Abstract
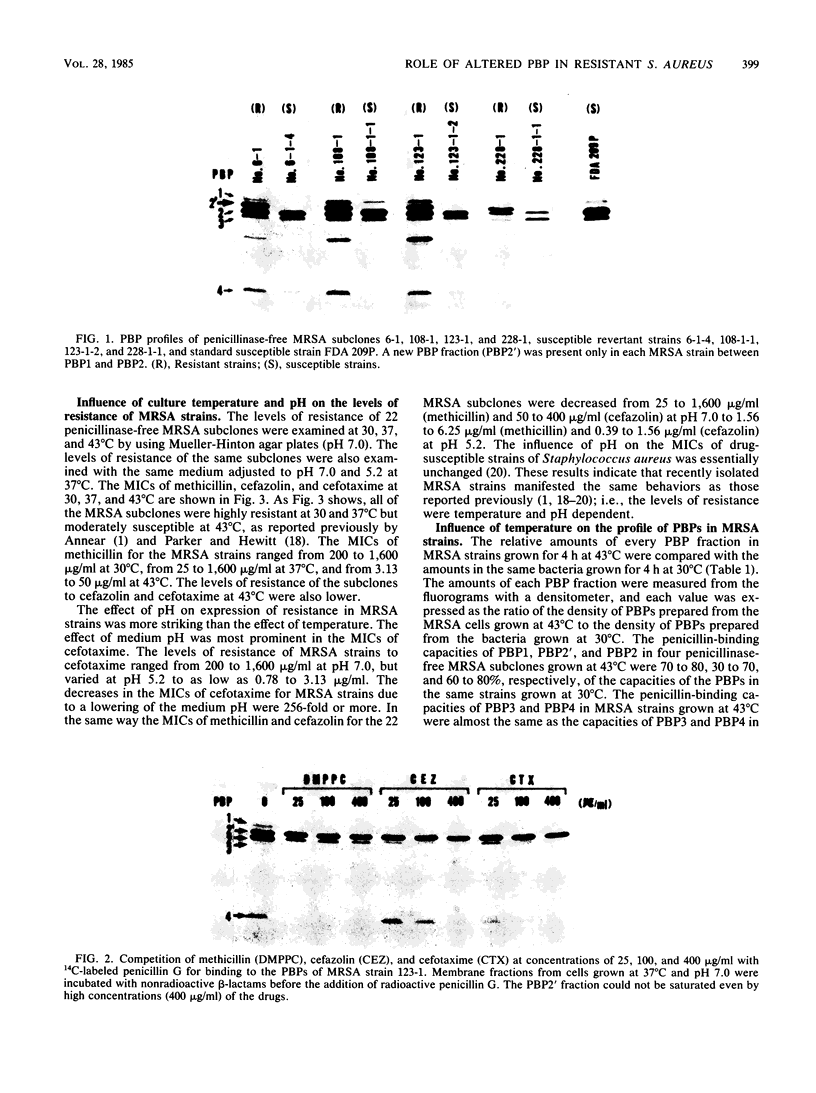
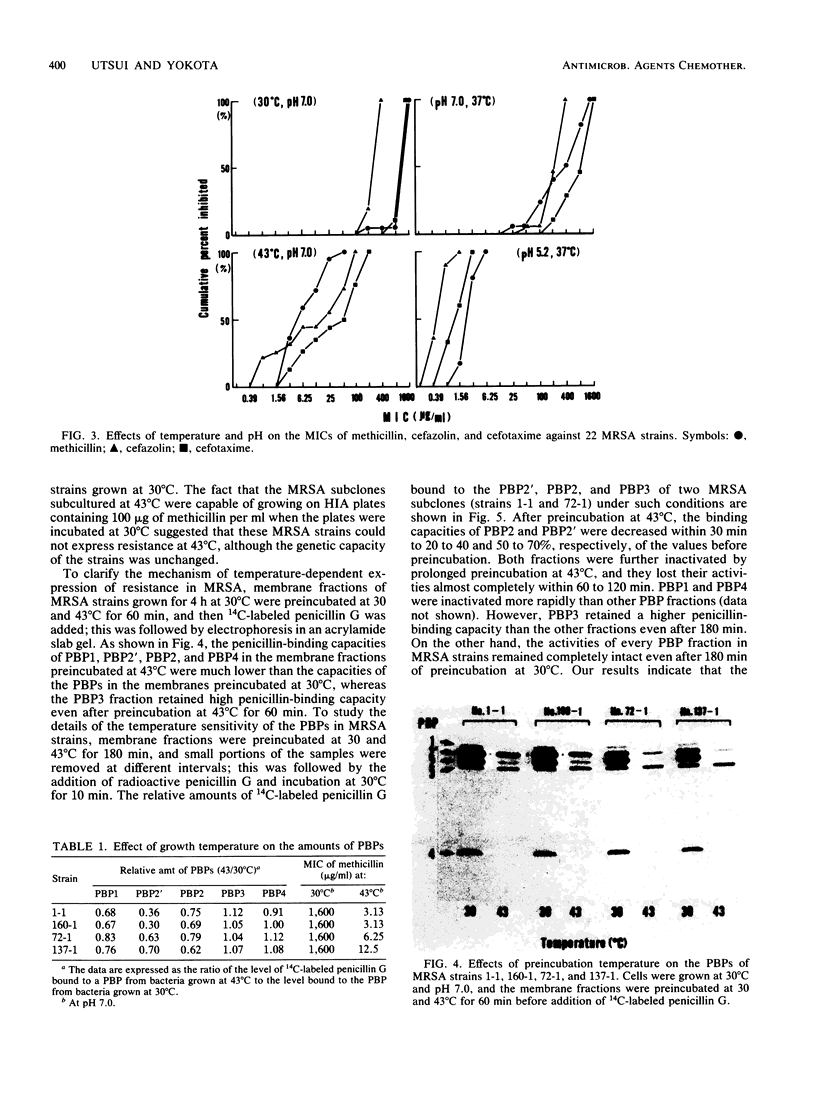
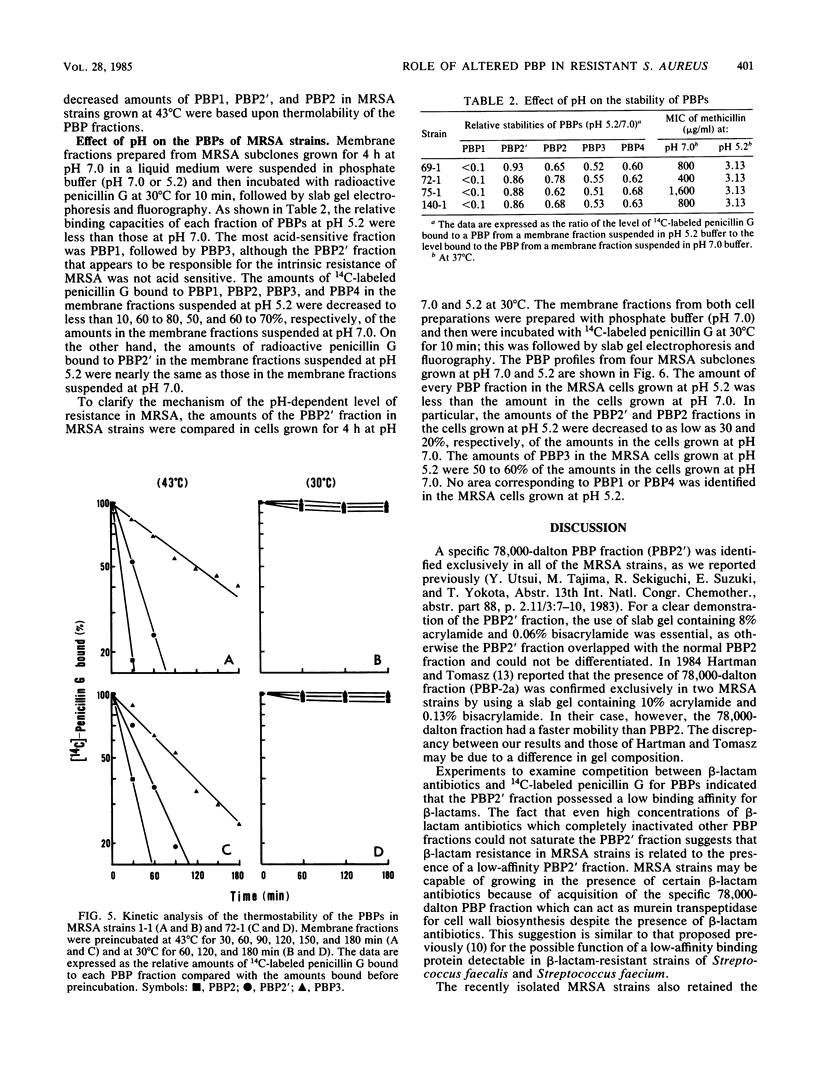
About 80% of methicillin- and cefazolin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus isolated clinically in Japan in 1982 retained their resistance even after elimination of penicillinase-encoding plasmids. The penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) of the penicillinase-free, methicillin- and cephem-resistant subclones of Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) were compared with those of spontaneous susceptible revertants which had been obtained by the replica method after 10 subcultures in drug-free media. A new PBP fraction (PBP2') having a molecular weight of 78,000 and low binding affinities for various beta-lactam antibiotics was found in MRSA exclusively. The levels of resistance of MRSA strains were reduced markedly by culturing them at 43 degrees C or at pH 5.2 or both. We found that the binding capacity of PBP2' for 14C-labeled penicillin G was decreased by preincubation of the membrane fractions of MRSA strains at 43 degrees C for 60 min and that the amount of PBP2' in MRSA strains grown at pH 5.2 was less than that the amount of PBP2' in MRSA strains grown at pH 7.0. Temperature- and pH-dependent expression of resistance in MRSA is likely to reflect the temperature sensitivity and neutral pH-dependent production of the specific PBP fraction (PBP2'). We suggest that MRSA strains can grow in the presence of beta-lactam antibiotics because of the low affinities of the specific PBP2' fraction for various beta-lactam antibiotics.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Annear D. I. The effect of temperature on resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to methicillin and some other antibioics. Med J Aust. 1968 Mar 16;1(11):444–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARBER M. NATURALLY OCCURING METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCI. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 May;35:183–190. doi: 10.1099/00221287-35-2-183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyce J. M., Landry M., Deetz T. R., DuPont H. L. Epidemiologic studies of an outbreak of nosocomial methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. Infect Control. 1981 Mar-Apr;2(2):110–116. doi: 10.1017/s0195941700053881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. F., Reynolds P. E. Intrinsic resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics in Staphylococcus aureus. FEBS Lett. 1980 Dec 29;122(2):275–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80455-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deguchi K., Kawamura S., Sugita R., Fujimaki Y., Ohsawa H. [Sensitivity to second-generation cephem agents of clinically isolated strains of bacteria in otorhinolaryngological field (author's transl)]. Jpn J Antibiot. 1982 Mar;35(3):812–820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deguchi K. [Sensitivity of Staphylococcus aureus isolated clinically to CEPs. Results obtained with strains originating in superficial abscess in infants (author's transl)]. Jpn J Antibiot. 1982 Mar;35(3):807–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyke K. G., Jevons M. P., Parker M. T. Penicillinase production and intrinsic resistance to penicillins in Staphylococcus aures. Lancet. 1966 Apr 16;1(7442):835–838. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90182-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana R., Cerini R., Longoni P., Grossato A., Canepari P. Identification of a streptococcal penicillin-binding protein that reacts very slowly with penicillin. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1343–1350. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1343-1350.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopapadakou N. H., Liu F. Y. Binding of beta-lactam antibiotics to penicillin-binding proteins of Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus faecalis: relation to antibacterial activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):834–836. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopapadakou N. H., Smith S. A., Bonner D. P. Penicillin-binding proteins in a Staphylococcus aureus strain resistant to specific beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jul;22(1):172–175. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.1.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman B. J., Tomasz A. Low-affinity penicillin-binding protein associated with beta-lactam resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):513–516. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.513-516.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAY J. W., HOUGHTON R. H., PERRET C. J. THE EFFECT OF GROWTH AT ELEVATED TEMPERATURES ON SOME HERITABLE PROPERTIES OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Nov;37:157–169. doi: 10.1099/00221287-37-2-157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. T., Hewitt J. H. Methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 1970 Apr 18;1(7651):800–804. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)92408-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTHERLAND R., ROLINSON G. N. CHARACTERISTICS OF METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Apr;87:887–899. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.4.887-899.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D. Chemical and physical factors influencing methicillin resistance of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1977 Nov;3 (Suppl 100):47–51. doi: 10.1093/jac/3.suppl_c.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Wallace S. J., Gerstein D. A. Suppression of intrinsic resistance to methicillin and other penicillins in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Nov;2(5):350–355. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.5.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapico F. L., Montgomerie J. Z., Canawati H. N., Aeilts G. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteriuria. Am J Med Sci. 1981 Mar-Apr;281(2):101–109. doi: 10.1097/00000441-198103000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Distinct penicillin binding proteins involved in the division, elongation, and shape of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ubukata K., Yamashita N., Konno M. Occurrence of a beta-lactam-inducible penicillin-binding protein in methicillin-resistant staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):851–857. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyke A. W., Ward J. B., Hayes M. V., Curtis N. A. A role in vivo for penicillin-binding protein-4 of Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Oct;119(2):389–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]