Abstract
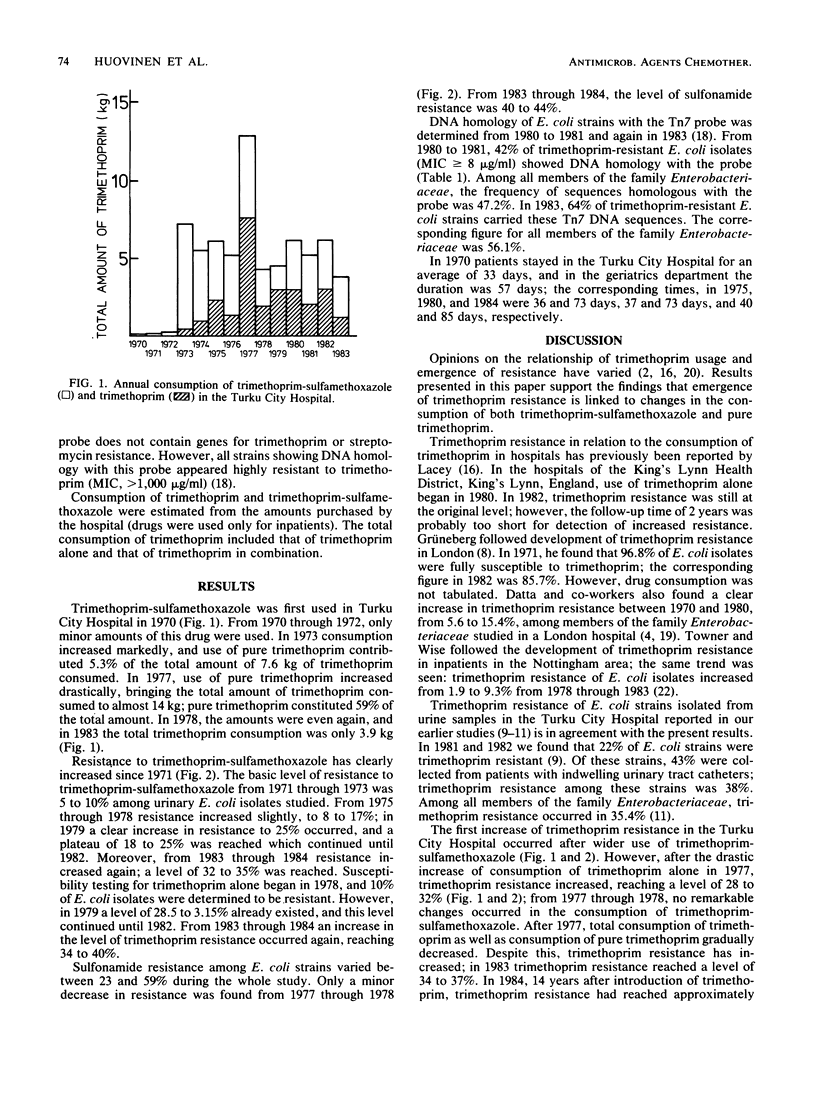
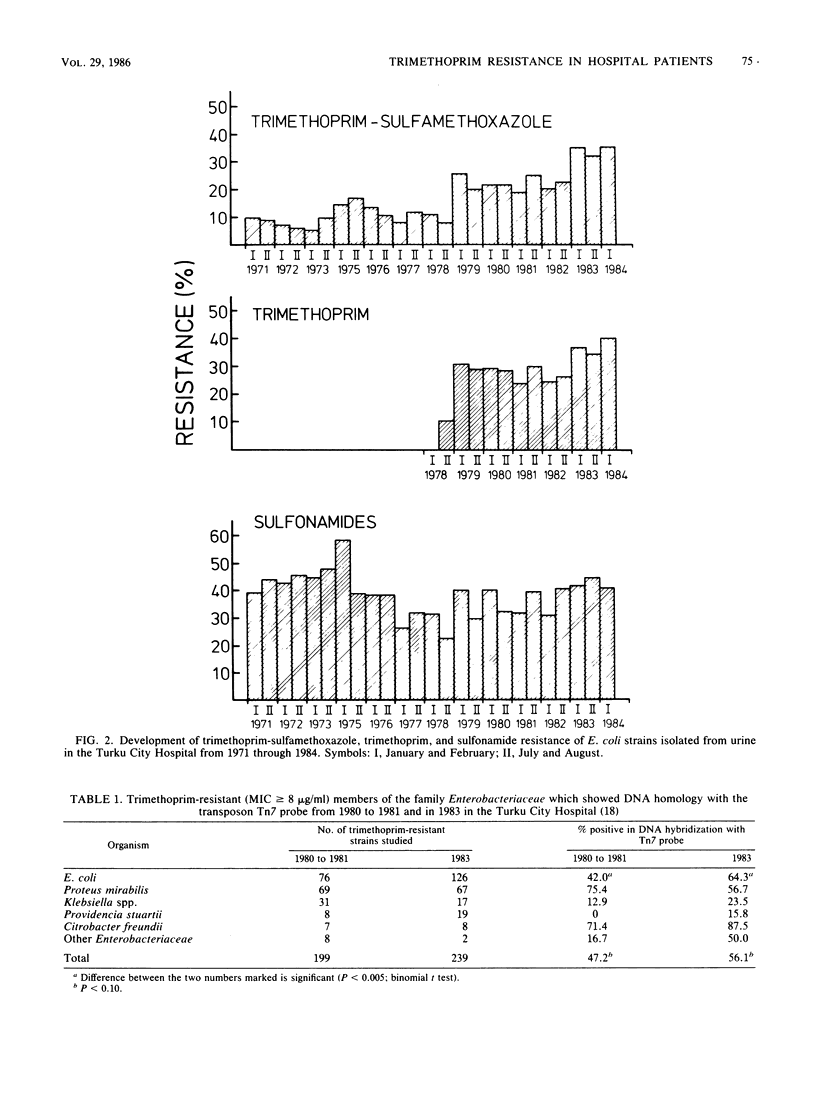
Emergence of trimethoprim resistance among urinary tract Escherichia coli strains, isolated mostly from long-term patients in the Turku City Hospital, Turku, Finland, was studied from 1971 through 1984. Emergence of resistance to trimethoprim was associated with changes in the consumption of both trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim, with occurrence of high-level trimethoprim resistance and sequences homologous to trimethoprim resistance transposon Tn7. Since 1971, resistance of E. coli to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole increased from 8 to between 32 and 35% in 1983 and 1984; resistance to sulfamethoxazole varied from 39 to between 40 and 44%. The frequency of DNA sequence homology with our Tn7 probe among trimethoprim-resistant E. coli strains was 42% from 1980 to 1981 and 64% in 1983 (P less than 0.005). Fourteen years after the introduction of trimethoprim therapy in this hospital, resistance has reached the level of resistance to sulfonamide.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barth P. T., Datta N., Hedges R. W., Grinter N. J. Transposition of a deoxyribonucleic acid sequence encoding trimethoprim and streptomycin resistances from R483 to other replicons. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):800–810. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.800-810.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brumfitt W., Hamilton-Miller J. M., Wood A. Evidence for a slowing in trimethoprim resistance during 1981--a comparison with earlier years. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Jun;11(6):503–509. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.6.503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchall J. J., Elwell L. P., Fling M. E. Molecular mechanisms of resistance to trimethoprim. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):246–254. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.2.246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Dacey S., Hughes V., Knight S., Richards H., Williams G., Casewell M., Shannon K. P. Distribution of genes for trimethoprim and gentamicin resistance in bacteria and their plasmids in a general hospital. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Jun;118(2):495–508. doi: 10.1099/00221287-118-2-495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Nugent M., Richards H. Transposons encoding trimethoprim or gentamicin resistance in medically important bacteria. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):45–51. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornbusch K., Toivanen P. Effect of trimethoprim or trimethoprim/sulphamethoxazole usage on the emergence of trimethoprim resistance in urinary tract pathogens. Scand J Infect Dis. 1981;13(3):203–210. doi: 10.3109/inf.1981.13.issue-3.08. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERICSSON H., TUNEVALL G., WICKMAN K. The paper disc method for determination of bacterial sensitivity to antibiotics. Relationship between the diameter of the zone of inhibition and the minimum inhibitory concentration. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1960;12(4):414–422. doi: 10.3109/00365516009065406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grüneberg R. N. Antibiotic sensitivities of urinary pathogens, 1971-82. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Jul;14(1):17–23. doi: 10.1093/jac/14.1.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huovinen P., Mäntyjärvi R., Toivanen P. Trimethoprim resistance in hospitals. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Mar 13;284(6318):782–784. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6318.782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huovinen P., Pulkkinen L., Toivanen P. Transferable trimethoprim resistance in three Finnish hospitals. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Sep;12(3):249–256. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.3.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huovinen P. Trimethoprim-resistant Escherichia coli in a geriatric hospital. J Infect. 1984 Mar;8(2):145–148. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(84)92530-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasanen A., Anttila M., Elfving R., Kahela P., Saarimaa H., Sundquist H., Tikkanen R., Toivanen P. Trimethoprim. Pharmacology, antimicrobial activity and clinical use in urinary tract infections. Ann Clin Res. 1978;10 (Suppl 22):1–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasanen A., Sundquist H., Elo J., Anttila M., Kangas L. Secondary prevention of urinary tract infections. The role of trimethoprim alone. Ann Clin Res. 1983;15(Suppl 36):1–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M., Bülow P. Rapid identification of Enterobacteriaceae. II. Use of a beta-glucuronidase detecting agar medium (PGUA agar) for the identification of E. coli in primary cultures of urine samples. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Oct;87(5):271–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey R. W. Do sulphonamide-trimethoprim combinations select less resistance to trimethoprim than the use of trimethoprim alone? J Med Microbiol. 1982 Nov;15(4):403–427. doi: 10.1099/00222615-15-4-403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulkkinen L., Huovinen P., Vuorio E., Toivanen P. Characterization of trimethoprim resistance by use of probes specific for transposon Tn7. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jul;26(1):82–86. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards H., Datta N., Sojka W. J., Wray C. Trimethoprim-resistance plasmids and transposons in Salmonella. Lancet. 1978 Dec 2;2(8101):1194–1195. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92171-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards H., Datta N. Transposons and trimethoprim resistance. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Apr 4;282(6270):1118–1119. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6270.1118-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J. A., Sporn P. Tn402: a new transposable element determining trimethoprim resistance that inserts in bacteriophage lambda. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1632–1635. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1632-1635.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


