Abstract
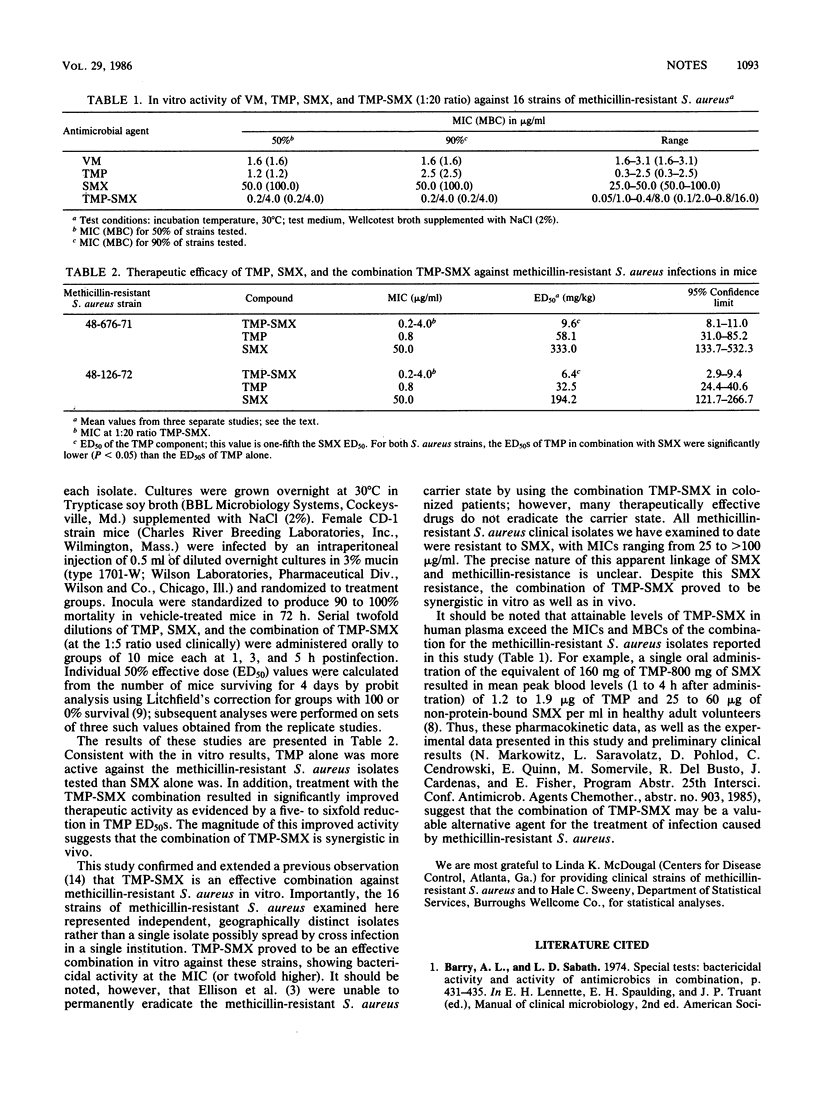
The in vitro susceptibilities of 16 independent, geographically distinct clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus to trimethoprim (TMP) in combination with sulfamethoxazole (SMX) were evaluated. Although methicillin-resistant S. aureus strains appear to be universally resistant to SMX, the combination TMP-SMX was found to be synergistic in vitro (in combination, the MICs of both drugs decreased 6- to 25-fold) as well as in vivo (5- to 6-fold reduction in TMP at 50% effective doses).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bengtsson E., Svanbom M., Tunevall G. Trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole treatment in staphylococcal endocarditis and gram-negative septicemia. Scand J Infect Dis. 1974;6(2):177–182. doi: 10.3109/inf.1974.6.issue-2.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison R. T., 3rd, Judson F. N., Peterson L. C., Cohn D. L., Ehret J. M. Oral rifampin and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole therapy in asymptomatic carriers of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. West J Med. 1984 May;140(5):735–740. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farid Z., Girgis N. I., Yassin W. Letter: Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and bacterial meningitis. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Jan;84(1):50–51. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-84-1-50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foldes M., Munro R., Sorrell T. C., Shanker S., Toohey M. In-vitro effects of vancomycin, rifampicin, and fusidic acid, alone and in combination, against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Jan;11(1):21–26. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopal V., Bisno A. L., Silverblatt F. J. Failure of vancomycin treatment in Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. In vivo and in vitro observations. JAMA. 1976 Oct 4;236(14):1604–1606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr Antimicrobial synergism--an elusive concept. J Infect Dis. 1979 Oct;140(4):639–641. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.4.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabel K. G., Brandberg A. Treatment of meningitis and septicemia in infancy with a sulphamethoxazole/trimethorpim combination. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1975 Jan;64(1):25–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1975.tb04376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefler S., Jones D., Perry W., Ruvinskaya L., Baradet T., Mayr E., Wilson M. E. Emergence of gentamicin- and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains in New York City hospitals. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Apr;13(4):754–759. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.4.754-759.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamer M. A., Bray J. D. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole treatment of multiantibiotic-resistant staphylococcal endocarditis and meningitis. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1982 Feb;21(2):125–126. doi: 10.1177/000992288202100211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel R. P. The emergence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Sep;97(3):440–442. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-3-440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


