Abstract
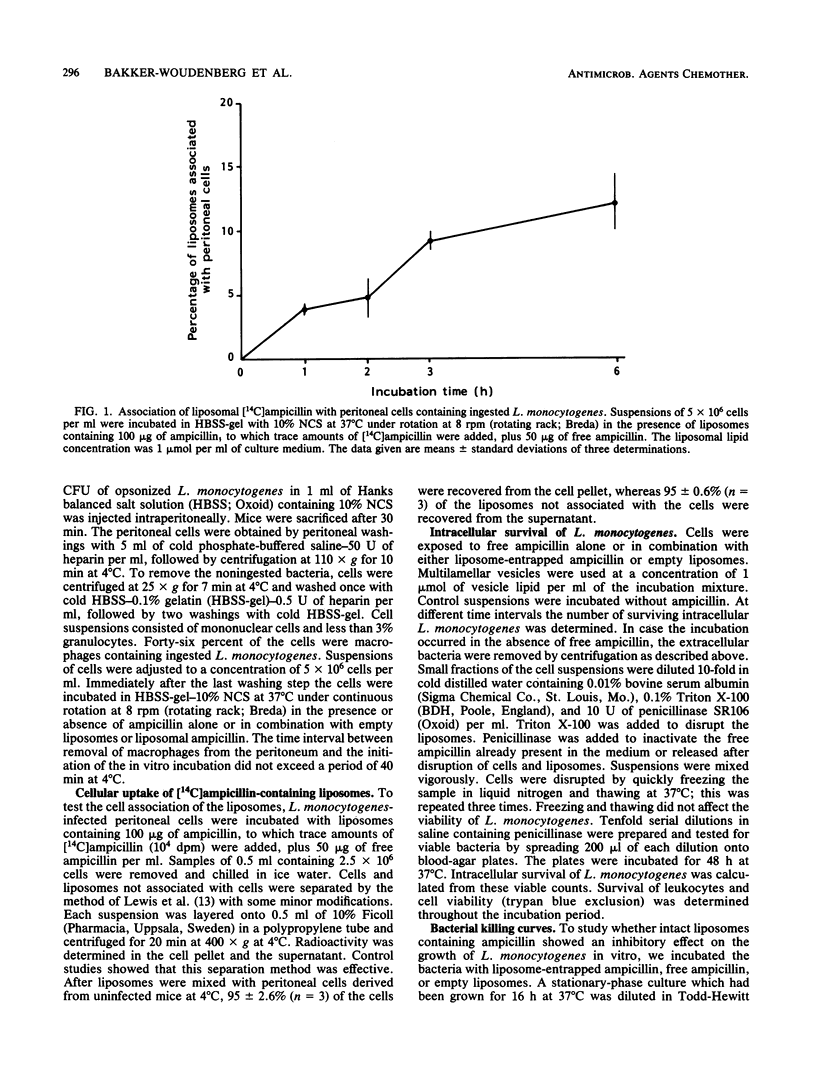
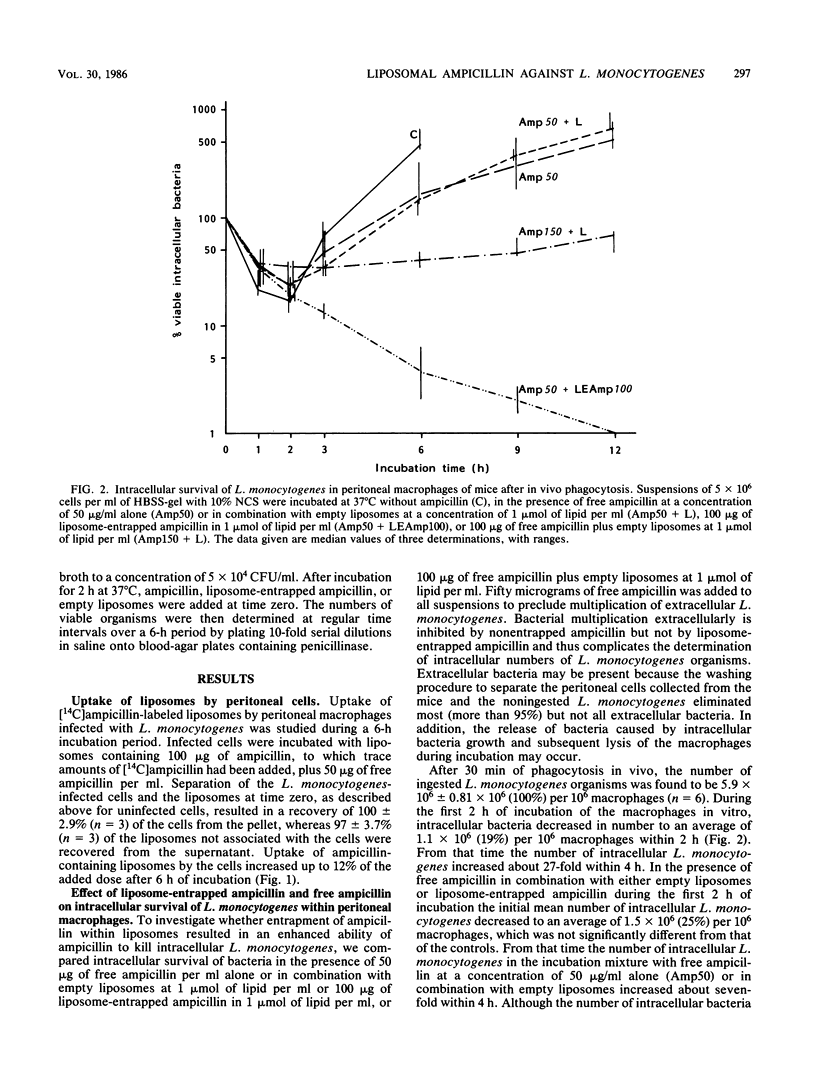
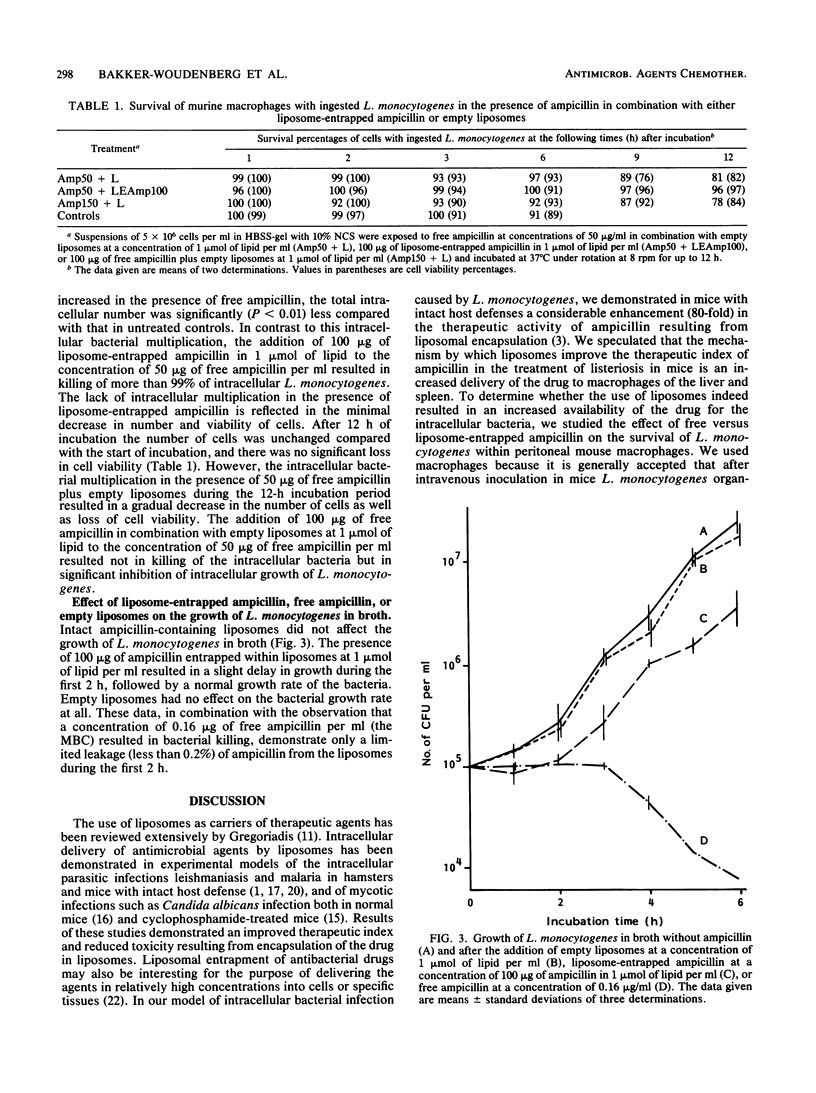
The effect of liposomal encapsulation of ampicillin on the antibacterial activity against intracellular Listeria monocytogenes was studied by comparing survival of L. monocytogenes within peritoneal mouse macrophages in the presence of free ampicillin alone or in combination with liposome-entrapped ampicillin. In the presence of 50 micrograms of free ampicillin per ml of the incubation medium, intracellular growth of L. monocytogenes was still observed, although less as compared with intracellular growth in the absence of ampicillin. At a concentration of 50 micrograms of free ampicillin plus 100 micrograms of liposome-entrapped ampicillin per ml, 99% of the intracellular bacteria were killed. On the other hand, a concentration of 150 micrograms of free ampicillin per ml plus empty liposomes only inhibited intracellular bacterial growth, and the bacteria were not killed. In addition, empty liposomes at a concentration of 1 mumol of lipid per ml had no effect on intracellular bacterial growth. In broth, liposome-entrapped ampicillin at a concentration of 100 micrograms/ml was not bactericidal for L. monocytogenes, indicating that significant leakage of ampicillin from the liposomes with subsequent killing of the bacteria by the free drug did not occur. Therefore, we concluded that liposomal encapsulation of ampicillin results in an increased availability of the antibiotic for the intracellular bacteria.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alving C. R., Steck E. A., Chapman W. L., Jr, Waits V. B., Hendricks L. D., Swartz G. M., Jr, Hanson W. L. Therapy of leishmaniasis: superior efficacies of liposome-encapsulated drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2959–2963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker-Woudenberg I. A., Lokerse A. F., Roerdink F. H., Regts D., Michel M. F. Free versus liposome-entrapped ampicillin in treatment of infection due to Listeria monocytogenes in normal and athymic (nude) mice. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):917–924. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker-Woudenberg I. A., de Bos P., van Leeuwen W. B., Michel M. F. Efficacy of ampicillin therapy in experimental listeriosis in mice with impaired T-cell-mediated immune response. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jan;19(1):76–81. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.1.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre P. F., Gregoriandis G. Killing of intraphagocytic Staphylococcus aureus by dihydrostreptomycin entrapped within liposomes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jun;13(6):1049–1051. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.6.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. N., Percival A. Penetration of antimicrobials into tissue culture cells and leucocytes. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1978;(14):251–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury M. K., Goswami R., Chakrabarti P. Liposome-trapped penicillins in growth inhibition of some penicillin-resistant bacteria. J Appl Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;51(2):223–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1981.tb01236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desiderio J. V., Campbell S. G. Intraphagocytic killing of Salmonella typhimurium by liposome-encapsulated cephalothin. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):563–570. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra J., van Galen M., Regts D., Scherphof G. Uptake and processing of liposomal phospholipids by Kupffer cells in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Apr 15;148(2):391–397. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08851.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra J., van Galen W. J., Hulstaert C. E., Kalicharan D., Roerdink F. H., Scherphof G. L. Interaction of liposomes with Kupffer cells in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Jan;150(1):161–176. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90711-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. T., Hafeman D. G., McConnell H. M. Kinetics of antibody-dependent binding of haptenated phospholipid vesicles to a macrophage-related cell line. Biochemistry. 1980 Nov 11;19(23):5376–5386. doi: 10.1021/bi00564a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo M. C., Mandell G. L. The effect of antibiotics on Escherichia coli ingested by macrophages. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Mar;142(3):1048–1050. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-37173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Berestein G., Hopfer R. L., Mehta R., Mehta K., Hersh E. M., Juliano R. L. Liposome-encapsulated amphotericin B for treatment of disseminated candidiasis in neutropenic mice. J Infect Dis. 1984 Aug;150(2):278–283. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.2.278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Berestein G., Mehta R., Hopfer R. L., Mills K., Kasi L., Mehta K., Fainstein V., Luna M., Hersh E. M., Juliano R. Treatment and prophylaxis of disseminated infection due to Candida albicans in mice with liposome-encapsulated amphotericin B. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):939–945. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- New R. R., Chance M. L. Treatment of experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis by liposome-entrapped Pentostam. Acta Trop. 1980 Sep;37(3):253–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieman R. E., Lorber B. Listeriosis in adults: a changing pattern. Report of eight cases and review of the literature, 1968-1978. Rev Infect Dis. 1980 Mar-Apr;2(2):207–227. doi: 10.1093/clinids/2.2.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirson P., Steiger R. F., Trouet A., Gillet J., Herman F. Primaquine liposomes in the chemotherapy of experimental murine malaria. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1980 Aug;74(4):383–391. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1980.11687359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raz A., Bucana C., Fogler W. E., Poste G., Fidler I. J. Biochemical, morphological, and ultrastructural studies on the uptake of liposomes by murine macrophages. Cancer Res. 1981 Feb;41(2):487–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson V. J. Liposomes in antimicrobial chemotherapy. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Dec;12(6):532–534. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.6.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roerdink F. H., Dijkstra J., Spanjer H. H., Scherphof G. L. Interaction of liposomes with hepatocytes and Kupffer cells in vivo and in vitro. Biochem Soc Trans. 1984 Apr;12(2):335–336. doi: 10.1042/bst0120335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roerdink F., Wassef N. M., Richardson E. C., Alving C. R. Effects of negatively charged lipids on phagocytosis of liposomes opsonized by complement. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 21;734(1):33–39. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90071-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M., Baillie A. J., Richards R. M. Enhanced activity of streptomycin and chloramphenicol against intracellular Escherichia coli in the J774 macrophage cell line mediated by liposome delivery. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Nov;24(5):742–749. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.5.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dissel J. T., Leijh P. C., van Furth R. Differences in initial rate of intracellular killing of Salmonella typhimurium by resident peritoneal macrophages from various mouse strains. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3404–3410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


