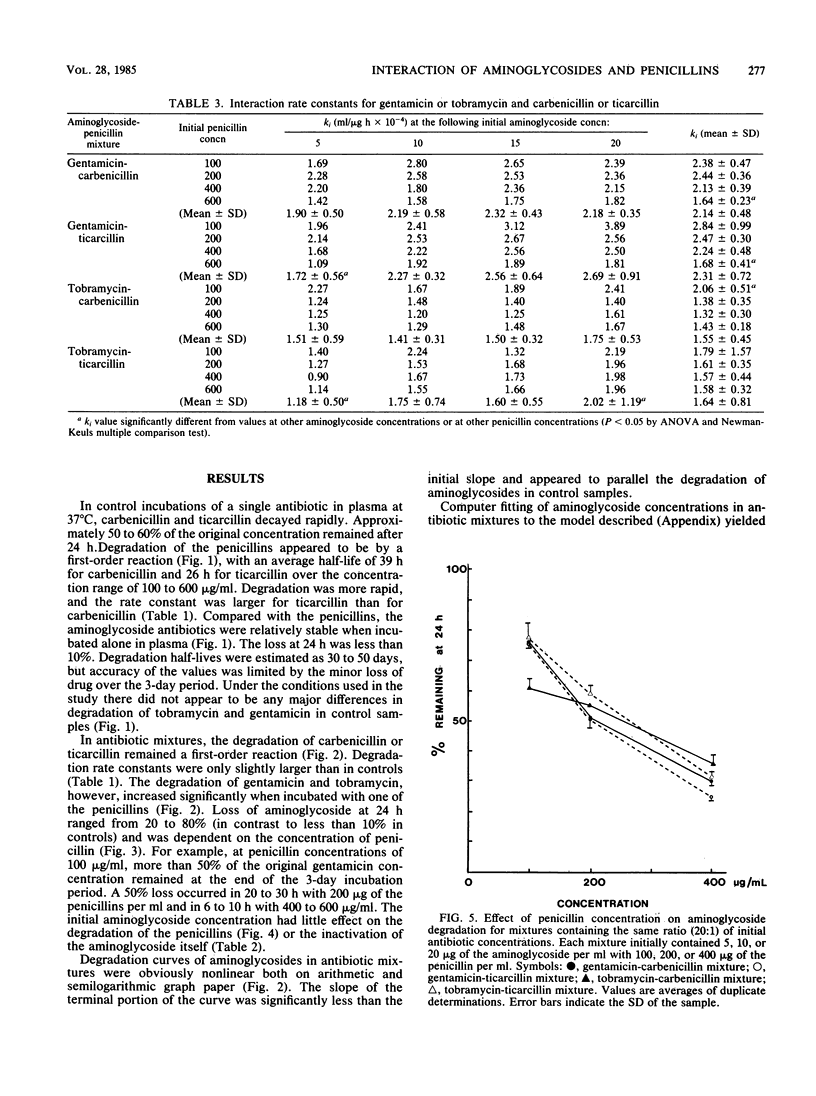
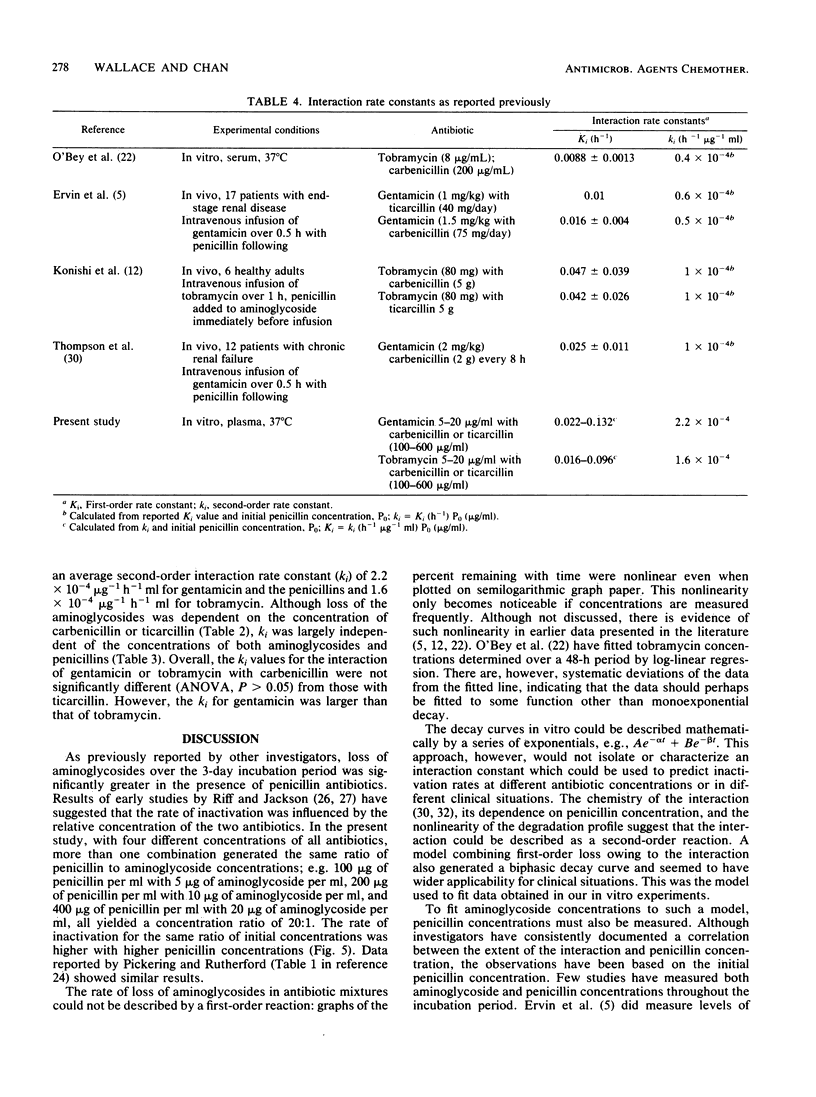
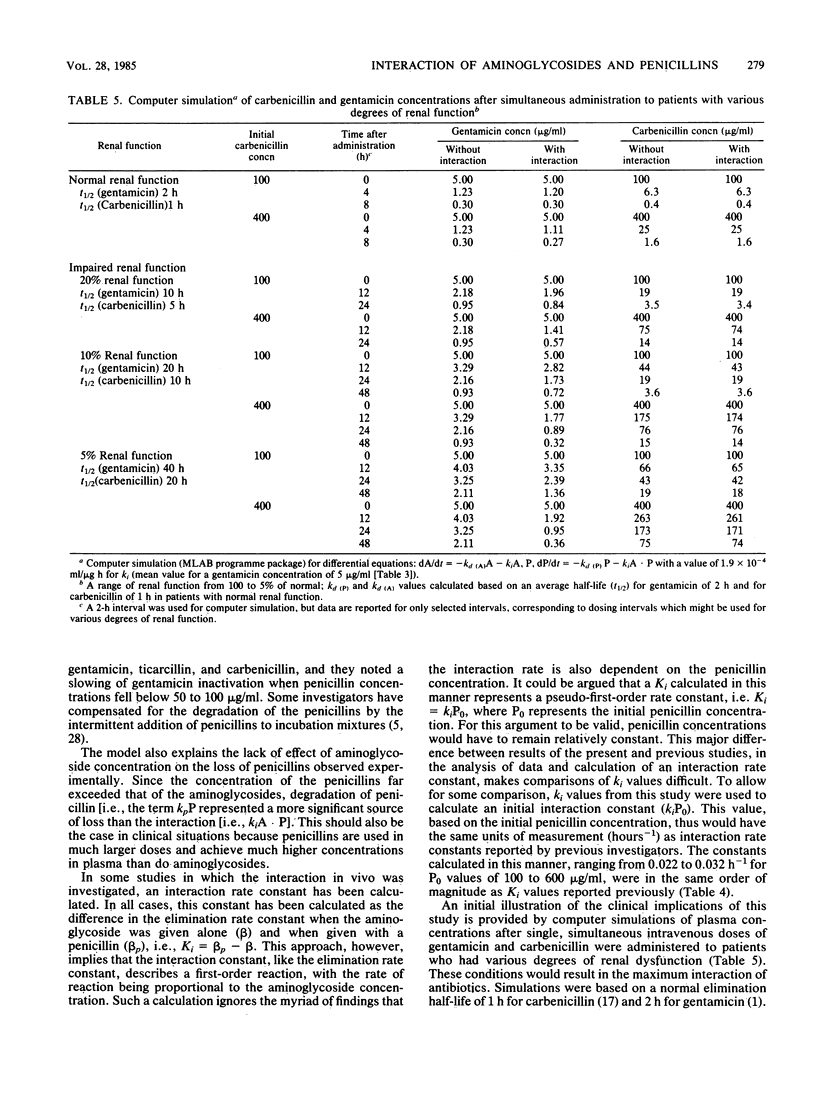
The aminoglycosides are used clinically in combination with beta-lactam antibiotics. The combined use, however, produces an interaction and inactivation of the antibiotics. A study was designed to investigate the kinetics of the interaction in vitro. Four concentrations of aminoglycosides (5 to 20 micrograms of gentamicin and tobramycin per ml) and penicillins (100 to 600 micrograms of carbenicillin and ticarcillin per ml) were incubated in plasma (3 days, 37 degrees C). Samples taken at 12-h intervals were analyzed for both aminoglycosides (radioimmunoassay) and penicillin (high-pressure liquid chromatography). In controls, degradation of all four antibiotics were by first-order reactions. In incubation mixtures of two antibiotics, the rate of loss of the aminoglycosides was greater than that in the controls, whereas the rate of loss of penicillins was not significantly increased. The loss of penicillins in incubation mixtures still appeared to be by first-order reactions. However, semilogarithmic plots of aminoglycoside concentrations were curvilinear, suggesting a second-order reaction. Aminoglycoside concentrations in incubation mixtures were fitted by computer to a model incorporating a second-order interaction between aminoglycosides and penicillins and the first-order loss of penicillin from the mixture. The interaction rate constant averaged 2.2 X 10(-4) (micrograms/ml h)-1 for interaction of both carbenicillin and ticarcillin with gentamicin and 1.6 X 10(-4) (micrograms/ml h)-1 for interaction of the penicillins with tobramycin. The effect of the interaction in vivo was examined by computer simulation using the kinetic parameters determined in vitro.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appel G. B., Neu H. C. Gentamicin in 1978. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Oct;89(4):528–538. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-4-528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronoff G. R., Brier M. E., Nierste D. M., Sloan R. S. Interactions of moxalactam and tobramycin in normal volunteers and in patients with impaired renal function. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jan;149(1):9–15. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. C., Duggan D. O., Schroeder E. T. Inactivation of amikacin and gentamicin by carbenicillin in patients with end-stage renal failure. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Sep;22(3):376–379. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.3.376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M., Morgan J. R., Anand C. Interactions of carbenicillin and ticarcillin with gentamicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Apr;7(4):431–434. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.4.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ervin F. R., Bullock W. E., Jr, Nuttall C. E. Inactivation of gentamicin by penicillins in patients with renal failure. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jun;9(6):1004–1011. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.6.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eykyn S., Phillips I., Ridley M. Gentamicin plus carbenicillin. Lancet. 1971 Mar 13;1(7698):545–546. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91144-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flournoy D. J. Inactivation of netilmicin by carbenicillin. Infection. 1978;6(5):241–241. doi: 10.1007/BF01642317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glew R. H., Pavuk R. A. Stability of gentamicin, tobramycin, and amikacin in combination with four beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Oct;24(4):474–477. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.4.474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson J. L., Polk R. E., Kline B. J. In vitro inactivation of gentamicin, tobramycin, and netilmicin by carbenicillin, azlocillin, or mezlocillin. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1981 Aug;38(8):1167–1170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt H. A., Broughall J. M., McCarthy M., Reeves D. S. Interactions between aminoglycoside antibiotics and carbenicillin or ticarillin. Infection. 1976;4(2):107–109. doi: 10.1007/BF01638726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. M., Blazevic D. J., Balfour H. H. Stability of gentamicin in serum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Nov;10(5):866–867. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.5.866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi H., Goto M., Nakamoto Y., Yamamoto I., Yamashina H. Tobramycin inactivation by carbenicillin, ticarcillin, and piperacillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 May;23(5):653–657. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.5.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwan R. H., MacLeod S. M., Spino M., Teare F. W. High-pressure liquid chromatographic assays for ticarcillin in serum and urine. J Pharm Sci. 1982 Oct;71(10):1118–1121. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600711010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau A., Lee M., Flascha S., Prasad R., Sharifi R. Effect of piperacillin on tobramycin pharmacokinetics in patients with normal renal function. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Oct;24(4):533–537. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.4.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levison M. E., Kaye D. Carbenicillin plus gentamicin. Lancet. 1971 Jul 3;2(7714):45–46. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levison M. E., Knight R., Kaye D. In vitro evaluation of tobramycin, a new aminoglycoside antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 May;1(5):381–384. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.5.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libke R. D., Clarke J. T., Ralph E. D., Luthy R. P., Kirby W. M. Ticarcillin vs carbenicillin: clinical pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Apr;17(4):441–446. doi: 10.1002/cpt1975174441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundergan F. S., Lombardi T. P., Neilan G. E., Nightingale C. H. Stability of tobramycin sulfate mixed with oxacillin sodium and nafcillin sodium in human serum. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1984 Jan;41(1):144–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin J. E., Reeves D. S. Clinical and laboratory evidence for inactivation of gentamicin by carbenicillin. Lancet. 1971 Feb 6;1(7693):261–264. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murillo J., Standiford H. C., Schimpff S. C., Tatem B. A. Gentamicin and ticarcillin serum levels. JAMA. 1979 Jun 1;241(22):2401–2403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noone P., Pattison J. R. Therapeutic implications of interaction of gentamicin and penicillins. Lancet. 1971 Sep 11;2(7724):575–578. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Bey K. A., Jim L. K., Gee J. P., Johnson R. M. Temperature dependence of the stability of tobramycin mixed with penicillins in human serum. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1982 Jun;39(6):1005–1008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering L. K., Gearhart P. Effect of time and concentration upon interaction between gentamicin, tobramycin, Netilmicin, or amikacin and carbenicillin or ticarcillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Apr;15(4):592–596. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.4.592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering L. K., Rutherford I. Effect of concentration and time upon inactivation of tobramycin, gentamicin, netilmicin and amikacin by azlocillin, carbenicillin, mecillinam, mezlocillin and piperacillin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 May;217(2):345–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieper J. A., Vidal R. A., Schentag J. J. Animal model distinguishing in vitro from in vivo carbenicillin-aminoglycoside interactions. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Oct;18(4):604–609. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.4.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riff L. J., Jackson G. G. Laboratory and clinical conditions for gentamicin inactivation by carbenicillin. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Dec;130(6):887–891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riff L. J., Thomason J. L. Comparative aminoglycoside inactivation by beta-lactam antibiotics. Effects of a cephalosporin and six penicillins on five aminoglycosides. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1982 Jul;35(7):850–857. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.35.850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riff L., Jackson G. G. Gentamicin plus carbenicillin. Lancet. 1971 Mar 20;1(7699):592–592. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91183-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teil S. M., Arwood L. L., Visconti J. A. Stability of gentamicin and cefamandole in serum. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1982 Mar;39(3):485–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson M. I., Russo M. E., Saxon B. J., Atkin-Thor E., Matsen J. M. Gentamicin inactivation by piperacillin or carbenicillin in patients with end-stage renal disease. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):268–273. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tindula R. J., Ambrose P. J., Harralson A. F. Aminoglycoside inactivation by penicillins and cephalosporins and its impact on drug-level monitoring. Drug Intell Clin Pharm. 1983 Dec;17(12):906–908. doi: 10.1177/106002808301701210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waitz J. A., Drube C. G., Moss E. L., Jr, Oden E. M., Bailey J. V. Biological aspects of the interaction between gentamicin and carbenicillin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Apr;25(4):219–225. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibert R., Keane W., Shapiro F. Carbenicillin inactivation of aminoglycosides in patients with severe renal failure. Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs. 1976;22:439–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



