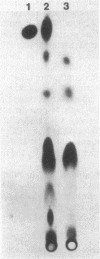
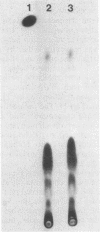
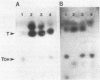
Abstract
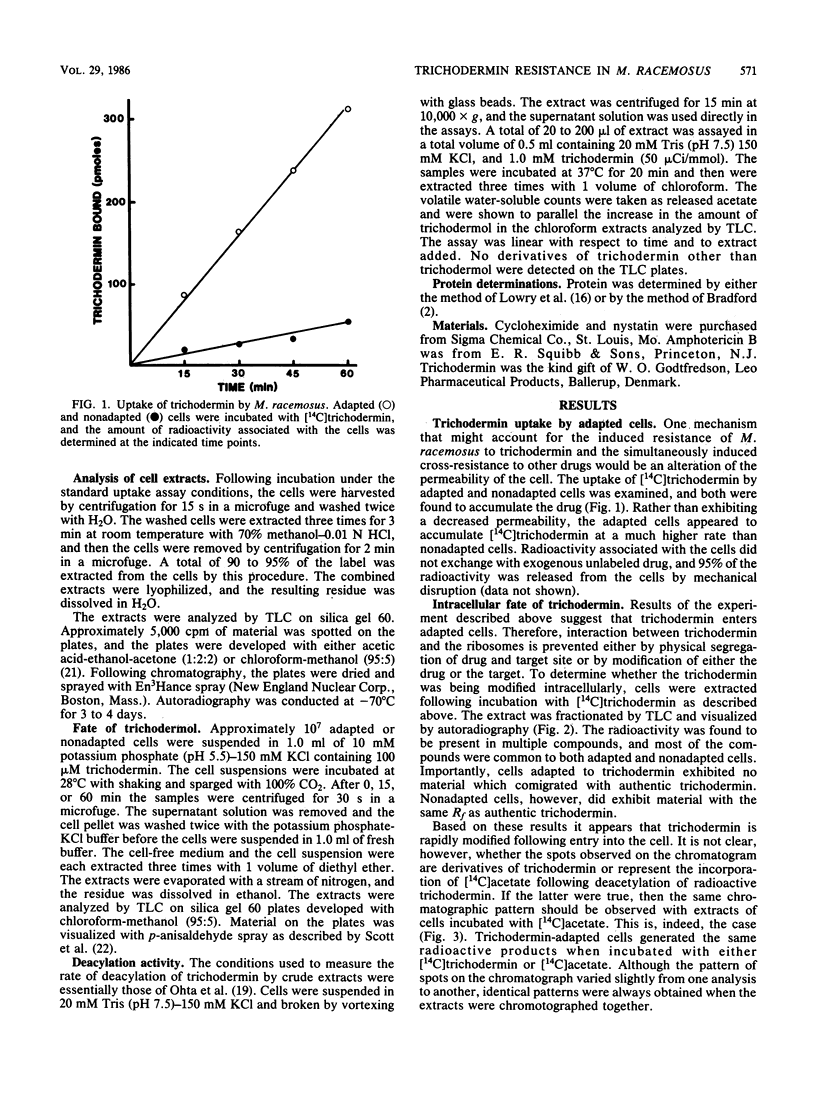
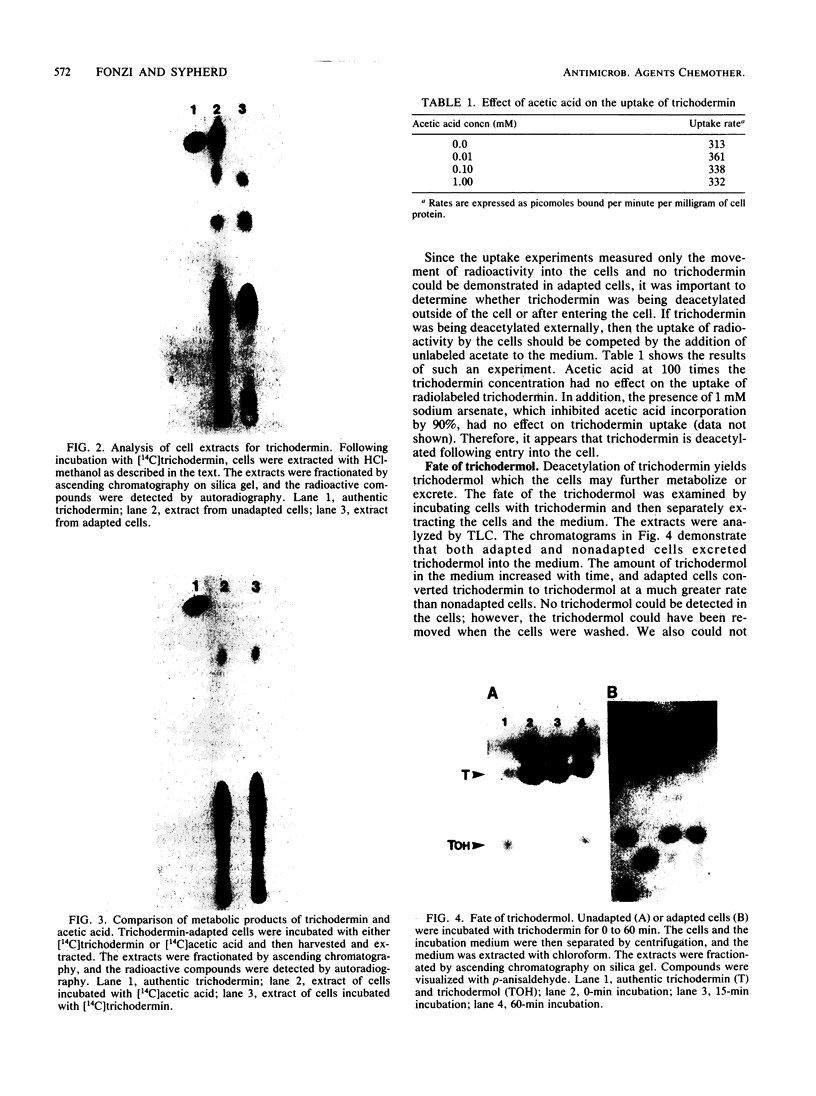
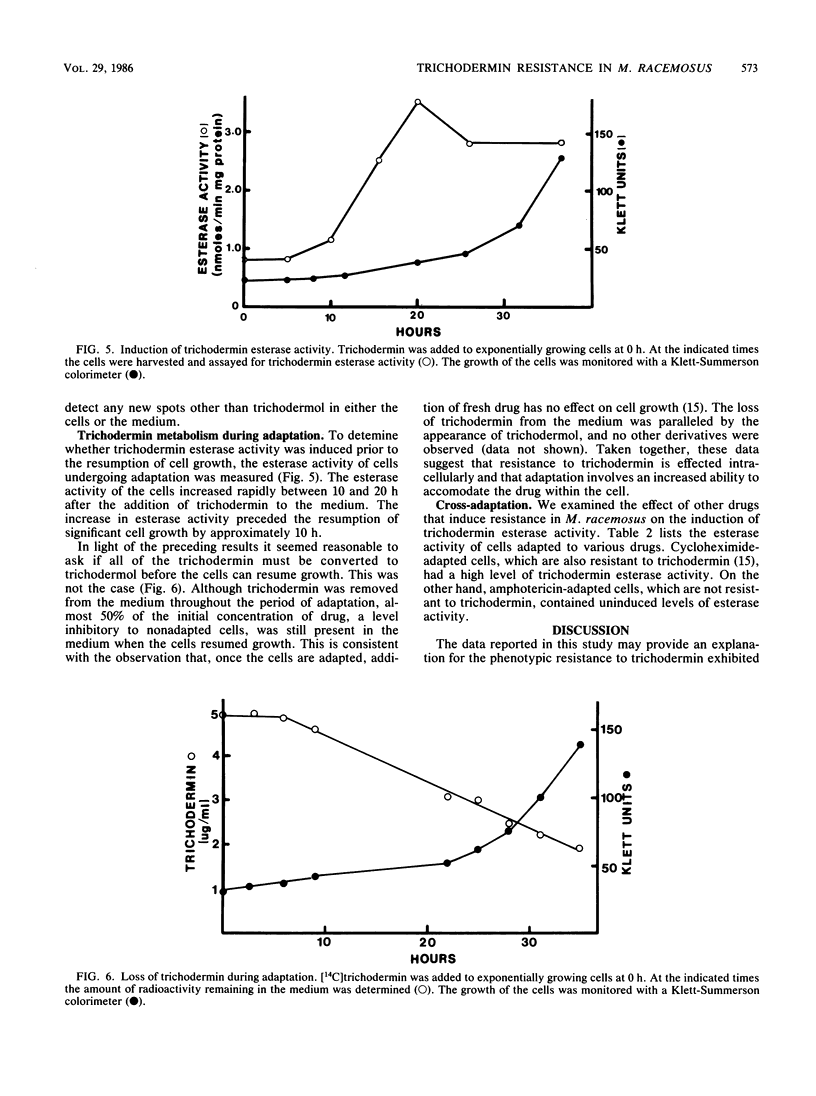
Mucor racemosus exhibited inducible phenotypic resistance toward the protein synthesis inhibitor trichodermin. Induction of resistance was elicited by exposure to trichodermin or to cycloheximide. Both adapted and nonadapted cells took up [14C]trichodermin from the medium. Trichodermin was found to be rapidly deacetylated to trichodermol upon entering the cell. Adapted cells deacetylated the drug more rapidly than nonadapted cells both in vivo and in vitro. The trichodermol resulting from deacetylation appeared in the medium, but the growth of adapting cells began well before the total conversion of trichodermin to trichodermol. Based on these data and the observation that trichodermol was a poor inhibitor of Mucor, adaptation appears to result from deacylation of the active antibiotic.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco L., Barbacid M., Vazquez D. The trichodermin group of antibiotics, inhibitors of peptide bond formation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 23;312(2):368–376. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90381-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba J., Nakano N., Morooka N., Nakazawa S., Watanabe Y. Inhibitory effects of fusarenon-X, a sesqui-terpene mycotoxin, on lipid synthesis and phosphate uptake in Tetrahymena pyriformis. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1972 Oct;25(5):291–296. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.25.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claridge C. A., Schmitz H. Microbial and chemical transformations of some 12,13-epoxytrichothec-9,10-enes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jul;36(1):63–67. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.1.63-67.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M. E., Exworth C. P. Transient inhibition by cycloheximide of protein synthesis in cultured plant cell suspensions: a dose response paradox. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Feb 20;50(4):1075–1080. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91516-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison R. A., Kotsonis F. N. In vitro metabolism of T-2 toxin. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Feb;27(2):423–424. doi: 10.1128/am.27.2.423-424.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel J. An analysis of the recovery of tetrahymena from effects of cycloheximide. J Cell Physiol. 1970 Aug;76(1):55–63. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040760109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godtfredsen W. O., Vangedal S. Trichodermin, a new sesquiterpene antibiotic. Acta Chem Scand. 1965;19(5):1088–1102. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.19-1088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman J. A. Adaptation to trichodermin and anisomycin in Physarum polycephalum. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Sep;92(3):447–456. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040920312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernández F., Cannon M. Inhibition of protein synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by the 12,13-epoxytrichothecenes trichodermol, diacetoxyscirpenol and verrucarin A. Reversibility of the effects. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1982 Jul;35(7):875–881. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.35.875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe R., Moore R. H. Acetylation of cycloheximide by Cunninghamella blakesleeana. Experientia. 1968 Sep 15;24(9):904–904. doi: 10.1007/BF02138641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling K. H., Pettersson H., Sandholm K., Olsen M. Metabolism of aflatoxin, ochratoxin, zearalenone, and three trichothecenes by intact rumen fluid, rumen protozoa, and rumen bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 May;47(5):1070–1073. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.5.1070-1073.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leathers T. D., Sypherd P. S. Inducible phenotypic multidrug resistance in the fungus Mucor racemosus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jun;27(6):892–896. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.6.892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOYED H. S. BIOCHEMICAL MECHANISMS OF DRUG RESISTANCE. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1964;18:347–366. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.18.100164.002023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notario V., Gale E. F., Kerridge D., Wayman F. Phenotypic resistance to amphotericin B in Candida albicans: relationship to glucan metabolism. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Apr;128(4):761–777. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-4-761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta M., Ishii K., Ueno Y. Metabolism of trichothecene mycotoxins. I. Microsomal deacetylation of T-2 toxin in animal tissues. J Biochem. 1977 Dec;82(6):1591–1598. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta M., Matsumoto H., Ishii K., Ueno Y. Metabolism of trichothecene mycotoxins. II. Substrate specificity of microsomal deacetylation of trichothecenes. J Biochem. 1978 Sep;84(3):697–706. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P. M., Lawrence J. W., van Walbeek W. Detection of mycotoxins by thin-layer chromatography: application to screening of fungal extracts. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Nov;20(5):839–842. doi: 10.1128/am.20.5.839-842.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei C. M., Campbell I. M., McLaughlin C. S., Vaughan M. H. Letter: Binding of trichodermin to mammalian ribosomes and its inhibition by other 12,13-epoxytrichothecenes. Mol Cell Biochem. 1974 May 30;3(3):215–219. doi: 10.1007/BF01686646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei C. M., McLaughlin C. S. Structure-function relationship in the 12,13-epoxytrichothecenes. Novel inhibitors of protein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Apr 8;57(3):838–844. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90622-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizawa T., Morooka N. Comparative studies on microbial and chemical modifications of trichothecene mycotoxins. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jul;30(1):38–43. doi: 10.1128/am.30.1.38-43.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]