Abstract
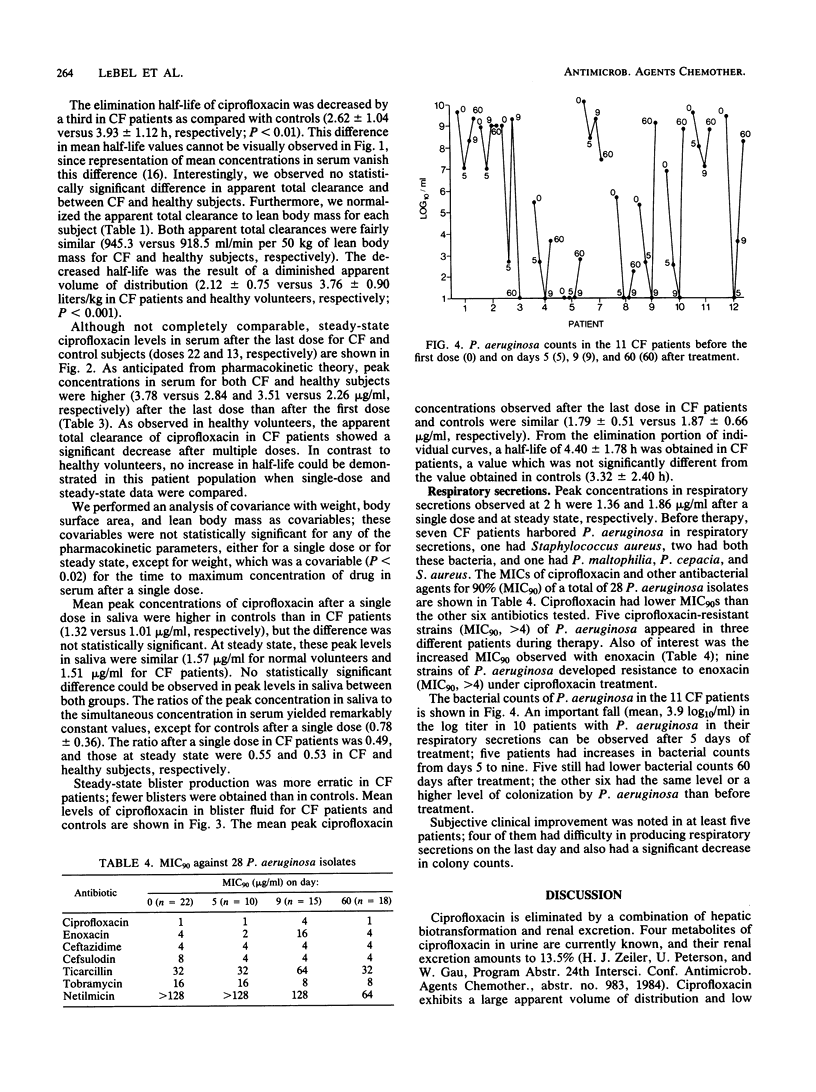
The pharmacokinetics and blister fluid penetration of oral ciprofloxacin were compared in 11 cystic fibrosis (CF) patients who had sputum colonization but were asymptomatic and in 12 healthy volunteers after a single dose (500 mg) and at steady state (500 mg every 8 h). The antibacterial effect of ciprofloxacin therapy was also evaluated by bacterial counts of colonizing pathogens in the respiratory secretions of CF patients. The CF patients were 15.9% lighter in weight than the controls (P less than 0.05). After a single dose, the elimination half-life of ciprofloxacin was decreased by a third in the CF patients as compared with the controls (2.62 versus 3.93 h, respectively; P less than 0.01). This was the result of a diminished apparent volume of distribution in CF subjects. Interestingly, we observed no statistically significant difference in total apparent and renal clearances between the groups. Suction-induced blister fluid penetration was not different between CF patients and healthy volunteers. In CF patients, ciprofloxacin exhibited levels in respiratory secretions above the reported MIC for Pseudomonas aeruginosa: 1.36 and 1.86 micrograms/ml at 2 h after a single dose and at steady state, respectively. An important fall (mean, 3.9 log10/ml) in the log titer in 10 patients with P. aeruginosa in their respiratory secretions was observed after 5 days of treatment. However, this improvement was short-lived; the secondary increase in bacterial counts observed in five patients and the development of five resistant strains were causes for concern. The pharmacokinetic results presented here showed that ciprofloxacin should be administered every 8 or even every 6 h in CF patients.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davis R. L., Koup J. R., Williams-Warren J., Weber A., Smith A. L. Pharmacokinetics of three oral formulations of ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jul;28(1):74–77. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.1.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliopoulos G. M., Gardella A., Moellering R. C., Jr In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin, a new carboxyquinoline antimicrobial agent. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):331–335. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb J., Wormser G. P., Inchiosa M. A., Jr, Guideri G., Diaz M., Gandhi R., Goltzman C., Mascia A. V. Single-dose pharmacokinetics of oral ciprofloxacin in patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Pharmacol. 1986 Mar;26(3):222–226. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1986.tb02938.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison C. J., Marks M. I., Welch D. F., Sharma B. B., Baker D., Dice J. A multicenter comparison of related pharmacologic features of cephalexin and dicloxacillin given for two months to young children with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pharmacol (New York) 1985;5(1):7–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höffken G., Lode H., Prinzing C., Borner K., Koeppe P. Pharmacokinetics of ciprofloxacin after oral and parenteral administration. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Mar;27(3):375–379. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.3.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höffler D., Dalhoff A., Gau W., Beermann D., Michl A. Dose- and sex-independent disposition of ciprofloxacin. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;3(4):363–366. doi: 10.1007/BF01977496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isles A., Spino M., Tabachnik E., Levison H., Thiessen J., MacLeod S. Theophylline disposition in cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Apr;127(4):417–421. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.4.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jusko W. J., Mosovich L. L., Gerbracht L. M., Mattar M. E., Yaffe S. J. Enhanced renal excretion of dicloxacillin in patients with cystic fibrosis. Pediatrics. 1975 Dec;56(6):1038–1044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen G. L., Barron R. J., Landay R. A., Cotton E. K., Gonzalez M. A., Brooks J. G. Intravenous aminophylline in patients with cystic fibrosis. Pharmacokinetics and effect on pulmonary function. Am J Dis Child. 1980 Dec;134(12):1143–1148. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1980.02130240027009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBel M., Vallée F., Bergeron M. G. Tissue penetration of ciprofloxacin after single and multiple doses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Mar;29(3):501–505. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.3.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeder J. S., Spino M., Isles A. F., Tesoro A. M., Gold R., MacLeod S. M. Ceftazidime disposition in acute and stable cystic fibrosis. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1984 Sep;36(3):355–362. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1984.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin E., Moll W., Schmid P., Dettli L. Problems and pitfalls in estimating average pharmacokinetic parameters. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1984;26(5):595–602. doi: 10.1007/BF00543492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahata M. C., Lubin A. H., Visconti J. A. Cephalexin pharmacokinetics in patients with cystic fibrosis. Dev Pharmacol Ther. 1984;7(4):221–228. doi: 10.1159/000457168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. D. Management of acute pulmonary exacerbations in cystic fibrosis: a critical appraisal. J Pediatr. 1985 Jun;106(6):1030–1034. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80264-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrier D., Mayersohn M. Noncompartmental determination of the steady-state volume of distribution for any mode of administration. J Pharm Sci. 1982 Mar;71(3):372–373. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600710332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed M. D., Stern R. C., Bertino J. S., Jr, Myers C. M., Yamashita T. S., Blumer J. L. Dosing implications of rapid elimination of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in patients with cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr. 1984 Feb;104(2):303–307. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)81019-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy C., Foz A., Segura C., Tirado M., Teixell M., Teruel D. Activity of ciprofloxacin (BAYo 9867) against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and ampicillin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Infection. 1983 Nov-Dec;11(6):326–328. doi: 10.1007/BF01641358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHWACHMAN H., KULCZYCKI L. L. Long-term study of one hundred five patients with cystic fibrosis; studies made over a five- to fourteen-year period. AMA J Dis Child. 1958 Jul;96(1):6–15. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1958.02060060008002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith I. L., Schentag J. J. Noncompartmental determination of the steady-state volume of distribution during multiple dosing. J Pharm Sci. 1984 Feb;73(2):281–282. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600730239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spino M., Chai R. P., Isles A. F., Thiessen J. J., Tesoro A., Gold R., MacLeod S. M. Cloxacillin absorption and disposition in cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr. 1984 Nov;105(5):829–835. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80317-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallée F., LeBel M., Bergeron M. G. Determination of ciprofloxacin in biological samples by reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography. Ther Drug Monit. 1986;8(3):340–345. doi: 10.1097/00007691-198609000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingender W., Graefe K. H., Gau W., Förster D., Beermann D., Schacht P. Pharmacokinetics of ciprofloxacin after oral and intravenous administration in healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;3(4):355–359. doi: 10.1007/BF01977494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Lockley R. M., Webberly M., Dent J. Pharmacokinetics of intravenously administered ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):208–210. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


