Abstract
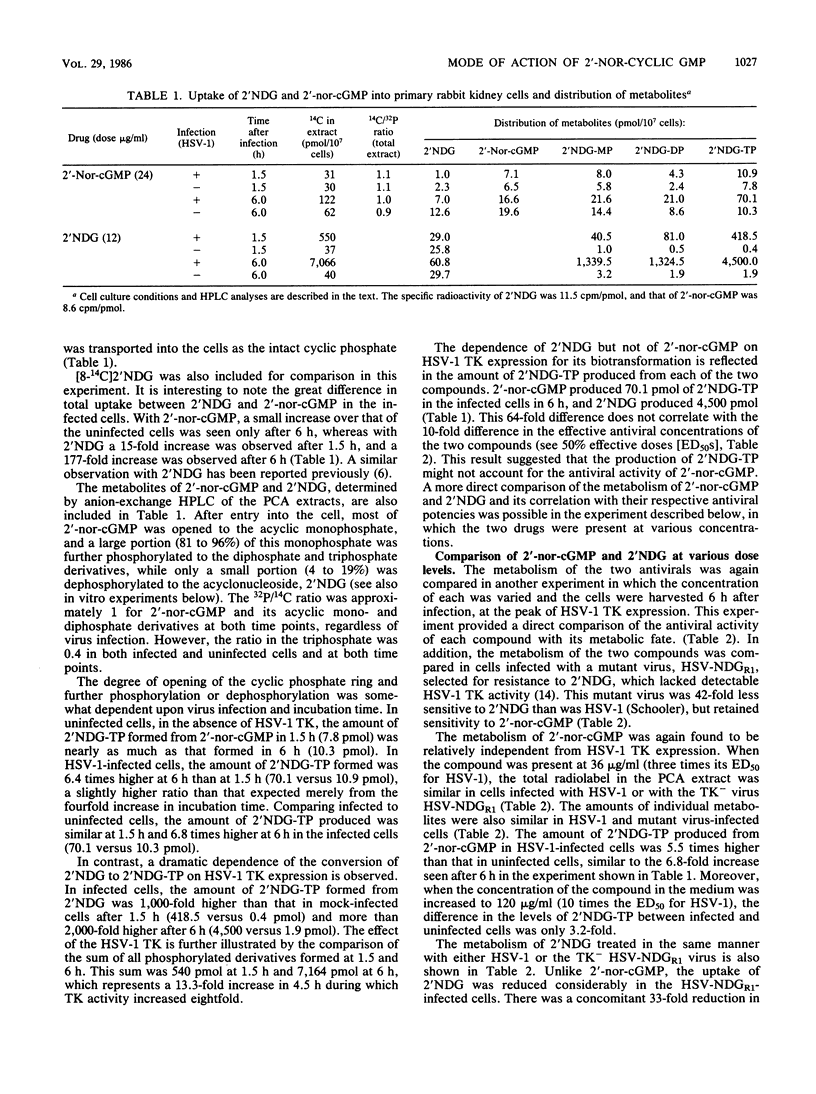
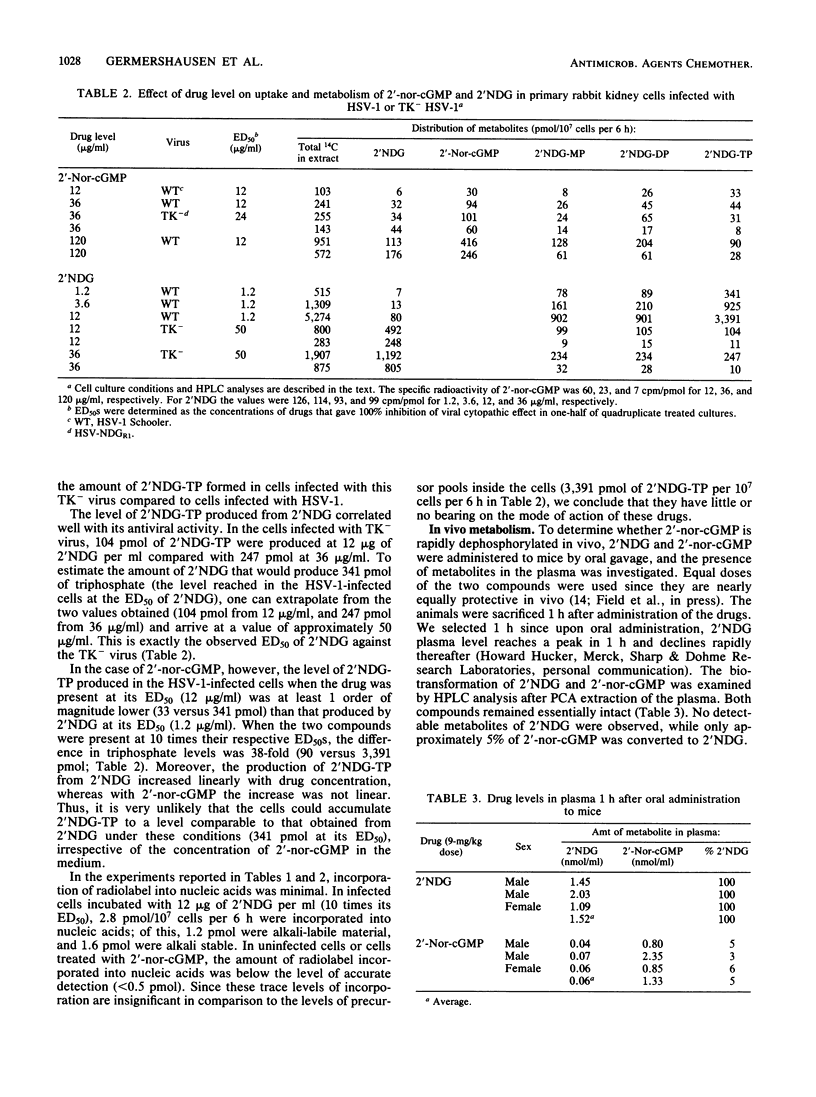
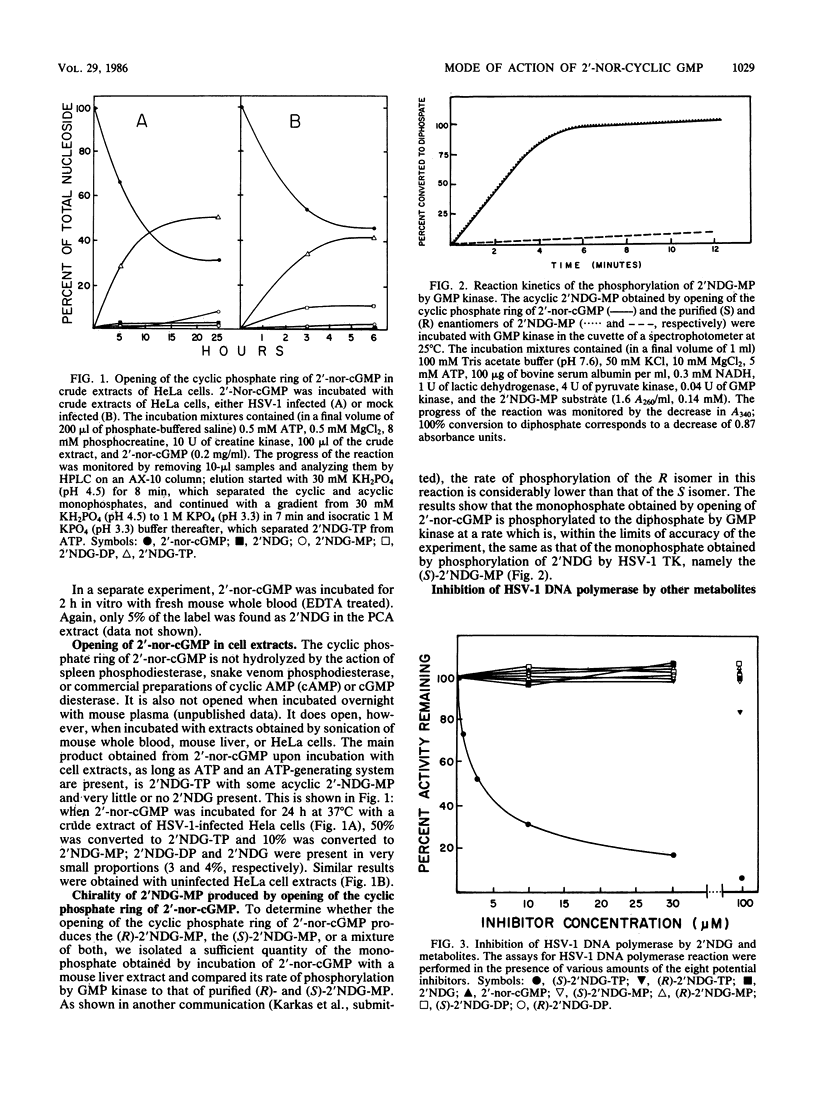
The metabolisms of 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine (2'NDG) and its cyclic phosphate, 9-[(2-hydroxy-1,3,2-dioxophosphorinan-5-yl) oxymethyl]guanine P-oxide (2'-nor-cGMP), were compared in cultures of primary rabbit kidney cells infected with herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1). 2'-Nor-cGMP was taken up by the cells essentially intact, after which it was opened to the acyclic monophosphate and phosphorylated further, ultimately to the triphosphate. Formation of the triphosphate was independent of HSV thymidine kinase expression, unlike what is observed with 2'NDG. In addition, there was a direct correlation between the antiviral activity of 2'NDG and the level of triphosphate formed in HSV-1-infected cells, whereas such a correlation was absent with 2'-nor-cGMP. In vivo experiments indicated that only a small percentage of free 2'NDG was formed in the bloodstream of mice after oral administration of 2'-nor-cGMP. Incubation of 2'-nor-cGMP with crude extracts of HSV-1-infected or uninfected HeLa cells resulted in the direct production of 2'NDG triphosphate. The possibility that the triphosphate of 2'NDG produced from 2'-nor-cGMP was the enantiomer of the triphosphate made from 2'NDG by viral and cellular kinases was investigated and disproved. Taken together, these data indicate that (i) 2'-nor-cGMP does not act simply as a prodrug of 2'NDG, (ii) 2'-nor-cGMP does not require viral thymidine kinase for its activity, and (iii) 2'-nor-cGMP may have an additional, triphosphate-independent mode of action.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashton W. T., Canning L. F., Reynolds G. F., Tolman R. L., Karkas J. D., Liou R., Davies M. E., DeWitt C. M., Perry H. C., Field A. K. Synthesis and antiherpetic activity of (S)-, (R)-, and (+/-)-9-[(2,3-dihydroxy-1-propoxy)methyl]guanine, linear isomers of 2'-nor-2'-deoxyguanosine. J Med Chem. 1985 Jul;28(7):926–933. doi: 10.1021/jm00145a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton W. T., Karkas J. D., Field A. K., Tolman R. L. Activation by thymidine kinase and potent antiherpetic activity of 2'-nor-2'-deoxyguanosine (2'NDG). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Oct 29;108(4):1716–1721. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(82)80109-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. C., Ostrander M. Deoxythymidine kinase induced in HeLa TK- cells by herpes simplex virus type I and type II. II. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 10;251(9):2605–2610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion G. B., Furman P. A., Fyfe J. A., de Miranda P., Beauchamp L., Schaeffer H. J. Selectivity of action of an antiherpetic agent, 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl) guanine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5716–5720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field A. K., Davies M. E., DeWitt C., Perry H. C., Liou R., Germershausen J., Karkas J. D., Ashton W. T., Johnston D. B., Tolman R. L. 9-([2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethoxy]methyl)guanine: a selective inhibitor of herpes group virus replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4139–4143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germershausen J., Bostedor R., Field A. K., Perry H., Liou R., Bull H., Tolman R. L., Karkas J. D. A comparison of the antiviral agents 2'-nor-2'-deoxyguanosine and acyclovir: uptake and phosphorylation in tissue culture and kinetics of in vitro inhibition of viral and cellular DNA polymerases by their respective triphosphates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Oct 31;116(2):360–367. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90530-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. C., Dvorak C. A., Smee D. F., Matthews T. R., Verheyden J. P. 9-[(1,3-Dihydroxy-2-propoxy)methyl]guanine: a new potent and selective antiherpes agent. J Med Chem. 1983 May;26(5):759–761. doi: 10.1021/jm00359a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. L., Adamczyk D. L., Spector T. Reassessment of the interactions of guanylate kinase and 6-thioguanosine 5'-phosphate. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Sep 1;26(17):1573–1576. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver S., Bubley G., Crumpacker C. Inhibition of HSV-transformed murine cells by nucleoside analogs, 2'-NDG and 2'-nor-cGMP: mechanisms of inhibition and reversal by exogenous nucleosides. Virology. 1985 Aug;145(1):84–93. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90203-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer H. J., Beauchamp L., de Miranda P., Elion G. B., Bauer D. J., Collins P. 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl) guanine activity against viruses of the herpes group. Nature. 1978 Apr 13;272(5654):583–585. doi: 10.1038/272583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smee D. F., Martin J. C., Verheyden J. P., Matthews T. R. Anti-herpesvirus activity of the acyclic nucleoside 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 May;23(5):676–682. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.5.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. O., Galloway K. S., Kennell W. L., Ogilvie K. K., Radatus B. K. A new nucleoside analog, 9-[[2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethoxyl]methyl]guanine, highly active in vitro against herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jul;22(1):55–61. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair M. H., Miller W. H., Miller R. L., Lambe C. U., Furman P. A. Inhibition of cellular alpha DNA polymerase and herpes simplex virus-induced DNA polymerases by the triphosphate of BW759U. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Feb;25(2):191–194. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.2.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolman R. L., Field A. K., Karkas J. D., Wagner A. F., Germershausen J., Crumpacker C., Scolnick E. M. 2'-Nor-cGMP: a seco-cyclic nucleotide with powerful anti-DNA-viral activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 May 16;128(3):1329–1335. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91086-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach A., Hong S. C., Aucker J., Muller R. Characterization of herpes simplex virus-induced deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6270–6277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



