Abstract
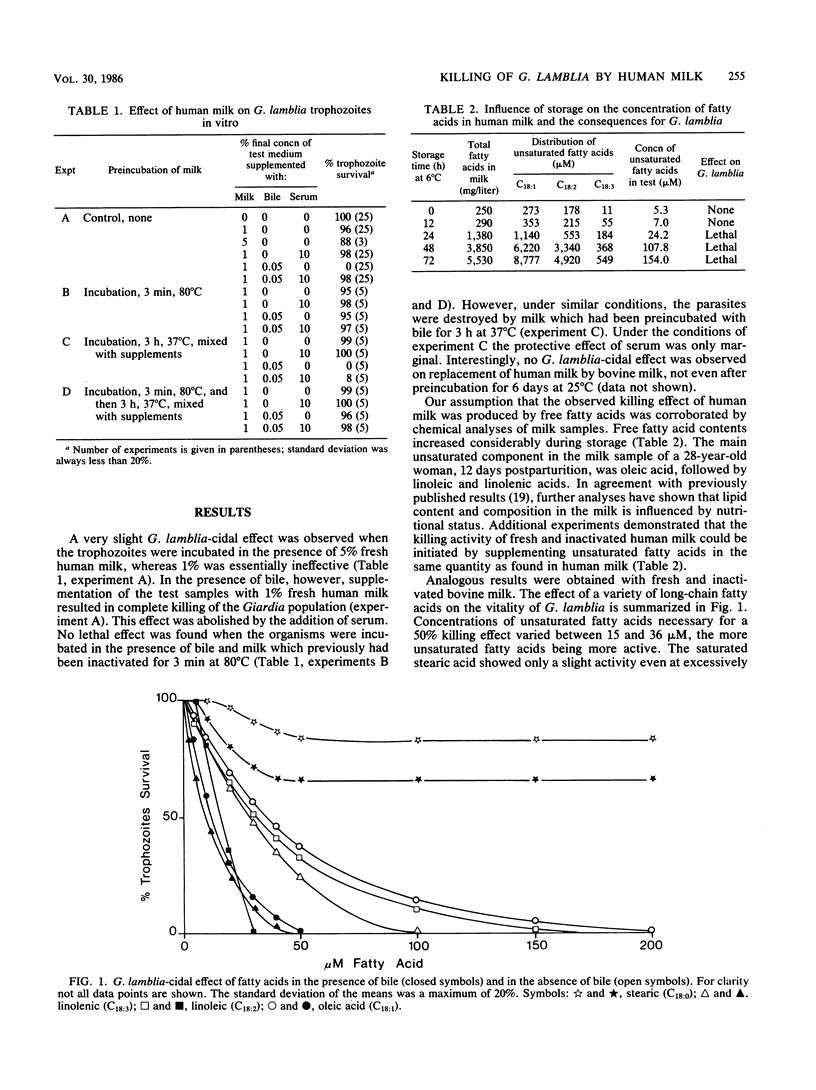
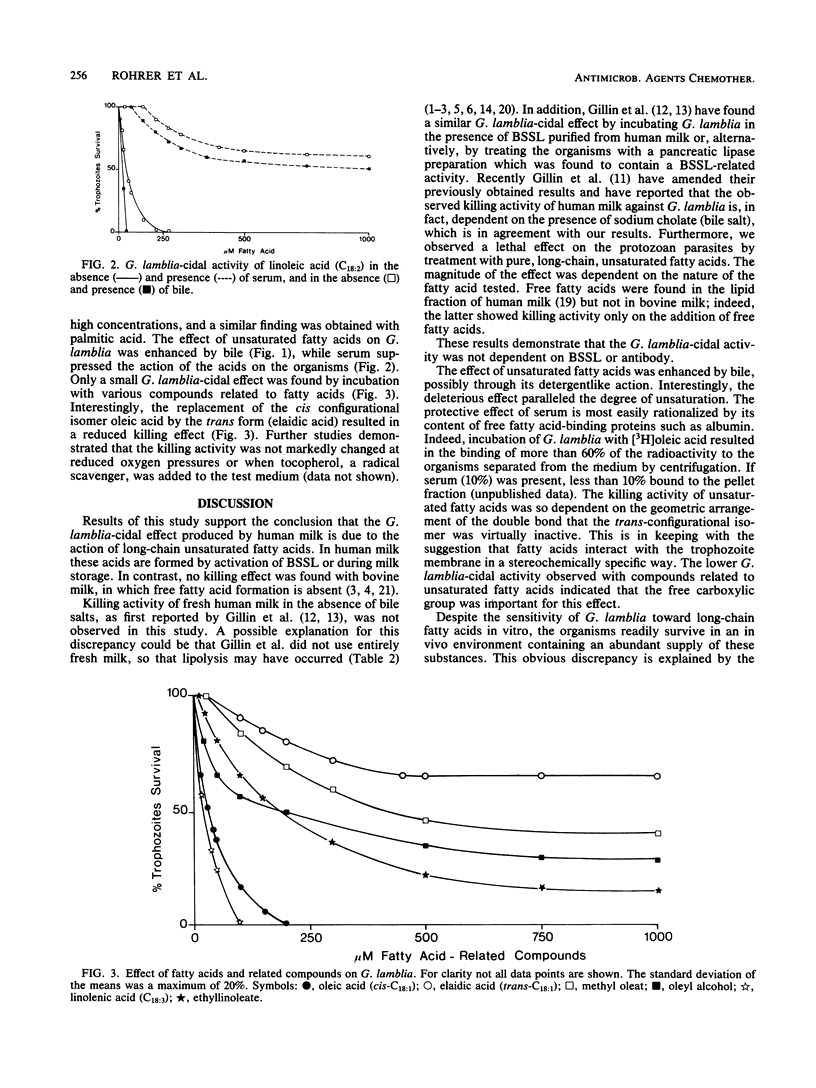
Giardia lamblia trophozoites were killed in vitro by 1% fresh human milk in the presence of bile. A similar effect was achieved in the absence of bile with milk which had been stored for at least 24 h at 6 degrees C. This killing activity was found to be caused by unsaturated fatty acids. Depending on their chain length and the number of double bonds, the concentrations of unsaturated fatty acids required for a 50% killing effect varied between 15 and 36 microM. The saturated palmitic and stearic acids, as well as various substances related to fatty acids, showed only a slight killing effect. Bile enhanced and serum suppressed the action of fatty acids on the protozoan parasite. The possible site of interference of unsaturated fatty acids within G. lamblia and the reasons for the obvious inefficacy of dietary fatty acids in giardiasis are discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berkow S. E., Freed L. M., Hamosh M., Bitman J., Wood D. L., Happ B., Hamosh P. Lipases and lipids in human milk: effect of freeze-thawing and storage. Pediatr Res. 1984 Dec;18(12):1257–1262. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198412000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitman J., Wood D. L., Mehta N. R., Hamosh P., Hamosh M. Lipolysis of triglycerides of human milk during storage at low temperatures: a note of caution. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1983;2(3):521–524. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198302030-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bläckberg L., Lombardo D., Hernell O., Guy O., Olivecrona T. Bile salt-stimulated lipase in human milk and carboxyl ester hydrolase in pancreatic juice: are they identical enzymes? FEBS Lett. 1981 Dec 28;136(2):284–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80636-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. M., Hundrieser K. H., Ross S., Brown P. B. Effect of temperature and length of storage on serum-stimulated and serum-independent lipolytic activities in human milk. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1984 Sep;3(4):567–570. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198409000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danciger M., Lopez M. Numbers of Giardia in the feces of infected children. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1975 Mar;24(2):237–242. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1975.24.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S., Harlow D. R., Cunnick C. C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(4):431–432. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillin F. D., Reiner D. S., Gault M. J. Cholate-dependent killing of Giardia lamblia by human milk. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):619–622. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.619-622.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillin F. D., Reiner D. S., Wang C. S. Human milk kills parasitic intestinal protozoa. Science. 1983 Sep 23;221(4617):1290–1292. doi: 10.1126/science.6310751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillin F. D., Reiner D. S., Wang C. S. Killing of Giardia lamblia trophozoites by normal human milk. J Cell Biochem. 1983;23(1-4):47–56. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240230106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamosh M., Berkow S., Bitman J., Freed L., Happ B., Jones J. B., Mehta N. R., Wood D. L., Hamosh P. Handling and storage of human milk specimens for research. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1984 Mar;3(2):284–289. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198403000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabara J. J. Lipids as host-resistance factors of human milk. Nutr Rev. 1980 Feb;38(2):65–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.1980.tb05843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabara J. J., Vrable R. Antimicrobial lipids: natural and synthetic fatty acids and monoglycerides. Lipids. 1977 Sep;12(9):753–759. doi: 10.1007/BF02570908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keister D. B. Axenic culture of Giardia lamblia in TYI-S-33 medium supplemented with bile. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1983;77(4):487–488. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(83)90120-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammi-Keefe C. J., Jensen R. G. Lipids in human milk: a review. 2: Composition and fat-soluble vitamins. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1984 Mar;3(2):172–198. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198403000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta N. R., Jones J. B., Hamosh M. Lipases in preterm human milk: ontogeny and physiologic significance. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1982;1(3):317–326. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198201030-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. D., Horsburgh C. R., Jr, Brown W. R. In vitro studies on bile acid deconjugation and lipolysis inhibition by Giardia lamblia. Dig Dis Sci. 1981 Aug;26(8):700–704. doi: 10.1007/BF01316858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



