Abstract
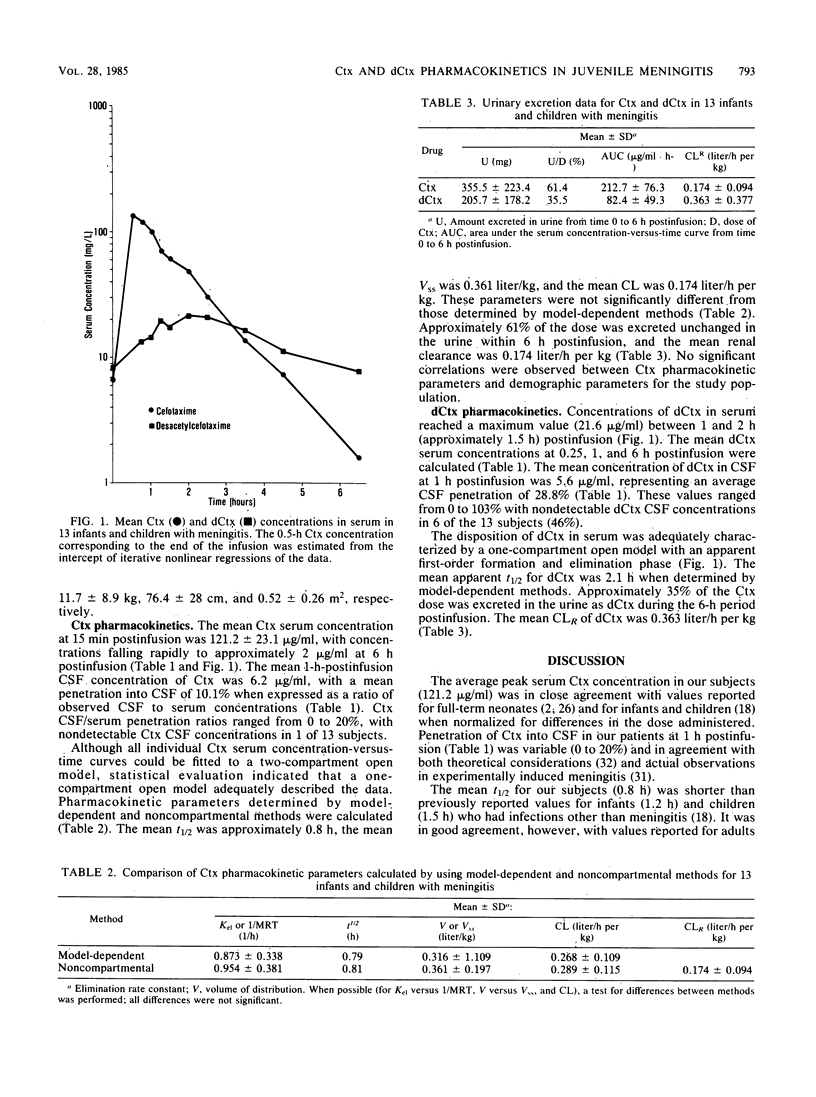
The pharmacokinetics and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) penetration of cefotaxime (Ctx) and desacetylcefotaxime (dCtx) were evaluated in 13 infants and children with meningitis after dose 6 of Ctx in a multiple-dose intermittent intravenous infusion regimen (50 mg/kg every 6 h). Model-dependent and noncompartmental pharmacokinetic parameters were determined and were found to be congruous. The disposition of both Ctx and dCtx was described adequately by a one-compartment, open model. Noncompartmental pharmacokinetic parameters are reported. The mean Ctx serum concentration at 0.25 h postinfusion was 121.2 micrograms/ml, and the mean CSF concentration at 1 h postinfusion was 6.2 micrograms/ml. The CSF/serum ratio was variable (0 to 20%), with a mean penetration of 10.1%. The mean Ctx elimination half-life, apparent steady-state volume of distribution, and total body clearance were 0.8 h, 0.361 liter/kg, and 0.289 liter/h per kg, respectively. For Ctx, 61% of the dose was excreted unchanged in the urine during the 6-h postinfusion period, and the estimated renal clearance was 0.174 liter/h per kg. No significant correlations were observed between Ctx pharmacokinetic parameters and demographic parameters. The mean peak concentration of dCtx in serum (21.6 micrograms/ml) occurred at approximately 1.5 h postinfusion, and the mean concentration in CSF at 1 h postinfusion was 5.6 micrograms/ml. The CSF/serum ratio was extremely variable (0 to 103%), and the mean penetration was 28.8%. The mean apparent elimination half-life for dCtx was 2.1 h. In infants and children with normal renal function, a 50-mg/kg dose of Ctx administered every 6 h should provide adequate concentrations in serum and CSF in the majority of patients with meningitis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asmar B. I., Thirumoorthi M. C., Buckley J. A., Kobos D. M., Dajani A. S. Cefotaxime diffusion into cerebrospinal fluid of children with meningitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jul;28(1):138–140. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.1.138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird-Lambert J., Doyle P. E., Thomas D., Cvejic M., Buchanan N. Pharmacokinetics of cefotaxime in neonates. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 May;13(5):471–477. doi: 10.1093/jac/13.5.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer L. A., Gibaldi M. Computation of model-independent pharmacokinetic parameters during multiple dosing. J Pharm Sci. 1983 Aug;72(8):978–979. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600720843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belohradsky B. H., Bruch K., Geiss D., Kafetzis D., Marget W., Peters G. Intravenous cefotaxime in children with bacterial meningitis. Lancet. 1980 Jan 12;1(8159):61–63. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90491-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benet L. Z., Galeazzi R. L. Noncompartmental determination of the steady-state volume of distribution. J Pharm Sci. 1979 Aug;68(8):1071–1074. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600680845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxenbaum H. G., Riegelman S., Elashoff R. M. Statistical estimations in pharmacokinetics. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1974 Apr;2(2):123–148. doi: 10.1007/BF01061504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. D., Manno J. E. ESTRIP, a BASIC computer program for obtaining initial polyexponential parameter estimates. J Pharm Sci. 1978 Dec;67(12):1687–1691. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600671214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drasar F. A., Farrell W., Howard A. J., Hince C., Leung T., Williams J. D. Activity of HR 756 against Haemophilus influenzae, Bacteroides fragilis and Gram-negative rods. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 Sep;4(5):445–450. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.5.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmieu F., Guibert J., Rosenkilde H. C., Ho I., Le Go A. Pharmacokinetics of cefotaxime in normal human volunteers. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Sep;6 (Suppl A):83–92. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.suppl_a.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fillastre J. P., Leroy A., Humbert G., Godin M. Pharmacokinetics of cefotaxime in subjects with normal and impaired renal function. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Sep;6 (Suppl A):103–111. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.suppl_a.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu K. P., Aswapokee P., Ho I., Matthijssen C., Neu H. C. Pharmacokinetics of cefotaxime. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Nov;16(5):592–597. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.5.592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humbert G., Leroy A., Nair S. R., Cherubin C. E. Concentrations of cefotaxime and the desacetyl metabolite in serum and CSF of patients with meningitis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 May;13(5):487–494. doi: 10.1093/jac/13.5.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ings R. M., Fillastre J. P., Godin M., Leroy A., Humbert G. The pharmacokinetics of cefotaxime and its metabolites in subjects with normal and impaired renal function. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Sep-Oct;4 (Suppl):S379–S391. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.supplement_2.s379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Barry A. L., Thornsberry C. Antimicrobial activity of desacetylcefotaxime alone and in combination with cefotaxime: evidence of synergy. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Sep-Oct;4 (Suppl):S366–S373. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.supplement_2.s366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafetzis D. A., Brater D. C., Kanarios J., Sinaniotis C. A., Papadatos C. J. Clinical pharmacology of cefotaxime in pediatric patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Oct;20(4):487–490. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.4.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafetzis D. A., Brater D. C., Kapiki A. N., Papas C. V., Dellagrammaticas H., Papadatos C. J. Treatment of severe neonatal infections with cefotaxime. Efficacy and pharmacokinetics. J Pediatr. 1982 Mar;100(3):483–489. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80466-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalager T., Digranes A., Bakke K., Hellum K. B., Bergan T., Solberg C. O. Cefotaxime in serious infections--a clinical and pharmacokinetic study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Feb;9(2):157–163. doi: 10.1093/jac/9.2.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karimi A., Seeger K., Stolke D., Knothe H. Cefotaxime concentration in cerebrospinal fluid. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Sep;6 (Suppl A):119–120. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.suppl_a.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kees F., Strehl E., Seeger K., Seidel G., Dominiak P., Grobecker H. Comparative determination of cefotaxime and desacetyl cefotaxime in serum and bile by bioassay and high-performance liquid chromatography. Arzneimittelforschung. 1981;31(2):362–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosmidis J., Stathakis C., Mantopoulos K., Pouriezi T., Papathanassiou B., Daikos G. K. Clinical pharmacology of cefotaxime including penetration into bile, sputum, bone and cerebrospinal fluid. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Sep;6 (Suppl A):147–151. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.suppl_a.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loo J. C., Riegelman S. Assessment of pharmacokinetic constants from postinfusion blood curves obtained after I.V. infusion. J Pharm Sci. 1970 Jan;59(1):53–55. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600590107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüthy R., Münch R., Blaser J., Bhend H., Siegenthaler W. Human pharmacology of cefotaxime (HR 756), a new cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Aug;16(2):127–133. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.2.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Jr, Threlkeld N. E., Thomas M. L. Pharmacokinetics of cefotaxime in newborn infants. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Apr;21(4):683–684. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.4.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. Antibacterial activity of desacetylcefotaxime alone and in combination with cefotaxime. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Sep-Oct;4 (Suppl):S374–S378. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.supplement_2.s374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen-Kudsk F. A microcomputer program in Basic for iterative, non-linear data-fitting to pharmacokinetic functions. Int J Biomed Comput. 1983 Mar;14(2):95–107. doi: 10.1016/0020-7101(83)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkawa M., Okasho A., Motoi I., Tokunaga S., Shoda R., Kawaguchi S., Sawaki M., Shimamura M., Hirano S., Kuroda K. Elimination kinetics of cefotaxime and desacetyl cefotaxime in patients with renal insufficiency and during hemodialysis. Chemotherapy. 1983;29(1):4–12. doi: 10.1159/000238166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Pulverer G. Comparative in vitro activity of cefotaxime (HR 756). Chemotherapy. 1980;26(3):177–183. doi: 10.1159/000237902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaad U. B., McCracken G. H., Jr, Loock C. A., Thomas M. L. Pharmacokinetics and bacteriologic efficacy of moxalactam, cefotaxime, cefoperazone, and rocephin in experimental bacterial meningitis. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):156–163. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheld W. M. Theoretical and practical considerations of antibiotic therapy for bacterial meningitis. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1985 Jan-Feb;4(1):74–83. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198501000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sosna J. P., Murray P. R., Medoff G. Comparison of the in vitro activities of HR756 with cephalothin, cefoxitin, and cefamandole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Dec;14(6):876–879. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.6.876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. G. Linear pharmacokinetic equations allowing direct calculation of many needed pharmacokinetic parameters from the coefficients and exponents of polyexponential equations which have been fitted to the data. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1976 Oct;4(5):443–467. doi: 10.1007/BF01062831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells T. G., Trang J. M., Brown A. L., Marmer B. C., Jacobs R. F. Cefotaxime therapy of bacterial meningitis in children. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Sep;14 (Suppl B):181–189. doi: 10.1093/jac/14.suppl_b.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Wright N., Wills P. J. Pharmacology of cefotaxime and its desacetyl metabolite in renal and hepatic disease. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Apr;19(4):526–531. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.4.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaoka K., Nakagawa T., Uno T. Statistical moments in pharmacokinetics. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1978 Dec;6(6):547–558. doi: 10.1007/BF01062109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



