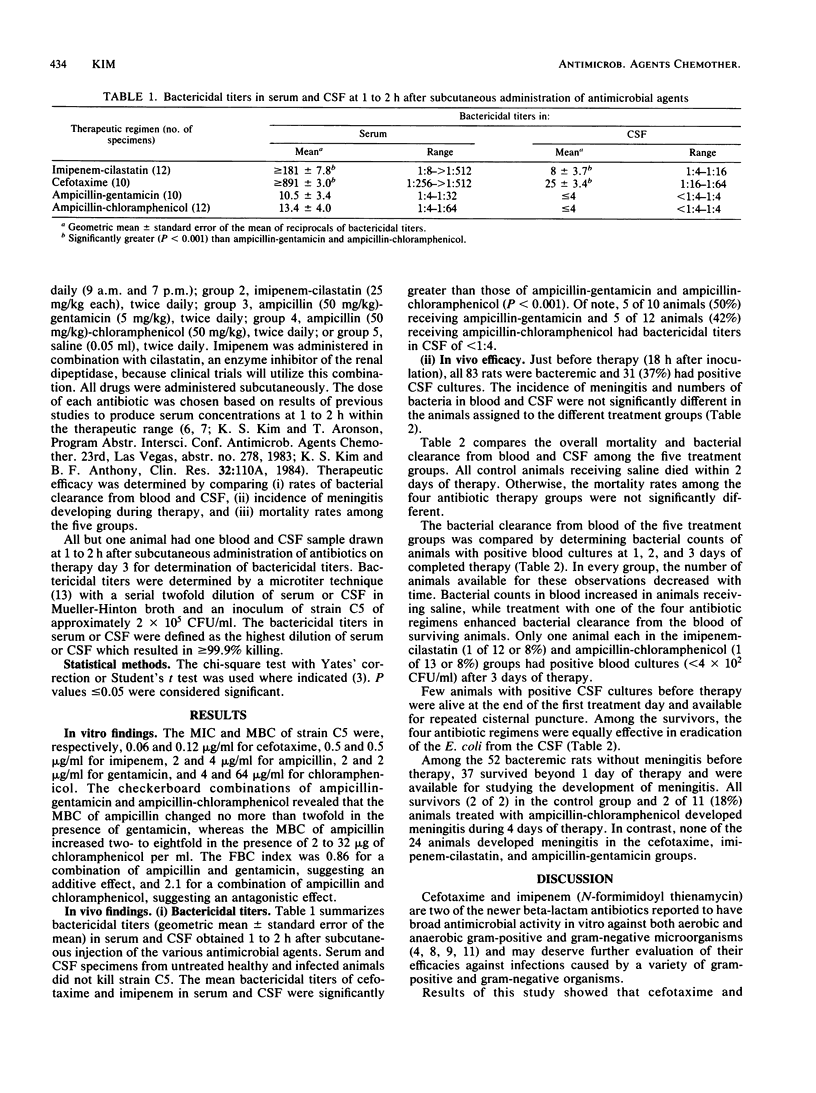
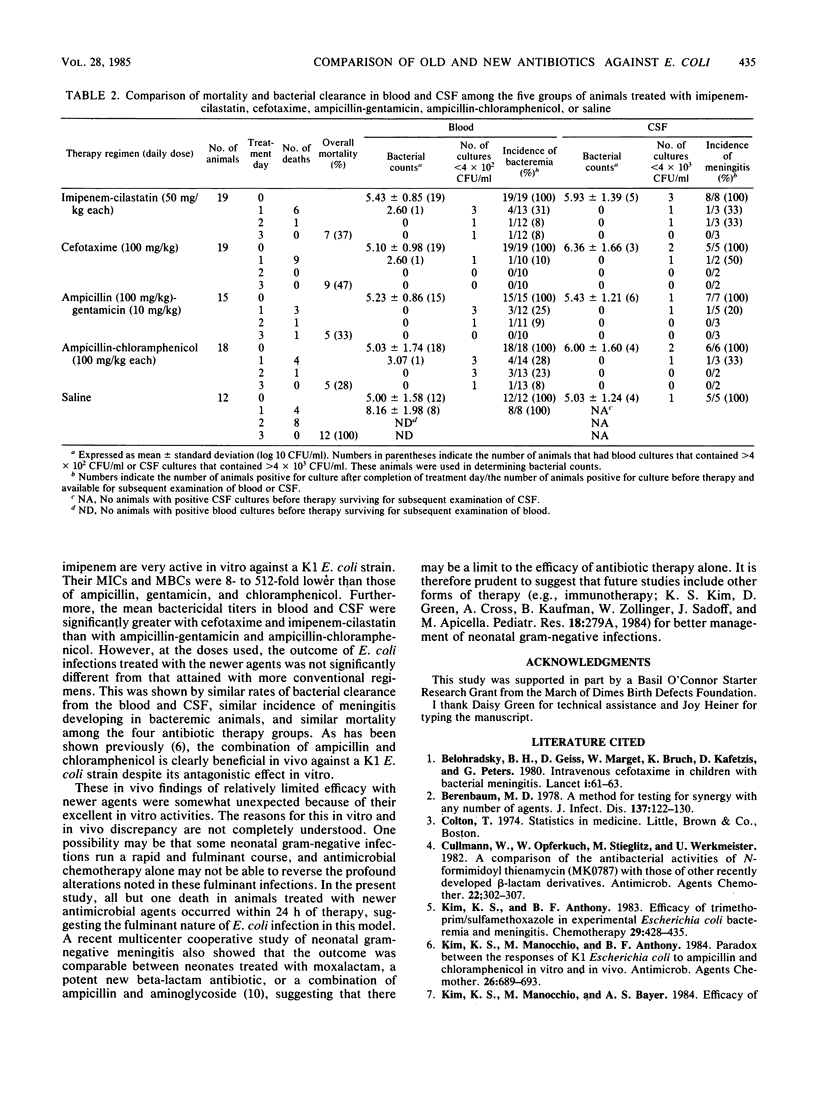
Abstract
In a search for more effective antimicrobial therapy of neonatal Escherichia coli infection, newer beta-lactam antibiotics, cefotaxime and imipenem, were evaluated for their activities against a K1 E. coli strain in vitro and in vivo, and the results were compared with those of conventional therapeutic regimens for neonatal E. coli infection: ampicillin-gentamicin and ampicillin-chloramphenicol. Measured by MICs and MBCs, cefotaxime and imipenem were 8- to 512-fold more active in vitro than the older agents. For in vivo studies, the following daily doses were used: 50 mg/kg for each of imipenem and cilastatin; 100 mg/kg for each of cefotaxime, ampicillin, and chloramphenicol; and 10 mg/kg for gentamicin. At these doses, the mean bactericidal titers in blood and cerebrospinal fluid were significantly greater with newer agents than with ampicillin-gentamicin and ampicillin-chloramphenicol. However, at the doses used, the newer agents were not more effective in vivo than the older agents. This was shown by the similarities in clearance of bacteria from blood and cerebrospinal fluid, incidences of meningitis in bacteremic animals, and mortality rates. Thus, although these two newer antibiotics are more active in vitro and produce greater bactericidal titers in vivo, they do not appear to be superior to conventional regimens for treatment of neonatal E. coli bacteremia and meningitis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belohradsky B. H., Bruch K., Geiss D., Kafetzis D., Marget W., Peters G. Intravenous cefotaxime in children with bacterial meningitis. Lancet. 1980 Jan 12;1(8159):61–63. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90491-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berenbaum M. C. A method for testing for synergy with any number of agents. J Infect Dis. 1978 Feb;137(2):122–130. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.2.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullmann W., Opferkuch W., Stieglitz M., Werkmeister U. A comparison of the antibacterial activities of N-formimidoyl thienamycin (MK0787) with those of other recently developed beta-lactam derivatives. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Aug;22(2):302–307. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.2.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Anthony B. F. Efficacy of trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole in experimental Escherichia coli bacteremia and meningitis. Chemotherapy. 1983;29(6):428–435. doi: 10.1159/000238231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Manocchio M., Anthony B. F. Paradox between the responses of Escherichia coli K1 to ampicillin and chloramphenicol in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Nov;26(5):689–693. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.5.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang S. D., Edwards D. J., Durack D. T. Comparison of cefoperazone, cefotaxime, and moxalactam (LY127935) against aerobic gram-negative bacilli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Mar;17(3):488–493. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.3.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuyoshi S., Arai S., Miyamoto M., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro antimicrobial activity of cefotaxime, a new cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jul;18(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Jr, Threlkeld N., Mize S., Baker C. J., Kaplan S. L., Faingezicht I., Feldman W. E., Schaad U. Moxalactam therapy for neonatal meningitis due to gram-negative enteric bacilli. A prospective controlled evaluation. JAMA. 1984 Sep 21;252(11):1427–1432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Labthavikul P. Comparative in vitro activity of N-formimidoyl thienamycin against gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic species and its beta-lactamase stability. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jan;21(1):180–187. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.1.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden C. W., Wentzel H., Keleti E. Comparison of techniques for measurement of in vitro antibiotic synergism. J Infect Dis. 1979 Oct;140(4):629–633. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.4.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prober C. G., Dougherty S. S., Vosti K. L., Yeager A. S. Comparison of a micromethod for performance of the serum bactericidal test with the standard tube dilution method. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jul;16(1):46–48. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaad U. B., McCracken G. H., Jr, Loock C. A., Thomas M. L. Pharmacokinetics and bacteriologic efficacy of moxalactam, cefotaxime, cefoperazone, and rocephin in experimental bacterial meningitis. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):156–163. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaad U. B., McCracken G. H., Jr, Threlkeld N., Thomas M. L. Clinical evaluation of a new broad-spectrum oxa-beta-lactam antibiotic, moxalactam, in neonates and infants. J Pediatr. 1981 Jan;98(1):129–136. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80559-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J. D., McCracken G. H., Jr Sepsis neonatorum. N Engl J Med. 1981 Mar 12;304(11):642–647. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198103123041105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


