Abstract
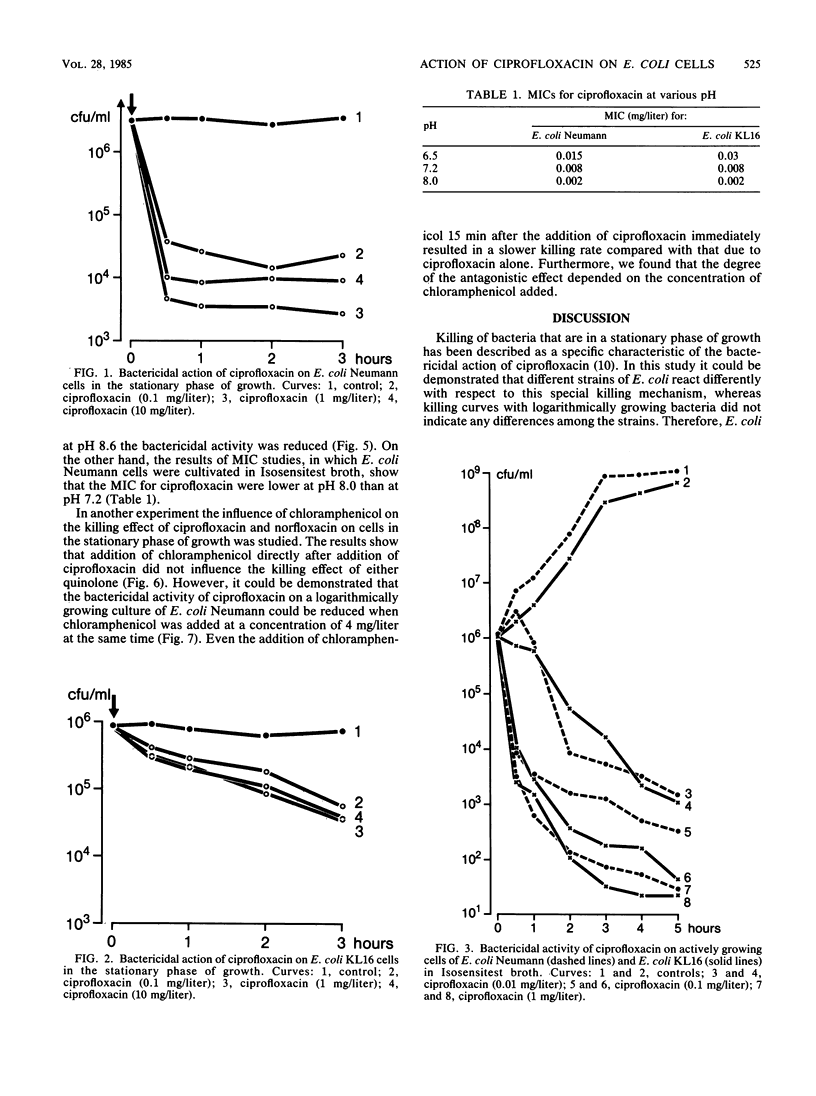
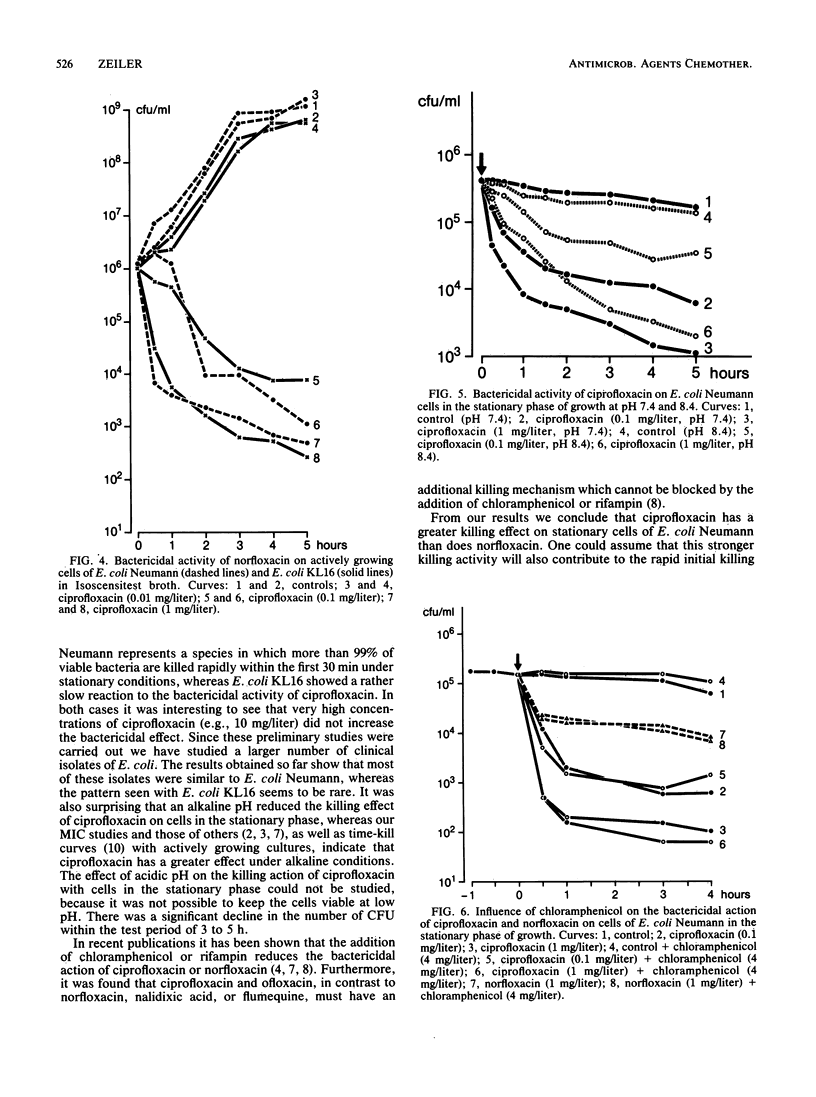
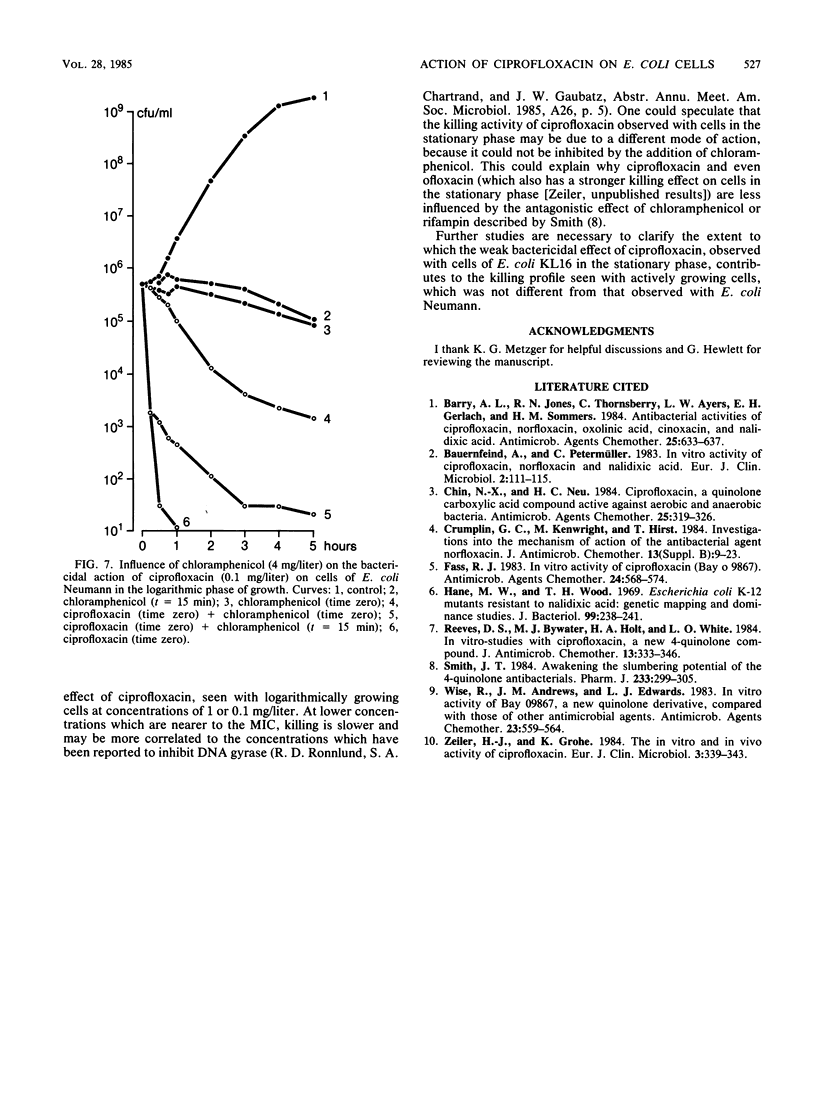
Cells of Escherichia coli Neumann and E. coli KL16 were suspended in phosphate-buffered saline pH 7.4 and allowed to reach stationary growth conditions. Ciprofloxacin was added at different concentrations, and time-kill curves were constructed. It could be demonstrated that the number of viable cells was reduced quickly by several logs for E. coli Neumann, whereas a weak and slow killing effect was observed with E. coli KL16. When ciprofloxacin or norfloxacin was added to logarithmically growing cultures of E. coli Neumann or E. coli KL16, no principal differences in the killing rate for the two strains could be observed. Ciprofloxacin, however, was more bactericidal than norfloxacin. It was also demonstrated that the bactericidal action of ciprofloxacin on cells in the stationary growth phase was better at pH 7.4 than at pH 8.6. This dependence is different from that observed in MIC studies, in which the MIC were lower at pH 8.0 than at pH 7.2. It was also found that the bactericidal action of ciprofloxacin or norfloxacin on cells of E. coli Neumann in the stationary phase of growth could not be reduced by the addition of chloramphenicol, whereas under conditions of logarithmic growth the rapid killing effect of ciprofloxacin was reduced in the presence of chloramphenicol.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry A. L., Jones R. N., Thornsberry C., Ayers L. W., Gerlach E. H., Sommers H. M. Antibacterial activities of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, oxolinic acid, cinoxacin, and nalidixic acid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 May;25(5):633–637. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.5.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauernfeind A., Petermüller C. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and nalidixic acid. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;2(2):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF02001575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin N. X., Neu H. C. Ciprofloxacin, a quinolone carboxylic acid compound active against aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):319–326. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crumplin G. C., Kenwright M., Hirst T. Investigations into the mechanism of action of the antibacterial agent norfloxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 May;13 (Suppl B):9–23. doi: 10.1093/jac/13.suppl_b.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R. J. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin (Bay o 9867). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Oct;24(4):568–574. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.4.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hane M. W., Wood T. H. Escherichia coli K-12 mutants resistant to nalidixic acid: genetic mapping and dominance studies. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):238–241. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.238-241.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves D. S., Bywater M. J., Holt H. A., White L. O. In-vitro studies with ciprofloxacin, a new 4-quinolone compound. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Apr;13(4):333–346. doi: 10.1093/jac/13.4.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Andrews J. M., Edwards L. J. In vitro activity of Bay 09867, a new quinoline derivative, compared with those of other antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Apr;23(4):559–564. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.4.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler H. J., Grohe K. The in vitro and in vivo activity of ciprofloxacin. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;3(4):339–343. doi: 10.1007/BF01977490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


