Abstract
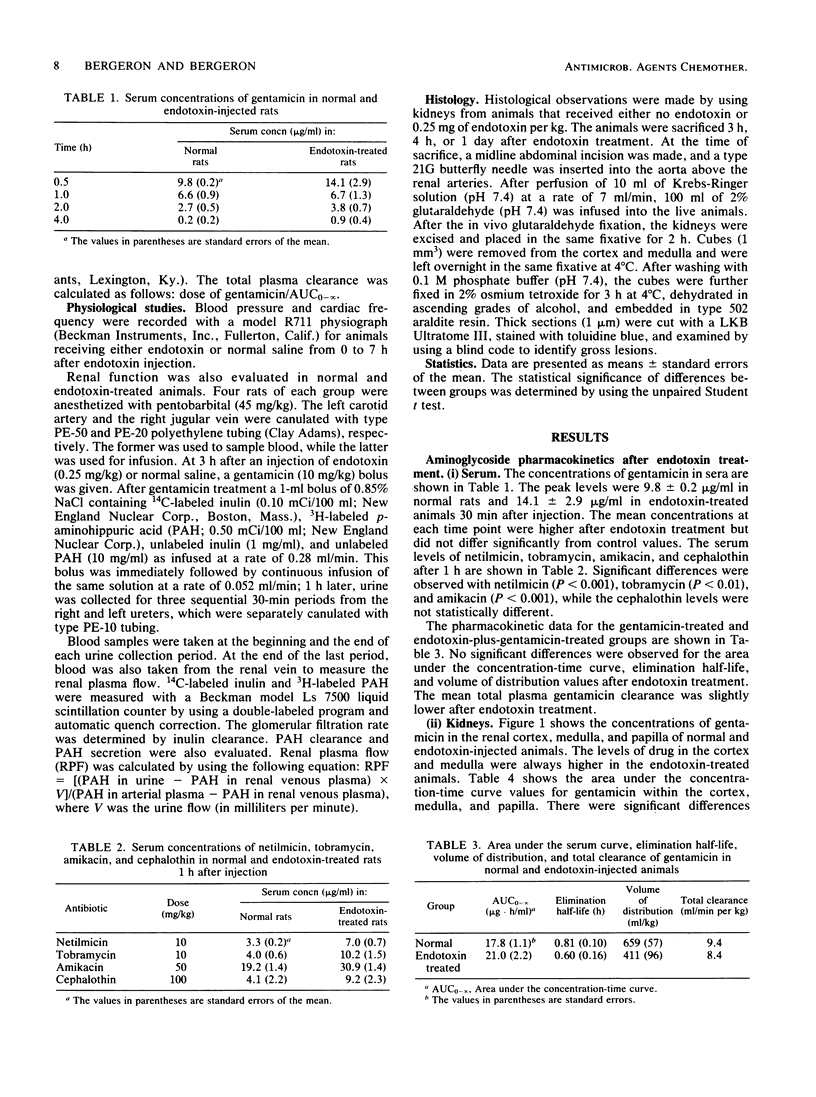
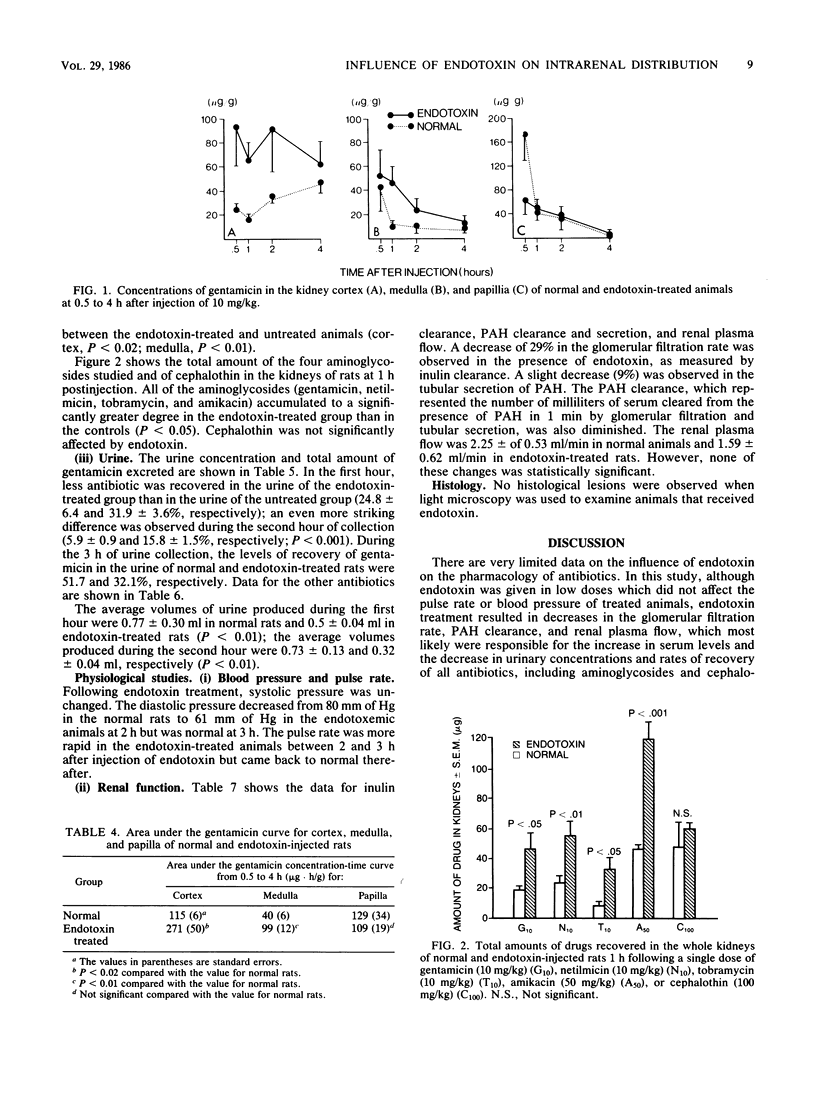
Multiple factors may modify the pharmacokinetics of aminoglycosides and increase their nephrotoxic potential. In this study, we investigated the influence of Escherichia coli endotoxin on the renal handling of several aminoglycosides and one cephalosporin. Drug levels in the renal parenchyma, as well as several parameters of renal function and histology, were compared in rats treated with endotoxin (0.25 mg/kg) and normal rats treated with either gentamicin (10 mg/kg), netilmicin (10 mg/kg), tobramycin (10 mg/kg), amikacin (50 mg/kg), or cephalothin (100 mg/kg). Blood pressure and pulse rate were recorded. Endotoxin was associated with a decrease in the half-life and in the apparent volume of distribution of gentamicin. The endotoxin-injected animals accumulated significantly (P less than 0.05) more aminoglycosides in their kidneys than the normal animals. The amount of cephalothin recovered in the renal parenchyma was identical in both groups. Slight decreases in the glomerular filtration rate and renal plasma flow were observed after endotoxin treatment. Blood pressure and cardiac frequency were minimally affected by endotoxin. No histological lesions were observed by light microscopy in animals receiving endotoxin. Thus, endotoxin modifies the renal handling of aminoglycosides in the absence of any major physiological disturbance or histological change. By increasing the total amount of drug within the kidneys, endotoxin might increase the nephrotoxic potential of aminoglycosides.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aubert-Tulkens G., Van Hoof F., Tulkens P. Gentamicin-induced lysosomal phospholipidosis in cultured rat fibroblasts. Quantitative ultrastructural and biochemical study. Lab Invest. 1979 Apr;40(4):481–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUDE A. I., CAREY F. J., ZALESKY M. Studies with radioactive endotoxin. II. Correlation of physiologic effects with distribution of radioactivity in rabbits injected with radioactive sodium chromate. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jun;34(6):858–866. doi: 10.1172/JCI103141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp D., Poirier A., Bergeron M. G. Increased nephrotoxicity of gentamicin in pyelonephritic rats. Kidney Int. 1985 Aug;28(2):106–113. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron M. G., Bastille A., Lessard C., Gagnon P. M. Significance of intrarenal concentrations of gentamicin for the outcome of experimental pyelonephritis in rats. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jul;146(1):91–96. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron M. G., Trottier S. Influence of single or multiple doses of gentamicin and netilmicin on their cortical, medullary, and papillary distribution. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 May;15(5):635–641. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.5.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron M. G., Trottier S., Lessard C., Beauchamp D., Gagnon P. M. Disturbed intrarenal distribution of gentamicin in experimental pyelonephritis due to Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1982 Sep;146(3):436–439. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.3.436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bona C., Chedid L., Lamensans A. In vitro attachment of radioactive endotoxins to lysosomes. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):532–536. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.532-536.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley S. G., Bond J. S. Toxicity, clearance, and metabolic effects of pactamycin in combination with bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1975 Feb;31(2):208–221. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(75)90157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley S. G. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of action of bacterial endotoxins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:67–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. E., Morrison D. C. Possible alteration of normal mechanisms of endotoxin toxicity in vivo by actinomycin D. J Infect Dis. 1982 Dec;146(6):746–750. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.6.746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh D., Rao P. S., Sutton D. M., Bhagat B. D., Bachmann F. Pathophysiology of endotoxin shock in the primate. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1970 Nov 1;108(5):705–722. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(70)90535-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto H., Nakamura S. Liberation of endotoxin from Escherichia coli by addition of antibiotics. Jpn J Exp Med. 1980 Feb;50(1):35–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HINSHAW L. B., BRADLEY G. M., CARLSON C. H. Effect of endotoxin on renal function in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1959 May;196(5):1127–1131. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.196.5.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halkin H., Lidji M., Rubinstein E. The influence of endotoxin-induced pyrexia on the pharmacokinetics of gentamicin in the rabbit. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Feb;216(2):415–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansön P. M., Kühn S. H., Geldenhuys J. J. Lysosomal disruption during the development of endotoxic shock in the baboon. S Afr Med J. 1975 Jun 21;49(26):1041–1047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manny J., Livni N., Schiller M., Guttman A., Boss J., Rabinovici N. Structural changes in the perfused canine kidney exposed to the direct action of endotoxin. Isr J Med Sci. 1980 Mar;16(3):153–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., Ulevitch R. J. The clearance, tissue distribution, and cellular localization of intravenously injected lipopolysaccharide in rabbits. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2133–2143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGivney A., Bradley S. G. Effects of bacterial endotoxin on lysosomal and mitochondrial enzyme activities of established cell cultures. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Sep;26(3):307–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. G., Margaretten W., Csavossy I. An electron microscope study of the effects of bacterial endotoxin on the blood-vascular system. Lab Invest. 1966 Dec;15(12):1815–1829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin J. P., Viotte G., Vandewalle A., Van Hoof F., Tulkens P., Fillastre J. P. Gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity: a cell biology approach. Kidney Int. 1980 Nov;18(5):583–590. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onji T., Liu M. S. Changes in surface charge density on liposomes induced by Escherichia coli endotoxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 12;558(3):320–324. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90267-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkind D., Palmer J. D. Neutralization of endotoxin toxicity in chick embryos by antibiotics. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):815–819. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.815-819.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands J. W., Jr Affinity of endotoxin for membranes. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jul;128(Suppl):197–201. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.supplement_1.s197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenep J. L., Mogan K. A. Kinetics of endotoxin release during antibiotic therapy for experimental gram-negative bacterial sepsis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Sep;150(3):380–388. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.3.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverblatt F. J., Kuehn C. Autoradiography of gentamicin uptake by the rat proximal tubule cell. Kidney Int. 1979 Apr;15(4):335–345. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS L. The physiological disturbances produced by endotoxins. Annu Rev Physiol. 1954;16:467–490. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.16.030154.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westenfelder M., Galanos C., Madsen P. O. Experimental lipid A-induced nephritis in the dog. Invest Urol. 1975 Mar;12(5):337–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. C., Moore J. N., Eakle N. Gentamicin pharmacokinetics in horses given small doses of Escherichia coli endotoxin. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Sep;44(9):1746–1749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


