Abstract
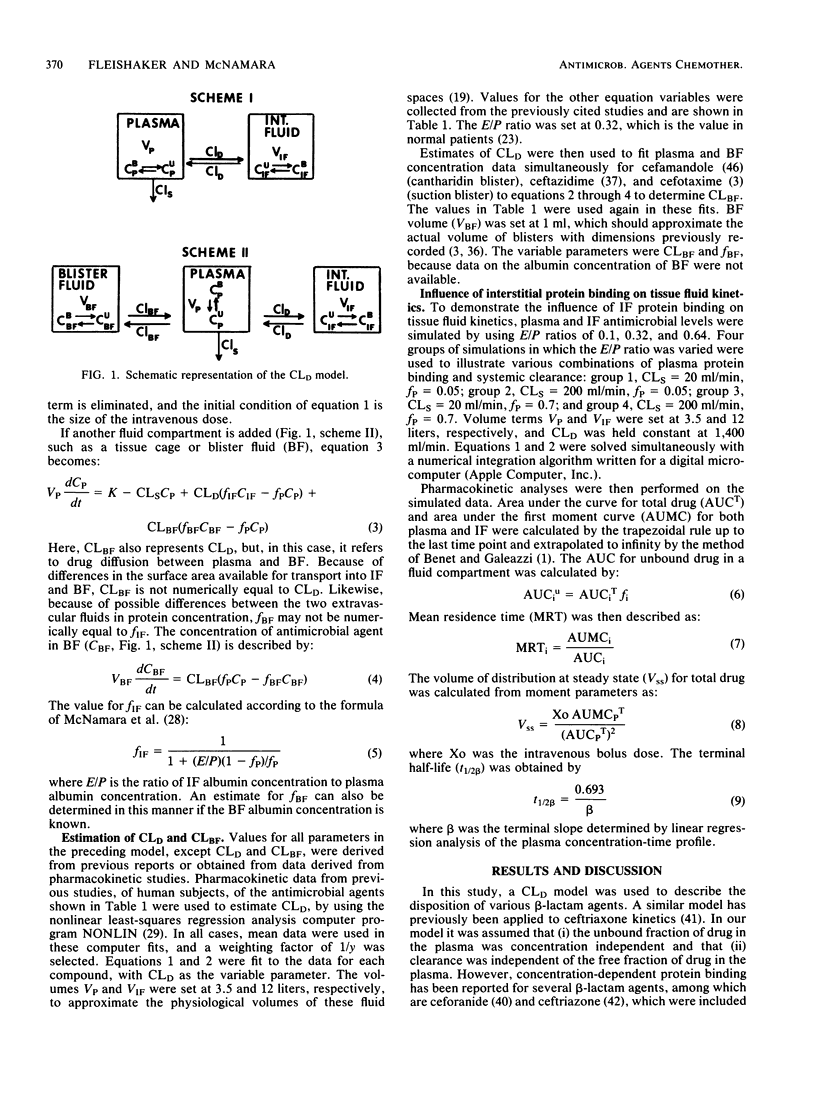
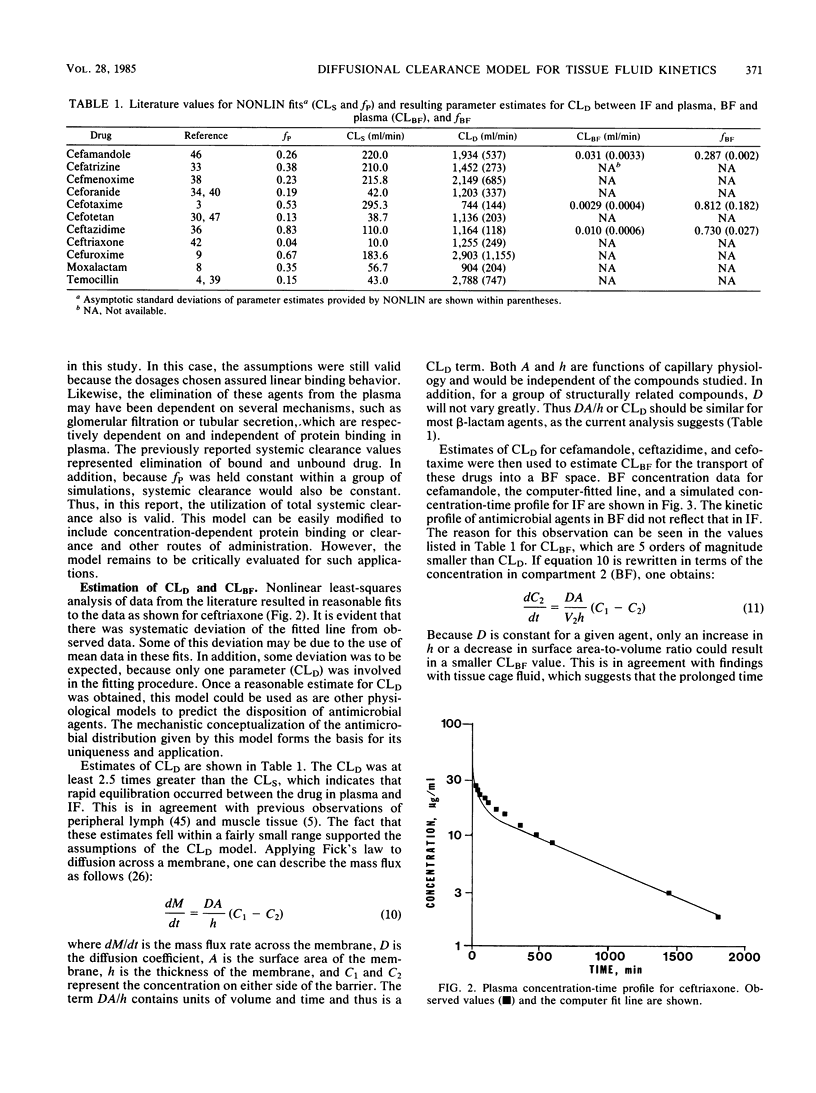
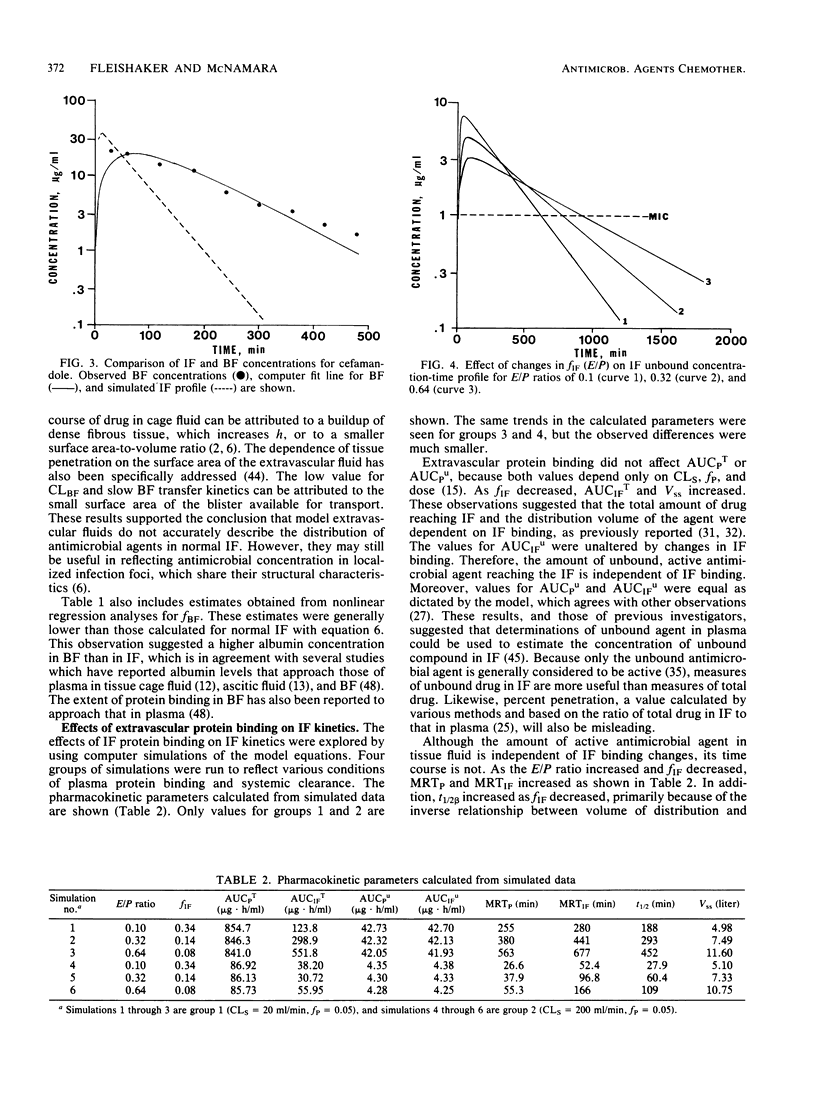
A physiological model based on diffusional clearance (CLD) of drug between plasma and interstitial fluid (IF) was used to describe the disposition of beta-lactam antimicrobial agents. The CLD represents the movement of drug in and out of physiological spaces and is dependent only on the transfer properties of the drug. Estimates of CLD obtained by fitting model equations to plasma concentration-time data for 11 cephalosporin studies in human subjects fell in a fairly narrow range, with a mean value of 1,604 ml/min. Estimates of the CLD between plasma and blister fluid for three of the cephalosporins were five orders of magnitude smaller than the CLD. These observations are explained in terms of diffusion principles. Computer simulations with this model were used to assess the effect of changes in IF protein binding on antimicrobial distribution. Increases in the bound fraction of drug in IF enhanced the penetration of total (bound and unbound) drug into IF, but had no effect on the amount of unbound, active antimicrobial agent reaching the IF. The time course of unbound drug in IF was altered, however, by changes in IF protein binding. This model may also be used to predict changes in the IF distribution of beta-lactam antimicrobial agents in disease states, particularly those in which the relative distribution of albumin between plasma and IF has been altered.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benet L. Z., Galeazzi R. L. Noncompartmental determination of the steady-state volume of distribution. J Pharm Sci. 1979 Aug;68(8):1071–1074. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600680845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergan T., Kalager T., Hellum K. B., Solberg C. O. Penetration of cefotaxime and desacetylcefotaxime into skin blister fluid. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Sep;10(3):193–196. doi: 10.1093/jac/10.3.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergan T. Kinetics of tissue penetration. Are high plasma peak concentrations or sustained levels preferable for effective antibiotic therapy? Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1978;(14):36–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boelaert J., Daneels R., Schurgers M., Lambert A. M., Van Landuyt H. W., Mellows G., Wolf J., Swaisland A. J. The pharmacokinetics of temocillin in patients with normal and impaired renal function. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Apr;11(4):349–356. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.4.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cars O., Ogren S. Tissue penetration of ampicillin: parallel determinations of levels in tissue cage fluid and rabbit muscle. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 May;6(3):408–410. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.3.408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisholm G. D. The tissue cage model in the distribution of antibacterial agents. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1978;(14):118–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig W. A., Suh B. Theory and practical impact of binding of antimicrobials to serum proteins and tissue. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1978;(14):92–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drusano G. L., Standiford H. C., Fitzpatrick B., Leslie J., Tangtatsawasdi P., Ryan P., Tatem B., Moody M. R., Schimpff S. C. Comparison of the pharmacokinetics of ceftazidime and moxalactam and their microbiological correlates in volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Sep;26(3):388–393. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.3.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng R. H., Gorski S., Person A., Mangura C., Chmel H. Clindamycin elimination in patients with liver disease. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Oct;8(4):277–281. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.4.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foord R. D. Cefuroxime: human pharmacokinetics.. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 May;9(5):741–747. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.5.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gengo F. M., Schentag J. J., Jusko W. J. Pharmacokinetics of capacity-limited tissue distribution of methicillin in rabbits. J Pharm Sci. 1984 Jul;73(7):867–873. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600730703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gengo F. M., Schentag J. J. Methicillin distribution in serum and extravascular fluid and its relevance to normal and damaged heart valves. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):836–841. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerding D. N., Hall W. H., Schierl E. A., Manion R. E. Cephalosporin and aminoglycoside concentrations in peritoneal capsular fluid in rabbits. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Dec;10(6):902–911. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.6.902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerding D. N., Peterson L. R., Salomonson J. K., Hall W. H., Schierl E. A. Prediction of the concentration of penicillins in ascitic fluid from serum kinetics and protein binding of the antibiotics in serum and ascitic fluid of dogs. J Infect Dis. 1978 Aug;138(2):166–173. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.2.166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibaldi M., Levy G., McNamara P. J. Effect of plasma protein and tissue binding on the biologic half-life of drugs. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978 Jul;24(1):1–4. doi: 10.1002/cpt19782411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillette J. R. Overview of drug-protein binding. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Nov 26;226:6–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb20464.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene D. S., Quintiliani R., Nightingale C. H. Physiological perfusion model for cephalosporin antibiotics I: Model selection based on blood drug concentrations. J Pharm Sci. 1978 Feb;67(2):191–196. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600670217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm S. E. Experimental models for studies on transportation of antibiotics to extravasal compartments. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1978;(13):47–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornguth M. L., Monson R. A., Kunin C. M. Binding of antibiotics to a soluble protein from rat liver. J Infect Dis. 1974 May;129(5):552–558. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.5.552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau Z., Halkin H., Rubinstein E. Interstitial fluid concentrations of cefsulodin, azlocillin and carbenicillin. Scand J Infect Dis. 1981;13(3):227–232. doi: 10.3109/inf.1981.13.issue-3.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattie H. Tissue penetration of antibiotics. Pharmacokinetic aspects of tissue penetration. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1978;(14):125–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara P. J., Gibaldi M., Stoeckel K. Fraction unbound in interstitial fluid. J Pharm Sci. 1983 Jul;72(7):834–836. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600720735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkawa M., Hirano S., Tokunaga S., Motoi I., Shoda R., Ikeda A., Sugata T., Sawaki M., Shimamura M., Okasho A. Pharmacokinetics of cefotetan in normal subjects and patients with impaired renal function. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jan;23(1):31–35. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. R., Gerding D. N. Influence of protein binding of antibiotics on serum pharmacokinetics and extravascular penetration: clinically useful concepts. Rev Infect Dis. 1980 May-Jun;2(3):340–348. doi: 10.1093/clinids/2.3.340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. R., Van Etta L. L., Fasching C. E., Gerding D. N. Effect of protein binding on simulated intravascular and extravascular kinetics of cefotaxime in an in vitro model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jan;25(1):58–61. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.1.58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer M., Gaver R. C., Ximenez J. Human intravenous pharmacokinetics and absolute oral bioavailability of cefatrizine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Dec;24(6):915–920. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.6.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ripa S., La Rosa F., Ghezzi A., Prenna M., Pfeffer M. Pharmacokinetics of ceforanide. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):323–326. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan D. M., Hodges B., Spencer G. R., Harding S. M. Simultaneous comparison of three methods for assessing ceftazidime penetration into extravascular fluid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Dec;22(6):995–998. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.6.995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan D. M. Implanted cotton threads; a novel method for measuring concentrations of antibiotics in tissue fluid. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1979 Nov;5(6):735–737. doi: 10.1093/jac/5.6.735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sennello L. T., Quinn D., Rollins D. E., Tolman K. G., Sonders R. C. Effect of probenecid on the pharmacokinetics of cefmenoxime. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):803–807. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slocombe B., Basker M. J., Bentley P. H., Clayton J. P., Cole M., Comber K. R., Dixon R. A., Edmondson R. A., Jackson D., Merrikin D. J. BRL 17421, a novel beta-lactam antibiotic, highly resistant to beta-lactamases, giving high and prolonged serum levels in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jul;20(1):38–46. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth R. D., Pfeffer M., Glick A., Van Harken D. R., Hottendorf G. H. Clinical pharmacokinetics and safety of high doses of ceforanide (BL-S786R) and cefazolin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Nov;16(5):615–621. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.5.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckel K., Koup J. R. Pharmacokinetics of ceftriaxone in patients with renal and liver insufficiency and correlations with a physiologic nonlinear protein binding model. Am J Med. 1984 Oct 19;77(4C):26–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckel K., McNamara P. J., Brandt R., Plozza-Nottebrock H., Ziegler W. H. Effects of concentration-dependent plasma protein binding on ceftriaxone kinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 May;29(5):650–657. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji A., Yoshikawa T., Nishide K., Minami H., Kimura M., Nakashima E., Terasaki T., Miyamoto E., Nightingale C. H., Yamana T. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic model for beta-lactam antibiotics I: Tissue distribution and elimination in rats. J Pharm Sci. 1983 Nov;72(11):1239–1252. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600721103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Etta L. L., Fasching C. E., Peterson L. R., Gerding D. N. Comparison study of the kinetics of ceftizoxime penetration into extravascular spaces with known surface area/volume ratio in vitro and in vivo in rabbits. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jan;23(1):49–53. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Donovan I. A., Drumm J., Dent J., Bennett S. A. Intraperitoneal penetration of cefotetan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Aug;24(2):279–281. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Gillett A. P., Cadge B., Durham S. R., Baker S. The influence of protein binding upon tissue fluid levels of six beta-lactam antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jul;142(1):77–82. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



