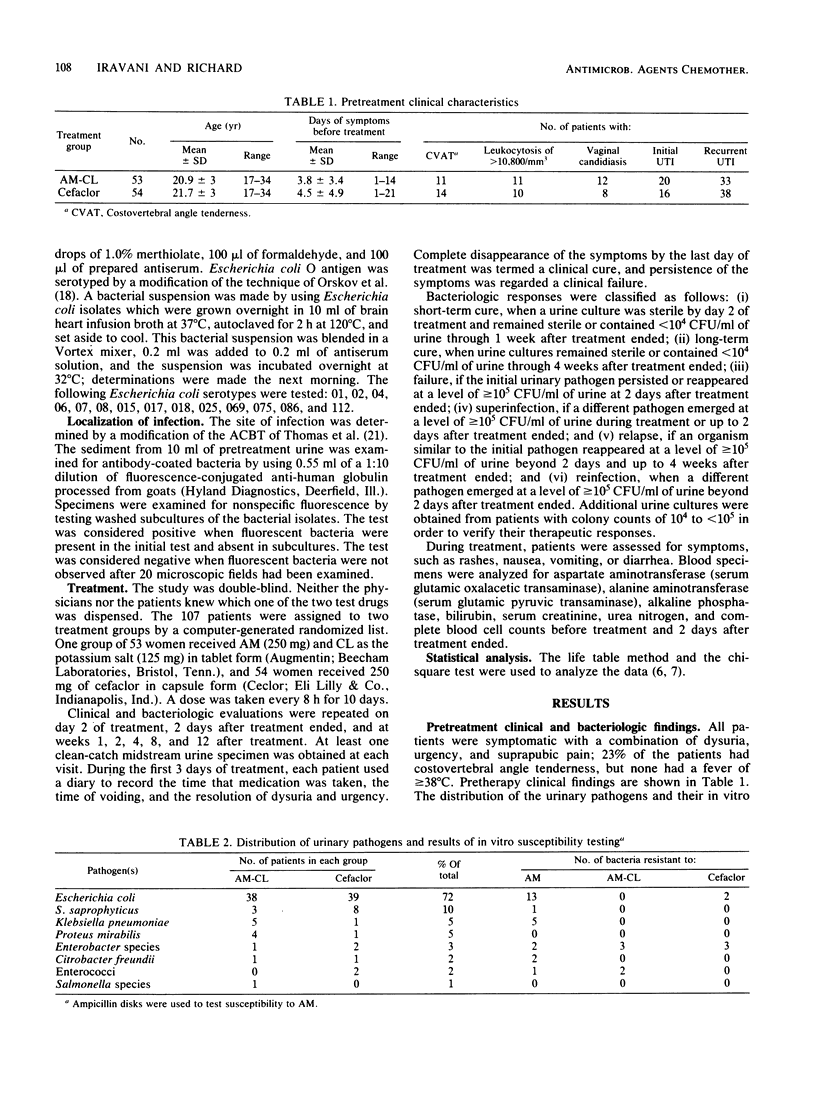
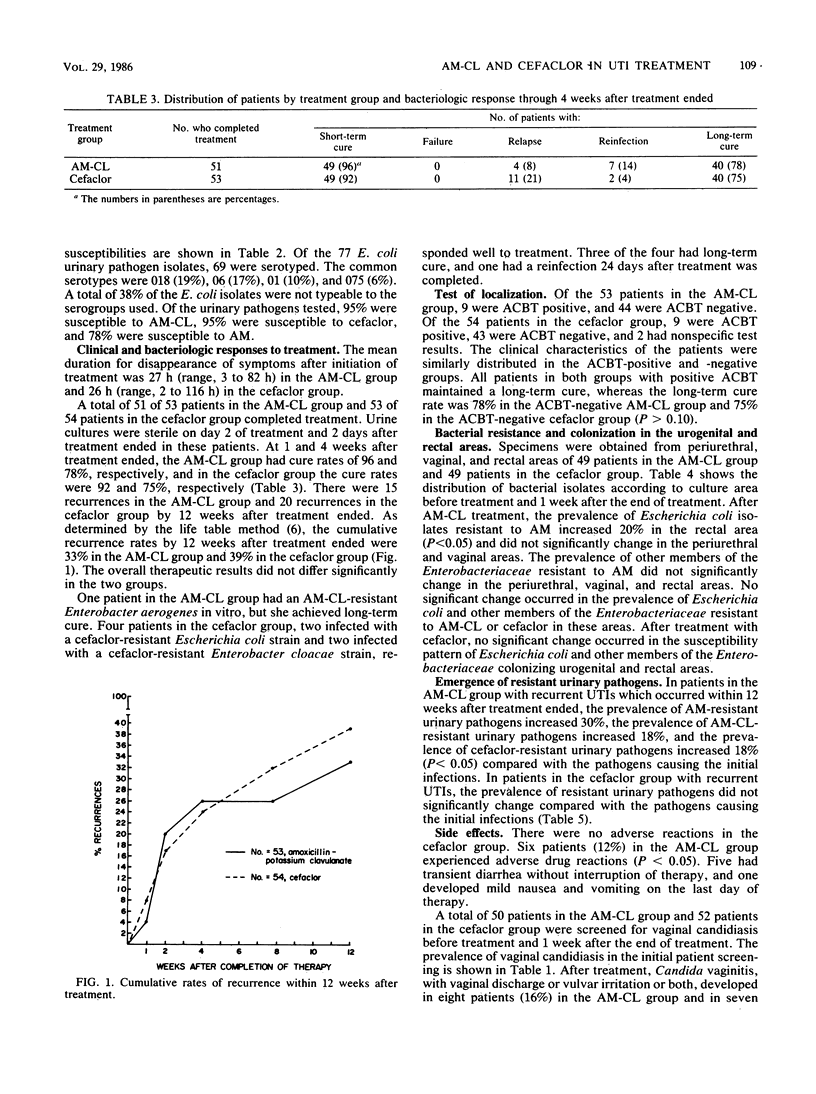
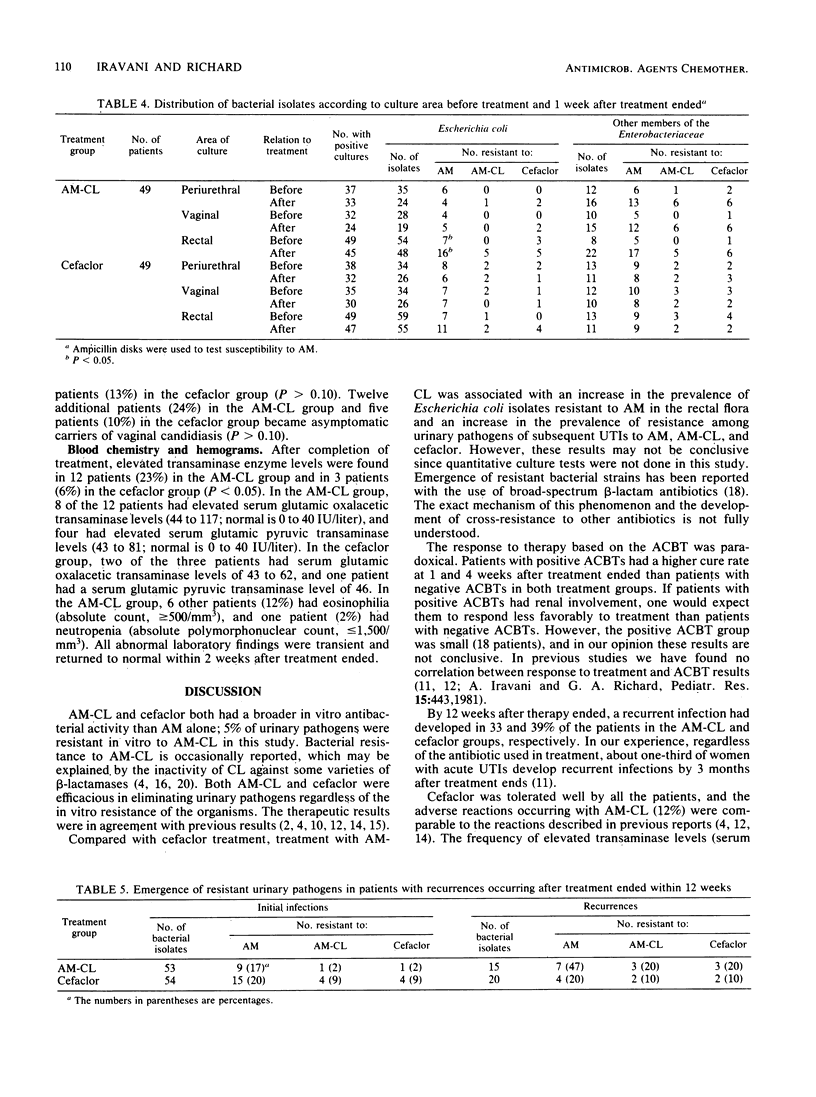
Abstract
In a double-blind randomized study, amoxicillin-clavulanic acid (AM-CL) was compared with cefaclor for the treatment of acute urinary tract infections in 107 college women. A total of 53 patients received amoxicillin (250 mg) and clavulanic acid as the potassium salt (125 mg), and 54 received cefaclor (250 mg); each drug was administered every 8 h for 10 days. The cure rates at 1 and 4 weeks after treatment were 96 and 78%, respectively, in the AM-CL group and 92 and 75%, respectively, in the cefaclor group (P greater than 0.10). After AM-CL treatment, the prevalence of amoxicillin-resistant Escherichia coli significantly increased in the rectal flora. Also, the frequency of bacterial resistance to amoxicillin, AM-CL, and cefaclor increased among the urinary pathogens causing subsequent urinary tract infections (P less than 0.05). There were no adverse reactions in the cefaclor group; however, six patients in the AM-CL group (12%) experienced diarrhea, nausea, or vomiting (P less than 0.05). Elevated transaminase enzyme levels were observed in 23% of the patients in the AM-CL group and in 6% of the patients in the cefaclor group (P less than 0.05). Symptomatic Candida vaginitis developed in 16 and 13% of the patients in the AM-CL and cefaclor groups, respectively (P greater than 0.10).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball A. P., Geddes A. M., Davey P. G., Farrell I. D., Brookes G. R. Clavulanic acid and amoxycillin: a clinical, bacteriological, and pharmacological study. Lancet. 1980 Mar 22;1(8169):620–623. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brogden R. N., Carmine A., Heel R. C., Morley P. A., Speight T. M., Avery G. S. Amoxycillin/clavulanic acid: a review of its antibacterial activity, pharmacokinetics and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1981 Nov;22(5):337–362. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198122050-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush K., Sykes R. B. beta-Lactamase inhibitors in perspective. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Feb;11(2):97–107. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.2.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUTLER S. J., EDERER F. Maximum utilization of the life table method in analyzing survival. J Chronic Dis. 1958 Dec;8(6):699–712. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(58)90126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein F. W., Kitzis M. D., Acar J. F. Effect of clavulanic acid and amoxycillin formulation against beta-lactamase producing Gram-negative bacteria in urinary tract infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1979 Nov;5(6):705–709. doi: 10.1093/jac/5.6.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iravani A., Pryor N., Richard G. A. Treatment of acute uncomplicated urinary tract infections by cephalexin, with special reference to the antibody-coated bacteria. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. 1982 Mar;20(3):97–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iravani A., Richard G. A. Treatment of urinary tract infections with a combination of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Oct;22(4):672–677. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.4.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan P. A., Iravani A., Richard G. A., Baer H. Urinary tract infection caused by Staphylococcus saprophyticus. J Infect Dis. 1980 Oct;142(4):510–515. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.4.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer R. B., Short L. J. Cefaclor--summary of clinical experience. Postgrad Med J. 1979;55 (Suppl 4):93–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinelli R., Lopes A. A., de Oliveira M. M., Rocha H. Amoxicillin-clavulanic acid in treatment of urinary tract infection due to gram-negative bacteria resistant to penicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Dec;20(6):800–802. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.6.800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Fu K. P. Clavulanic acid, a novel inhibitor of beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Nov;14(5):650–655. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.5.650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F., Jann B., Jann K. Serology, chemistry, and genetics of O and K antigens of Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):667–710. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.667-710.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr Emergence of resistance during therapy with the newer beta-lactam antibiotics: role of inducible beta-lactamases and implications for the future. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jul-Aug;5(4):639–648. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.4.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. B., Tomfohrde K. M., Rhoden D. L., Balows A. API system: a multitube micromethod for identification of Enterobacteriaceae. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Sep;24(3):449–452. doi: 10.1128/am.24.3.449-452.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Matthew M. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their role in resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1976 Jun;2(2):115–157. doi: 10.1093/jac/2.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas V., Shelokov A., Forland M. Antibody-coated bacteria in the urine and the site of urinary-tract infection. N Engl J Med. 1974 Mar 14;290(11):588–590. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197403142901102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


