Abstract
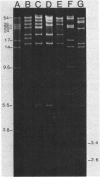
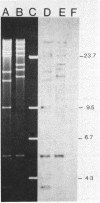
In spite of extensive DNA homology among IncHI1 plasmids, ApaI and XbaI restriction digests of plasmids from Peruvian Salmonella typhi varied considerably from other IncHI1 plasmids isolated previously. IncHI1 plasmids appear to be undergoing a process of modular evolution, probably by sequential acquisition of resistance determinants.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alton N. K., Vapnek D. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the chloramphenicol resistance transposon Tn9. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):864–869. doi: 10.1038/282864a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson E. S., Humphreys G. O., Willshaw G. A. The molecular relatedness of R factors in enterobacteria of human and animal origin. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Dec;91(2):376–382. doi: 10.1099/00221287-91-2-376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson E. S. The problem and implications of chloramphenicol resistance in the typhoid bacillus. J Hyg (Lond) 1975 Apr;74(2):289–299. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400024360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth P. T., Datta N., Hedges R. W., Grinter N. J. Transposition of a deoxyribonucleic acid sequence encoding trimethoprim and streptomycin resistances from R483 to other replicons. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):800–810. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.800-810.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. Determination of pili by conjugative bacterial drug resistance plasmids of incompatibility groups B, C, H, J, K, M, V, and X. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):828–837. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.828-837.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E., Hughes V. M., Richards H., Datta N. R plasmids of a new incompatibility group determine constitutive production of H pili. Plasmid. 1982 May;7(3):230–238. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. D., Duong Hong M. o., Rhoades E. R. Chloramphenicol-resistant Salmonella typhi in Saigon. JAMA. 1975 Jan 13;231(2):162–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler T., Rumans L., Arnold K. Response of typhoid fever caused by chloramphenicol-susceptible and chloramphenicol-resistant strains of Salmonella typhi to treatment with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):551–561. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.2.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabbert Y. A., Gerbaud G. R. Surveillance épidémiologique des plasmides responsables de la résistance au chloramphénicol de Salmonella typhi. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1974 Feb-Mar;125A(2):153–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Olarte J. R factors in strains of Salmonella typhi and Shigella dysenteriae 1 isolated during epidemics in Mexico: classification by compatibility. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Mar;5(3):310–317. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.3.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Richards H., Datta C. Salmonella typhi in vivo acquires resistance to both chloramphenicol and co-trimoxazole. Lancet. 1981 May 30;1(8231):1181–1183. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92350-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fling M. E., Walton L., Elwell L. P. Monitoring of plasmid-encoded, trimethoprim-resistant dihydrofolate reductase genes: detection of a new resistant enzyme. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Nov;22(5):882–888. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.5.882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster T. J., Davis M. A., Roberts D. E., Takeshita K., Kleckner N. Genetic organization of transposon Tn10. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):201–213. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90285-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindley N. D., Humphreys G. O., Anderson E. S. Molecular studies of R factor compatibility groups. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):387–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.387-398.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffron F., Sublett R., Hedges R. W., Jacob A., Falkow S. Origin of the TEM-beta-lactamase gene found on plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):250–256. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.250-256.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labigne-Roussel A., Witchitz J., Courvalin P. Modular evolution of disseminated Inc 7-M plasmids encoding gentamicin resistance. Plasmid. 1982 Nov;8(3):215–231. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendez B., Tachibana C., Levy S. B. Heterogeneity of tetracycline resistance determinants. Plasmid. 1980 Mar;3(2):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90101-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olarte J., Galindo E. Salmonella typhi resistant to chloramphenicol, ampicillin, and other antimicrobial agents: strains isolated during an extensive typhoid fever epidemic in Mexico. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Dec;4(6):597–601. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.6.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Cohen S. N., Davidson N. Electron microscope heteroduplex studies of sequence relations among plasmids of Escherichia coli. II. Structure of drug resistance (R) factors and F factors. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 5;75(2):235–255. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. R., Grindley N. D., Humphreys G. O., Anderson E. S. Interactions of group H resistance factors with the F factor. J Bacteriol. 1973 Aug;115(2):623–628. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.2.623-628.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W. Letter: Thermosensitive transfer factors in chloramphenicol-resistant strains of Salmonella typhi. Lancet. 1974 Aug 3;2(7875):281–282. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91435-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., Brose E. C., Kwan S., Yan W. Mapping of transfer regions within incompatibility group HI plasmid R27. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):1221–1226. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.1221-1226.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., Brose E. C. Restriction endonuclease mapping of R27 (TP117), an incompatibility group HI subgroup 1 plasmid from Salmonella typhimurium. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):75–77. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., Levine J. G. Studies of temperature-sensitive transfer and maintenance of H incompatibility group plasmids. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Feb;116(2):475–484. doi: 10.1099/00221287-116-2-475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E. Transfer-defective and tetracycline-sensitive mutants of the incompatibility group HI plasmid R27 generated by insertion of transposon 7. Plasmid. 1983 May;9(3):227–239. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(83)90001-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley M., Taylor D. E. Identification of DNA homologies among H incompatibility group plasmids by restriction enzyme digestion and Southern transfer hybridization. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Aug;24(2):194–200. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.2.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]