Abstract
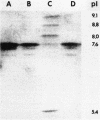
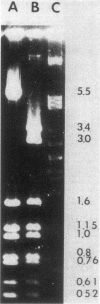
A clinical isolate of Klebsiella ozaenae with transferable resistance to broad-spectrum cephalosporins produces a beta-lactamase determined by plasmid pBP60. The beta-lactamase had the same isoelectric point as SHV-1 (7.6). From heteroduplex analysis, an extensive homology between the two bla genes could be deduced; therefore, the new beta-lactamase was designated SHV-2. Enzymatic studies revealed that SHV-2 was able to hydrolyze broad-spectrum cephalosporins due to an increased affinity of these compounds for the enzyme. The assumption that SHV-2 is a natural mutant of SHV-1 was strongly supported by the isolation of a laboratory mutant of SHV-1 that showed activities similar to those of SHV-2.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu K. P., Neu H. C. beta-lactamase stability of HR 756, a novel cephalosporin, compared to that of cefuroxime and cefoxitin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):322–326. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinsted J., Saunders J. R., Ingram L. C., Sykes R. B., Richmond M. H. Properties of a R factor which originated in Pseudomonas aeruginosa 1822. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):529–537. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.529-537.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A., Knowles J. R. Directed selective pressure on a beta-lactamase to analyse molecular changes involved in development of enzyme function. Nature. 1976 Dec 23;264(5588):803–804. doi: 10.1038/264803a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges R. W., Datta N., Kontomichalou P., Smith J. T. Molecular specificities of R factor-determined beta-lactamases: correlation with plasmid compatibility. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):56–62. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.56-62.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Iyobe S., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Purification and properties of a new beta-lactamase from Pseudomonas cepacia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Mar;17(3):355–358. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.3.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Sato K., Matsubara N., Katsumata R., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Immunological properties of beta-lactamases that hydrolyze cefuroxime and cefotaxime. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Aug;20(2):262–264. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.2.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knothe H., Shah P., Krcmery V., Antal M., Mitsuhashi S. Transferable resistance to cefotaxime, cefoxitin, cefamandole and cefuroxime in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Serratia marcescens. Infection. 1983 Nov-Dec;11(6):315–317. doi: 10.1007/BF01641355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labia R., Le Goffic F., Andrillon J. Etude cinétique de deux beta lactamases responsables d'un møeme phénotype. Biochimie. 1974;56(8):1025–1030. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(74)80092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew M., Hedges R. W., Smith J. T. Types of beta-lactamase determined by plasmids in gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;138(3):657–662. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.3.657-662.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J. F., Nies B. A., Wiedemann B. Amikacin resistance mediated by multiresistance transposon Tn2424. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):755–760. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.755-760.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roupas A., Pitton J. S. R factor-mediated and chromosomal resistance to ampicillin in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Feb;5(2):186–191. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.2.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr Emergence of resistance to cefamandole: possible role of cefoxitin-inducible beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jun;15(6):792–797. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.6.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeberg A. H., Tolxdorff-Neutzling R. M., Wiedemann B. Chromosomal beta-lactamases of Enterobacter cloacae are responsible for resistance to third-generation cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):918–925. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seibert G., Limbert M. Purification and characterization of a cephalosporinase from E. coli. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1982 Dec;253(3):358–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Nordström K. Microiodometric determination of beta-lactamase activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Feb;1(2):94–99. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.2.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajima M., Takenouchi Y., Sugawara S., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Purification and properties of chromosomally mediated beta-lactamase from Citrobacter freundii GN7391. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Dec;121(2):449–456. doi: 10.1099/00221287-121-2-449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu H., Nikaido H. Role of beta-lactam hydrolysis in the mechanism of resistance of a beta-lactamase-constitutive Enterobacter cloacae strain to expanded-spectrum beta-lactams. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Mar;27(3):393–398. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.3.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Treeck U., Schmidt F., Wiedemann B. Molecular nature of a streptomycin and sulfonamide resistance plasmid (pBP1) prevalent in clinical Escherichia coli strains and integration of an ampicillin resistance transposon (TnA). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Mar;19(3):371–380. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.3.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]