Abstract
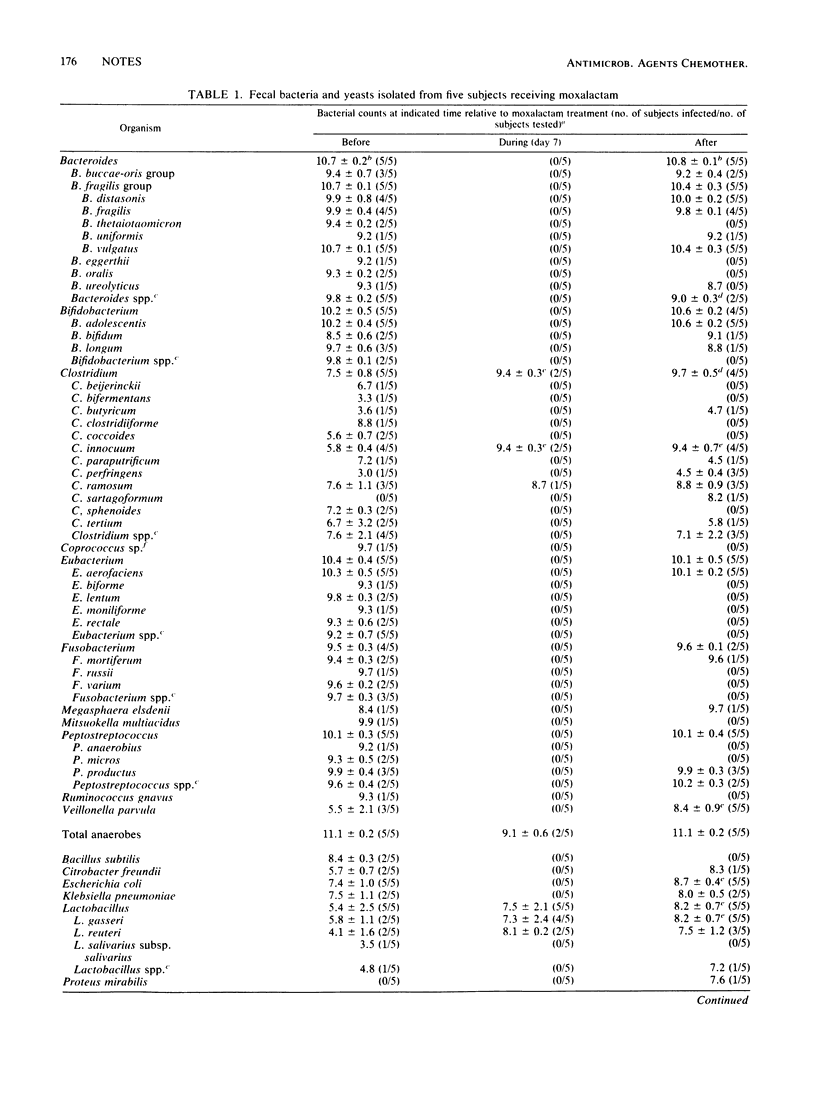
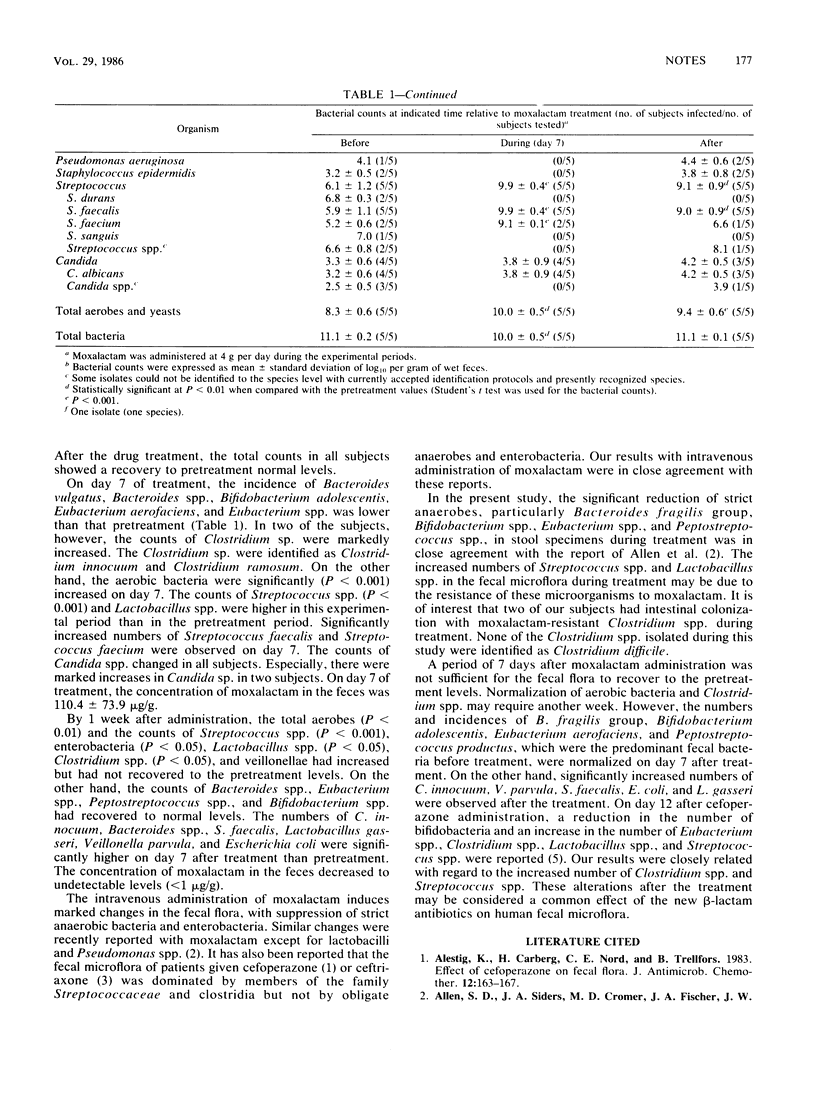
Five healthy male adults received 2 g of moxalactam every 12 h for 7 days. The alterations of fecal microflora were investigated before, during, and after treatment with moxalactam. On day 7 of treatment, the number of total bacteria was decreased in all subjects. There was marked suppression of the obligate anaerobic bacteria and enterobacteria to undetectable levels, but the counts of Streptococcus spp. and Lactobacillus spp. increased. On day 7, two subjects had Clostridium innocuum and Clostridium ramosum in their feces but not Clostridium difficile. On day 7 after treatment, the counts of Streptococcus spp., enterobacteria, Lactobacillus spp., and Clostridium spp. in all subjects were still not normal.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alestig K., Carlberg H., Nord C. E., Trollfors B. Effect of cefoperazone on faecal flora. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Aug;12(2):163–167. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.2.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvidsson A., Alván G., Angelin B., Borgå O., Nord C. E. Ceftriaxone: renal and biliary excretion and effect on the colon microflora. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Sep;10(3):207–215. doi: 10.1093/jac/10.3.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benno Y., Sawada K., Mitsuoka T. The intestinal microflora of infants: composition of fecal flora in breast-fed and bottle-fed infants. Microbiol Immunol. 1984;28(9):975–986. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1984.tb00754.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. L., Sutter V. L., Citron D., Finegold S. M. Selective and differential medium for isolation of Clostridium difficile. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):214–219. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.214-219.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWBURY E. J., LILLY H. A. A selective plate medium for Cl. welchii. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1955 Jul;70(1):105–109. doi: 10.1002/path.1700700110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuoka T., Ohno K., Benno Y., Suzuki K., Namba K. Die Faekalflora bei Menschen. IV. Mitteilung: Vergleich des neu entwickelten Verfahrens mit dem bisherigen üblichen Verfahren zur Darmfloraanalyse. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1976 Mar;234(2):219–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuoka T., Sega T., Yamamoto S. Eine verbesserte Methodik der qualitativen und quantitativen Analyse der Darmflora von Menschen und Tieren. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1965 Mar;195(4):455–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKER C. A. Anaerobiosis with iron wool. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1955 Feb;33(1):33–37. doi: 10.1038/icb.1955.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. The effect of antimicrobial agents on human faecal flora: studies with cephalexin, cyclacillin and clindamycin. Soc Appl Bacteriol Symp Ser. 1974;3(0):229–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T., Matsuura S., Mayama M., Kameda Y., Kuwahara S. Moxalactam (6059-S), a novel 1-oxa-beta-lactam with an expanded antibacterial spectrum: laboratory evaluation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Mar;17(3):302–312. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.3.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


