Abstract
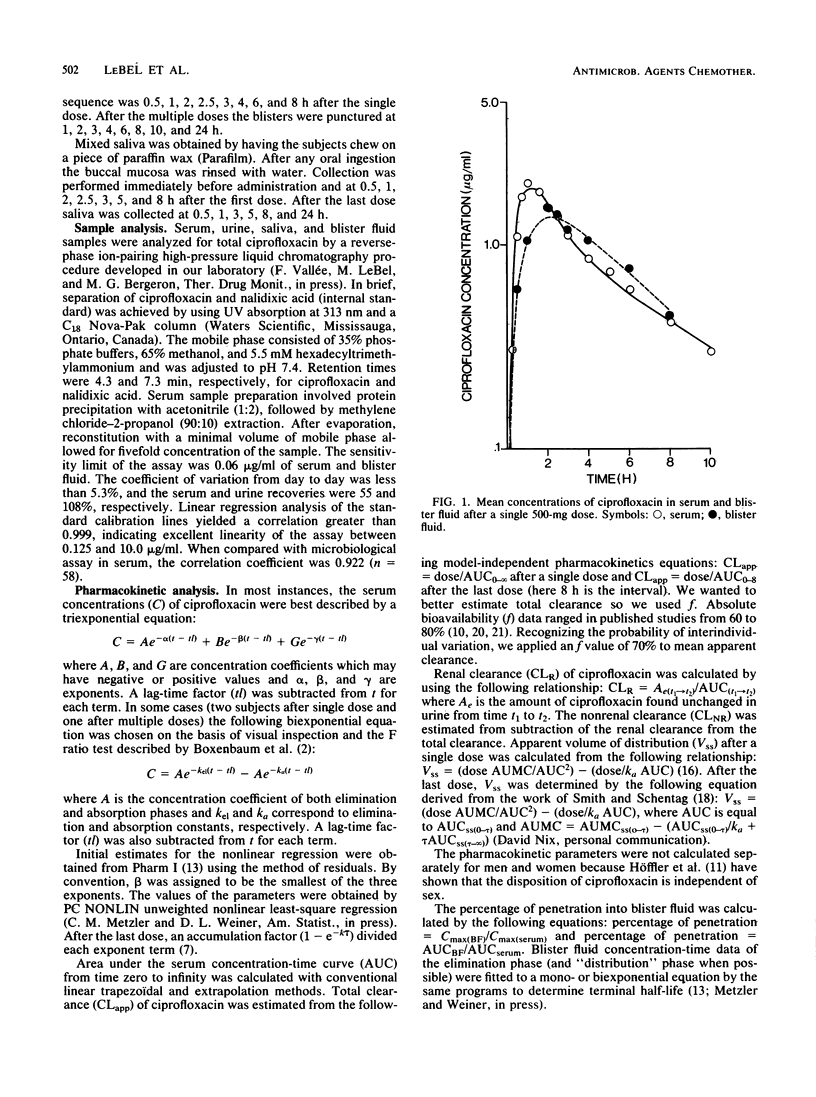
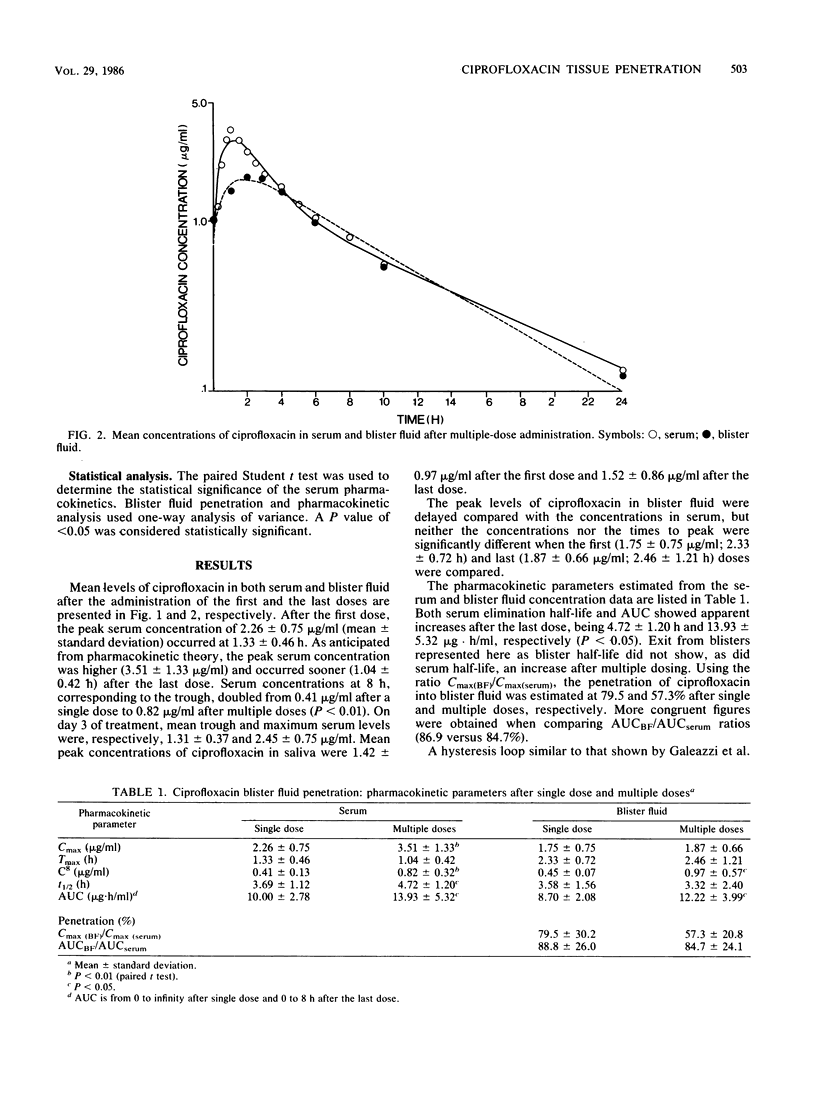
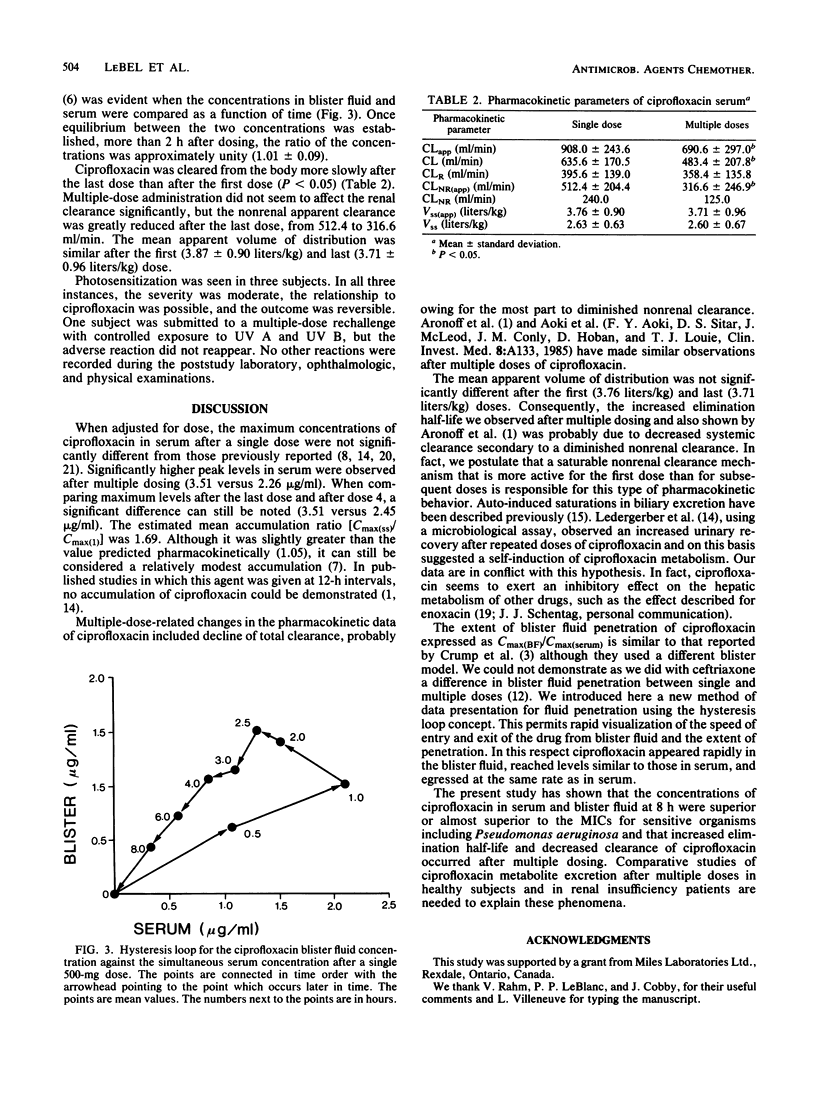
The pharmacokinetics and the suction-induced blister fluid penetration of ciprofloxacin were compared after a single dose (500 mg) and after multiple dosing (500 mg q8h for 13 doses). Significantly higher peak levels of ciprofloxacin in serum were observed after multiple dosing (3.51 versus 2.26 micrograms/ml; P less than 0.01). Increased elimination half-life occurred after multiple dosing; this seems to be mostly related to decreased systemic clearance secondary to a diminished nonrenal clearance (240.0 versus 125.0 ml/min). Ciprofloxacin appeared rapidly in the blister fluid, and the percentage of penetration (AUC0-tBF/AUC0-t serum) yielded values of 88.8 versus 84.7% after single and multiple doses, respectively. Ciprofloxacin levels in serum and blister fluid at the end of the dosing interval (8 h) were superior or almost superior to MICs for sensitive organisms including Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Comparative studies of ciprofloxacin metabolite excretion after multiple doses in healthy subjects and in renal insufficiency patients are needed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronoff G. E., Kenner C. H., Sloan R. S., Pottratz S. T. Multiple-dose ciprofloxacin kinetics in normal subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1984 Sep;36(3):384–388. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1984.192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxenbaum H. G., Riegelman S., Elashoff R. M. Statistical estimations in pharmacokinetics. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1974 Apr;2(2):123–148. doi: 10.1007/BF01061504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crump B., Wise R., Dent J. Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Nov;24(5):784–786. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.5.784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalhoff A., Weidner W. Diffusion of ciprofloxacin into prostatic fluid. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;3(4):360–362. doi: 10.1007/BF01977495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliopoulos G. M., Gardella A., Moellering R. C., Jr In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin, a new carboxyquinoline antimicrobial agent. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):331–335. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galeazzi R. L., Benet L. Z., Sheiner L. B. Relationship between the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of procainamide. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1976 Sep;20(3):278–289. doi: 10.1002/cpt1976203278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez M. A., Uribe F., Moisen S. D., Fuster A. P., Selen A., Welling P. G., Painter B. Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics and safety of ciprofloxacin in normal volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Nov;26(5):741–744. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.5.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höffken G., Lode H., Prinzing C., Borner K., Koeppe P. Pharmacokinetics of ciprofloxacin after oral and parenteral administration. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Mar;27(3):375–379. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.3.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höffler D., Dalhoff A., Gau W., Beermann D., Michl A. Dose- and sex-independent disposition of ciprofloxacin. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;3(4):363–366. doi: 10.1007/BF01977496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Blanc P. P., Dumas J. Calcul des valeurs initiales des paramètres pharmacocinétiques à l'aide d'un calculateur programmable. Therapie. 1983 Jan-Feb;38(1):21–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBel M., Grégoire S., Caron M., Bergeron M. G. Difference in blister fluid penetration after single and multiple doses of ceftriaxone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jul;28(1):123–127. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledergerber B., Bettex J. D., Joos B., Flepp M., Lüthy R. Effect of standard breakfast on drug absorption and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Mar;27(3):350–352. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.3.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine W. G. Biliary excretion of drugs and other xenobiotics. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1978;18:81–96. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.18.040178.000501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrier D., Mayersohn M. Noncompartmental determination of the steady-state volume of distribution for any mode of administration. J Pharm Sci. 1982 Mar;71(3):372–373. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600710332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy C., Foz A., Segura C., Tirado M., Teixell M., Teruel D. Activity of ciprofloxacin (BAYo 9867) against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and ampicillin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Infection. 1983 Nov-Dec;11(6):326–328. doi: 10.1007/BF01641358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith I. L., Schentag J. J. Noncompartmental determination of the steady-state volume of distribution during multiple dosing. J Pharm Sci. 1984 Feb;73(2):281–282. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600730239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijnands W. J., van Herwaarden C. L., Vree T. B. Enoxacin raises plasma theophylline concentrations. Lancet. 1984 Jul 14;2(8394):108–109. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90283-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingender W., Graefe K. H., Gau W., Förster D., Beermann D., Schacht P. Pharmacokinetics of ciprofloxacin after oral and intravenous administration in healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;3(4):355–359. doi: 10.1007/BF01977494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Lockley R. M., Webberly M., Dent J. Pharmacokinetics of intravenously administered ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):208–210. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


