Abstract
During the first 6 years after appearing in one hospital, a 92-kilobase conjugative plasmid, pBWH1, which encoded resistance to chloramphenicol and sulfonamides and determined TEM-1 beta-lactamase and 2''-aminoglycoside nucleotidyltransferase, underwent a variety of molecular changes. It was most prevalent initially in isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae, then in isolates of Serratia marcescens, and finally, after nearly disappearing, in isolates of Enterobacter cloacae. Evolutionary changes in the plasmid did not account for its shifts in species distribution, since the original molecule was found in isolates of each species. The late resurgence of pBWH1 occurred after a copy of its original molecule entered a distinctive ornithine decarboxylase-negative strain of E. cloacae, new to the hospital. The resulting transconjugant strain, chromosomally resistant to topical silver salts and to cephalosporins, and with the addition of pBWH1-encoded aminoglycoside resistance, spread in the hospital by causing an outbreak of sepsis in the burn unit, where these were commonly used antibacterial agents. Thus, an endemic plasmid became prevalent in a new host species because one of its genes supplemented the fitness of an uncommon strain of the species for a particular clinical niche.
Full text
PDF
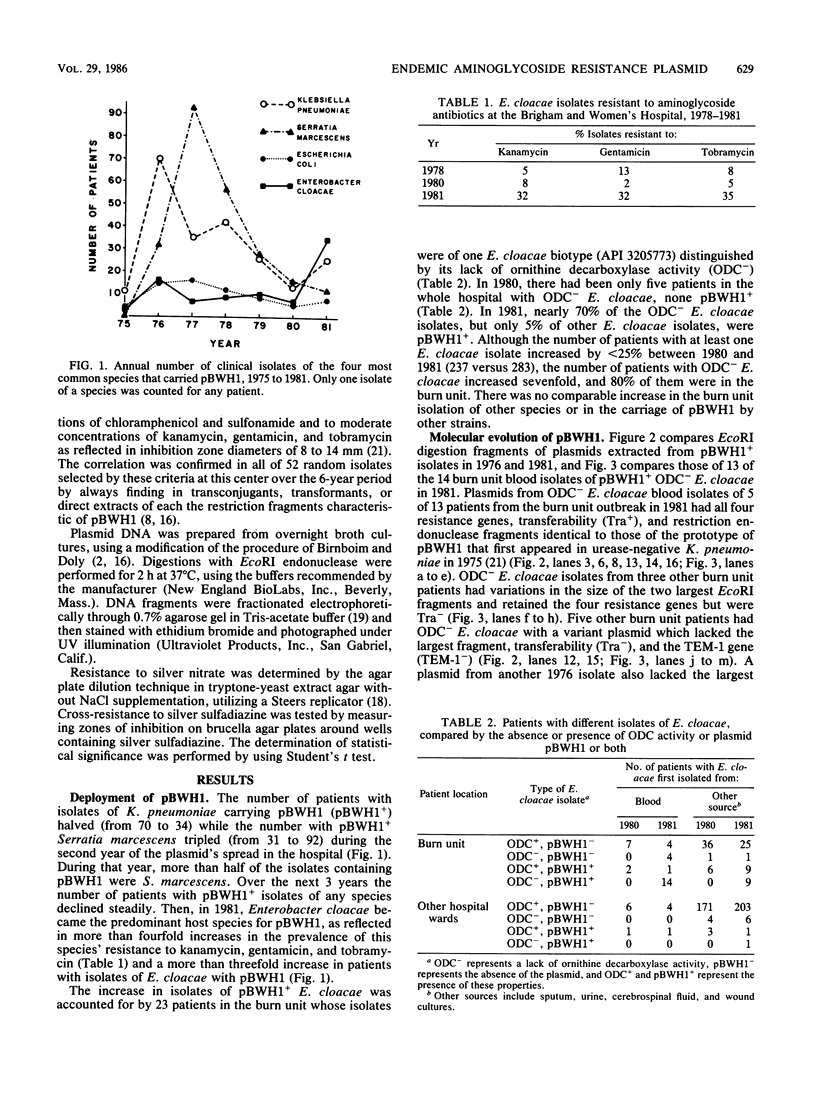

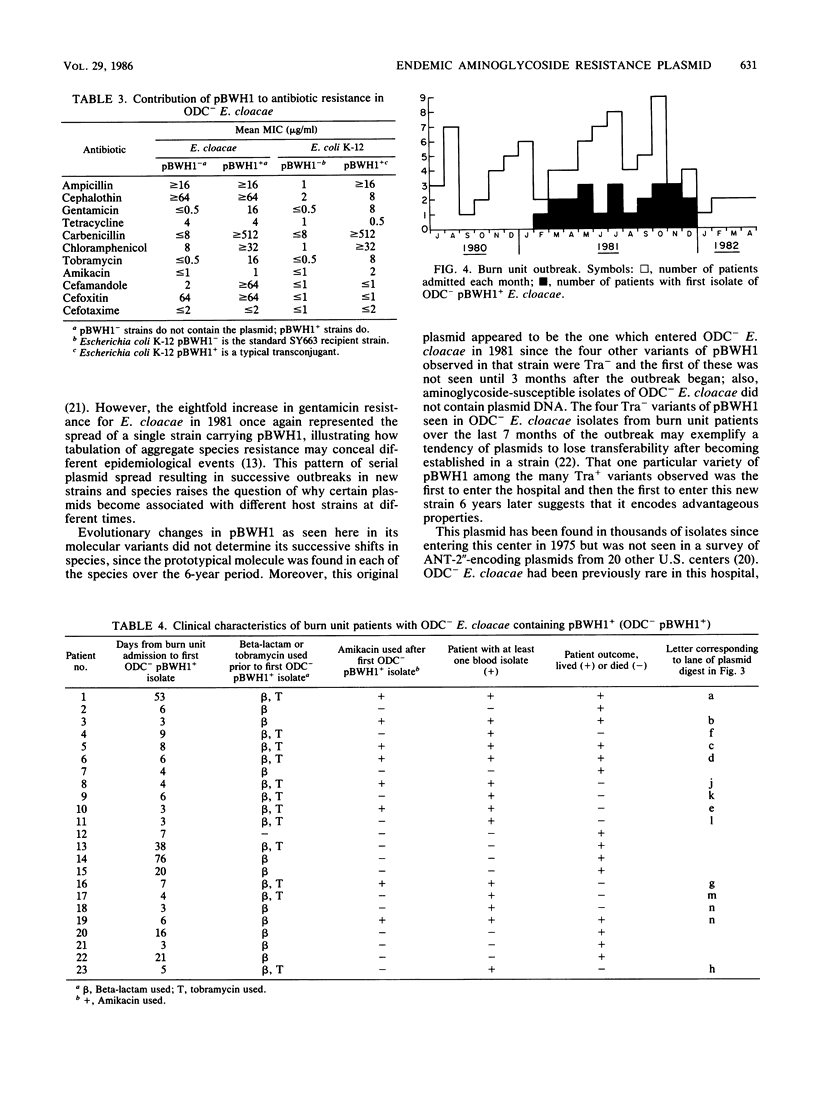


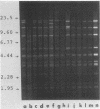
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Annear D. I., Mee B. J., Bailey M. Instability and linkage of silver resistance, lactose fermentation, and colony structure in Enterobacter cloacae from burn wounds. J Clin Pathol. 1976 May;29(5):441–443. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.5.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson B. A., Lorian V. Antimicrobial agent susceptibility patterns of bacteria in hospitals from 1971 to 1982. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):791–796. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.791-796.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler D. A., Lobregat C. M., Gavan T. L. Reproducibility of the analytab (API 20E) system. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Oct;2(4):322–326. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.4.322-326.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Smith D. I. Plasmid-determined resistance to antimicrobial agents. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:469–518. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.002345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar W. E., Jr Molecular analysis of plasmids in epidemiologic investigation. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jul;148(1):1–6. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gayle W. E., Mayhall C. G., Lamb V. A., Apollo E., Haynes B. W., Jr Resistant Enterobacter cloacae in a burn center: the ineffectiveness of silver sulfadiazine. J Trauma. 1978 May;18(5):317–323. doi: 10.1097/00005373-197805000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins J. D., Mayer K. H., Gilleece E. S., O'Brien T. F., Syvanen M. Genetic and physical characterization of IncM plasmid pBWH1 and its variance among natural isolates. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):47–52. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.47-52.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John J. F., Jr, McKee K. T., Jr, Twitty J. A., Schaffner W. Molecular epidemiology of sequential nursery epidemics caused by multiresistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Pediatr. 1983 Jun;102(6):825–830. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John J. F., Jr, McNeill W. F. Characteristics of Serratia marcescens containing a plasmid coding for gentamicin resistance in nosocomial infections. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jun;143(6):810–817. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.6.810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John J. F., Jr, Sharbaugh R. J., Bannister E. R. Enterobacter cloacae: bacteremia, epidemiology, and antibiotic resistance. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Jan-Feb;4(1):13–28. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishi H., Evans D., Hopkins J. D., Medeiros A. A., O'Brien T. F. Diagnostic microbiology laboratory susceptibility test results discriminate distinctive antibiotic resistance plasmids. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1984 Sep;2(4):309–316. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(84)90062-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz S. M., Smith S. M., Williams D. S. Retrospective analysis of plasmid patterns in a study of burn unit outbreaks of infection due to Enterobacter cloacae. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jul;148(1):18–23. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.1.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz S. M., Veazey J. M., Jr, Macrina F. L., Mayhall C. G., Lamb V. A. Sequential outbreaks of infection due to Klebsiella pneumoniae in a neonatal intensive care unit: implication of a conjugative R plasmid. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jul;142(1):106–112. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.1.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayhall C. G., Lamb V. A., Gayle W. E., Jr, Haynes B. W., Jr Enterobacter cloacae septicemia in a burn center: epidemiology and control of an outbreak. J Infect Dis. 1979 Feb;139(2):166–171. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.2.166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHugh G. L., Moellering R. C., Hopkins C. C., Swartz M. N. Salmonella typhimurium resistant to silver nitrate, chloramphenicol, and ampicillin. Lancet. 1975 Feb 1;1(7901):235–240. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien T. F., Pla M. P., Mayer K. H., Kishi H., Gilleece E., Syvanen M., Hopkins J. D. Intercontinental spread of a new antibiotic resistance gene on an epidemic plasmid. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):87–88. doi: 10.1126/science.2994226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien T. F., Ross D. G., Guzman M. A., Medeiros A. A., Hedges R. W., Botstein D. Dissemination of an antibiotic resistance plasmid in hospital patient flora. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Apr;17(4):537–543. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.4.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennie R. P., Duncan I. B. Emergence of gentamicin-resistant Klebsiella in a general hospital. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Feb;11(2):179–184. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.2.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenkranz H. S., Coward J. E., Wlodkowski T. J., Carr H. S. Properties of silver sulfadiazine-resistant Enterobacter cloacae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Feb;5(2):199–201. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.2.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski P. L., Peterson B. C., Gerding D. N., Cleary P. P. Physical characterization of ten R plasmids obtained from an outbreak of nosocomial Klebsiella pneumoniae infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Apr;15(4):616–624. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.4.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C. Novel resistance selected by the new expanded-spectrum cephalosporins: a concern. J Infect Dis. 1983 Mar;147(3):585–589. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.3.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins L. S., Plorde J. J., Falkow S. Molecular analysis of R-factors from multiresistant nosocomial isolates. J Infect Dis. 1980 May;141(5):625–636. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.5.625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]