Abstract
Norfloxacin is a quinolone (pyridonecarboxylic acid derivative) effective against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. We studied the effects of this drug on DNA metabolism in P. aeruginosa. Norfloxacin inhibits DNA replication immediately on its addition to a logarithmically growing culture of P. aeruginosa. It inhibits the ability of P. aeruginosa DNA gyrase to supercoil relaxed, closed circular DNA in vitro. At intermediate concentrations of the drug, inhibition of DNA replication in vivo is followed by secondary (recovery) synthesis. Both recovery synthesis and the bactericidal effects of norfloxacin are dependent on continued protein synthesis, suggesting that these are inducible functions. Neither norfloxacin nor nalidixic acid induces Weigle-reactivation (inducible DNA repair) or mutagenesis in P. aeruginosa.
Full text
PDF
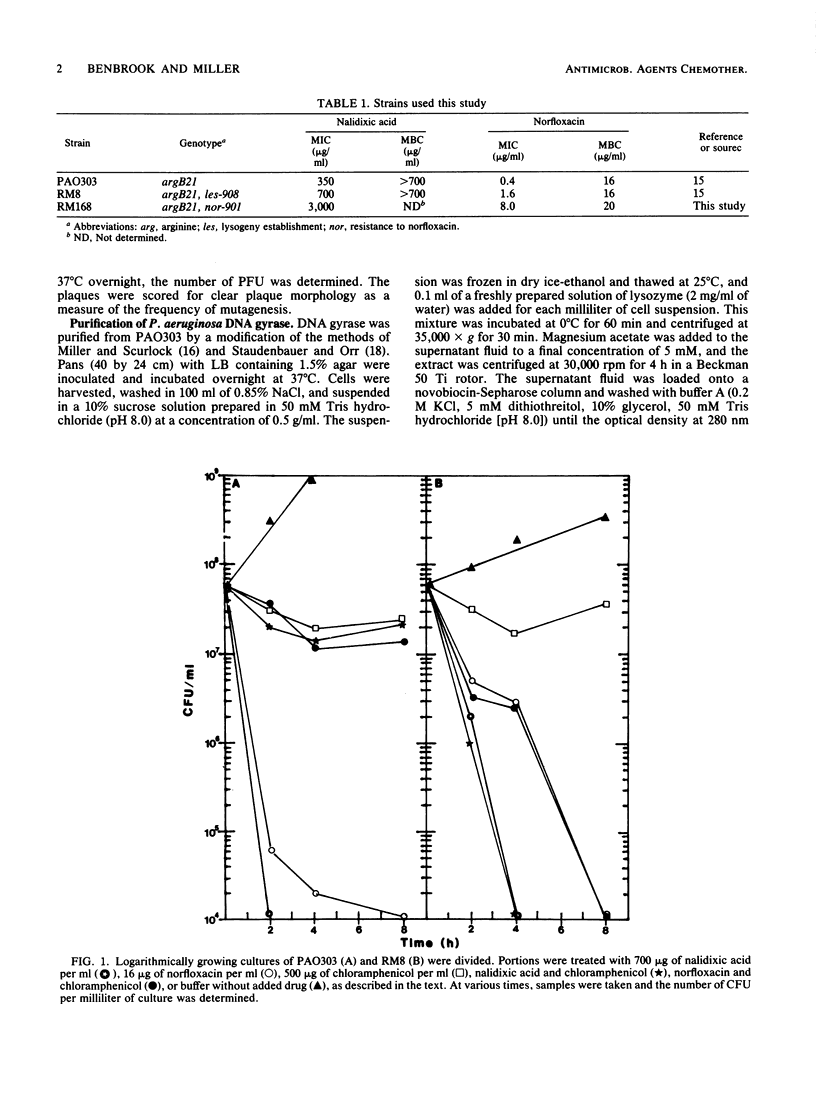
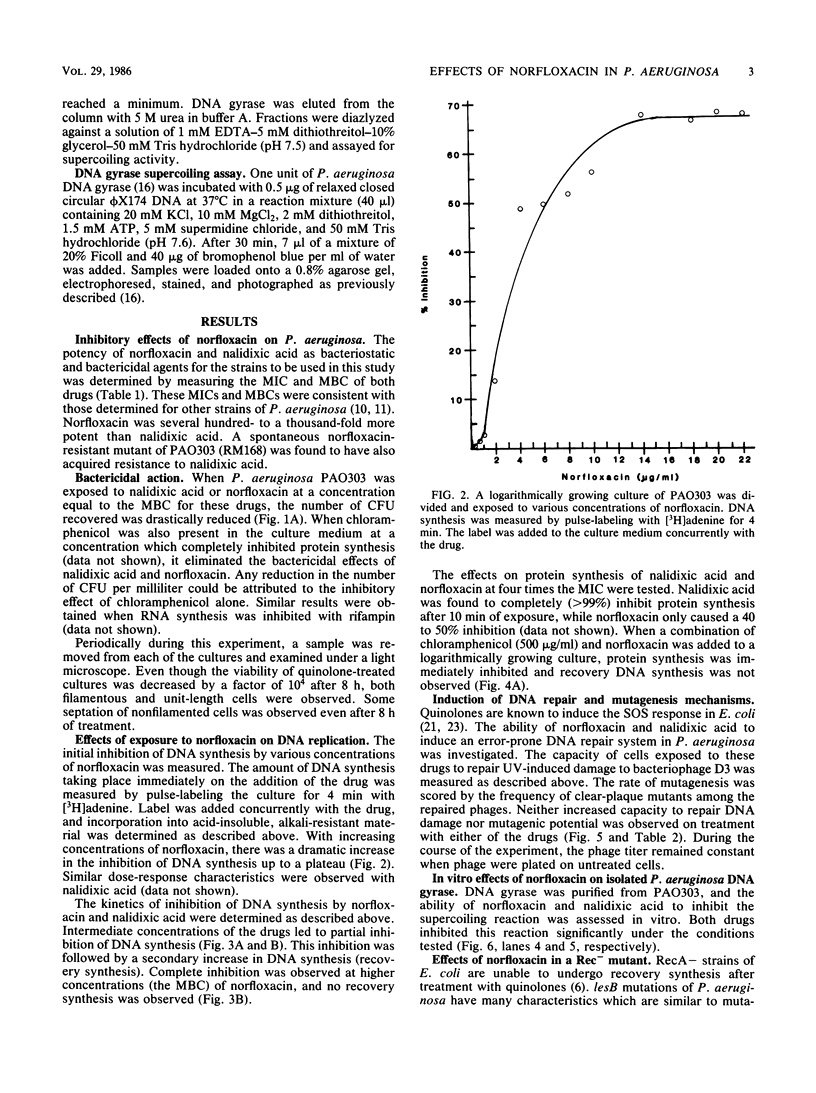
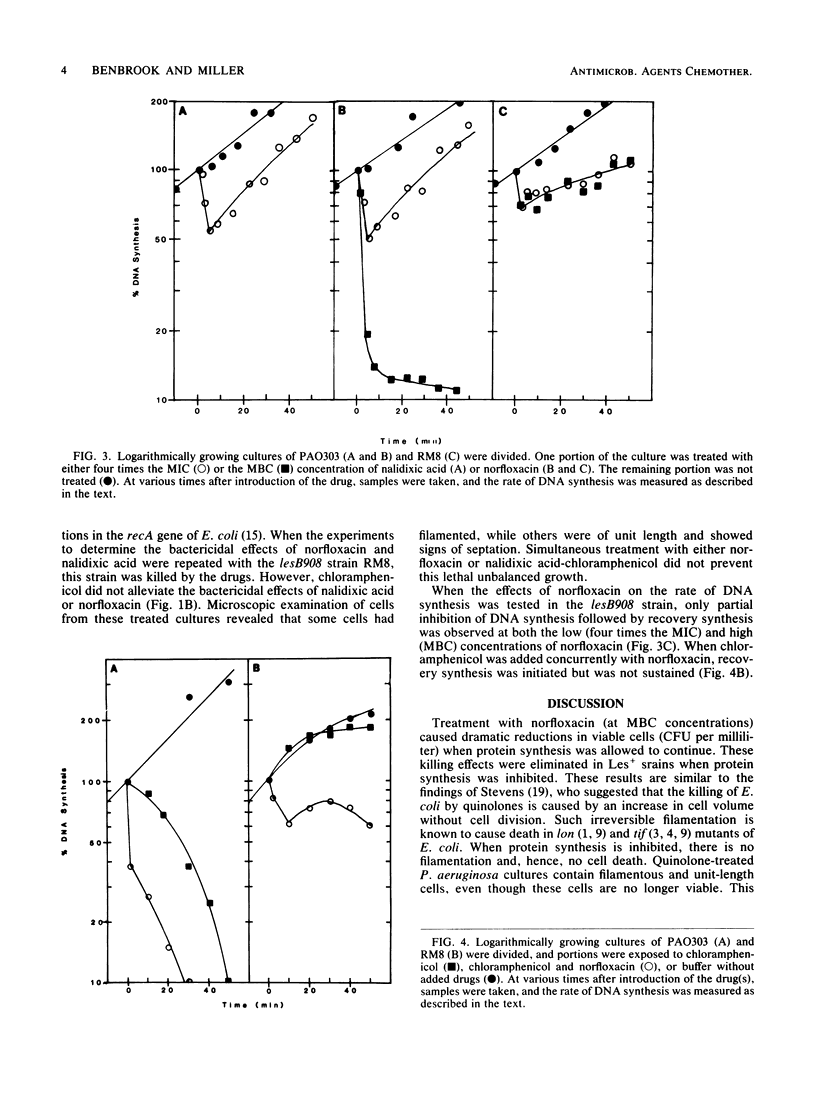
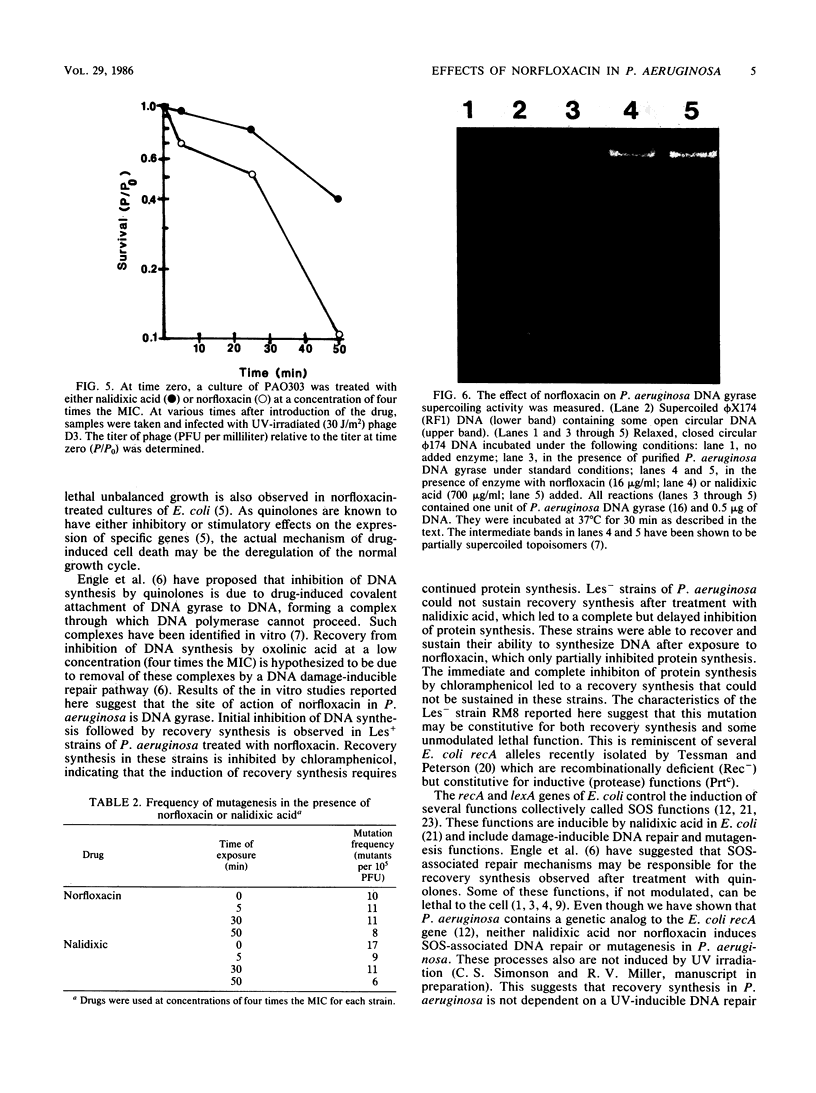

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADLER H. I., HARDIGREE A. A. ANALYSIS OF A GENE CONTROLLING CELL DIVISION AND SENSITIVITY TO RADIATION IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Mar;87:720–726. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.3.720-726.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellazzi M., George J., Buttin G. Prophage induction and cell division in E. coli. I. Further characterization of the thermosensitive mutation tif-1 whose expression mimics the effect of UV irradiation. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(2):139–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00269133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellazzi M., George J., Buttin G. [Prophage induction and cell division in E. coli. II. Linked (recA, zab) and unlinked (lex) suppressors of tif-1-mediated induction and filamentation]. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(2):153–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00269134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crumplin G. C., Kenwright M., Hirst T. Investigations into the mechanism of action of the antibacterial agent norfloxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 May;13 (Suppl B):9–23. doi: 10.1093/jac/13.suppl_b.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engle E. C., Manes S. H., Drlica K. Differential effects of antibiotics inhibiting gyrase. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):92–98. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.92-98.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:879–910. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.004311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Nash H. A. DNA gyrase: an enzyme that introduces superhelical turns into DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3872–3876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J., Castellazzi M., Buttin G. Prophage induction and cell division in E. coli. III. Mutations sfiA and sfiB restore division in tif and lon strains and permit the expression of mutator properties of tif. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Oct 22;140(4):309–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Ito A., Abe Y., Suzue S., Irikura T., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Comparative activities of AM-715 and pipemidic and nalidixic acids against experimentally induced systemic and urinary tract infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jan;19(1):188–189. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito A., Hirai K., Inoue M., Koga H., Suzue S., Irikura T., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro antibacterial activity of AM-715, a new nalidixic acid analog. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Feb;17(2):103–108. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.2.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokjohn T. A., Miller R. V. Molecular cloning and characterization of the recA gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):568–572. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.568-572.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Mount D. W. The SOS regulatory system of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel R., Gellert M. Regulation of the genes for E. coli DNA gyrase: homeostatic control of DNA supercoiling. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. V., Ku C. M. Characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants deficient in the establishment of lysogeny. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):875–883. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.875-883.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. V., Scurlock T. R. DNA gyrase (Topoisomerase II) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 27;110(2):694–700. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91205-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royle P. L., Matsumoto H., Holloway B. W. Genetic circularity of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):145–155. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.145-155.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudenbauer W. L., Orr E. DNA gyrase: affinity chromatography on novobiocin-Sepharose and catalytic properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3589–3603. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens P. J. Bactericidal effect against Escherichia coli of nalidixic acid and four structurally related compounds. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Jul;6(4):535–542. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.4.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessman E. S., Peterson P. K. Isolation of protease-proficient, recombinase-deficient recA mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):688–695. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.688-695.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C. Mutagenesis and inducible responses to deoxyribonucleic acid damage in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Mar;48(1):60–93. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.1.60-93.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Ultraviolet mutagenesis and inducible DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):869–907. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.869-907.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




