Abstract
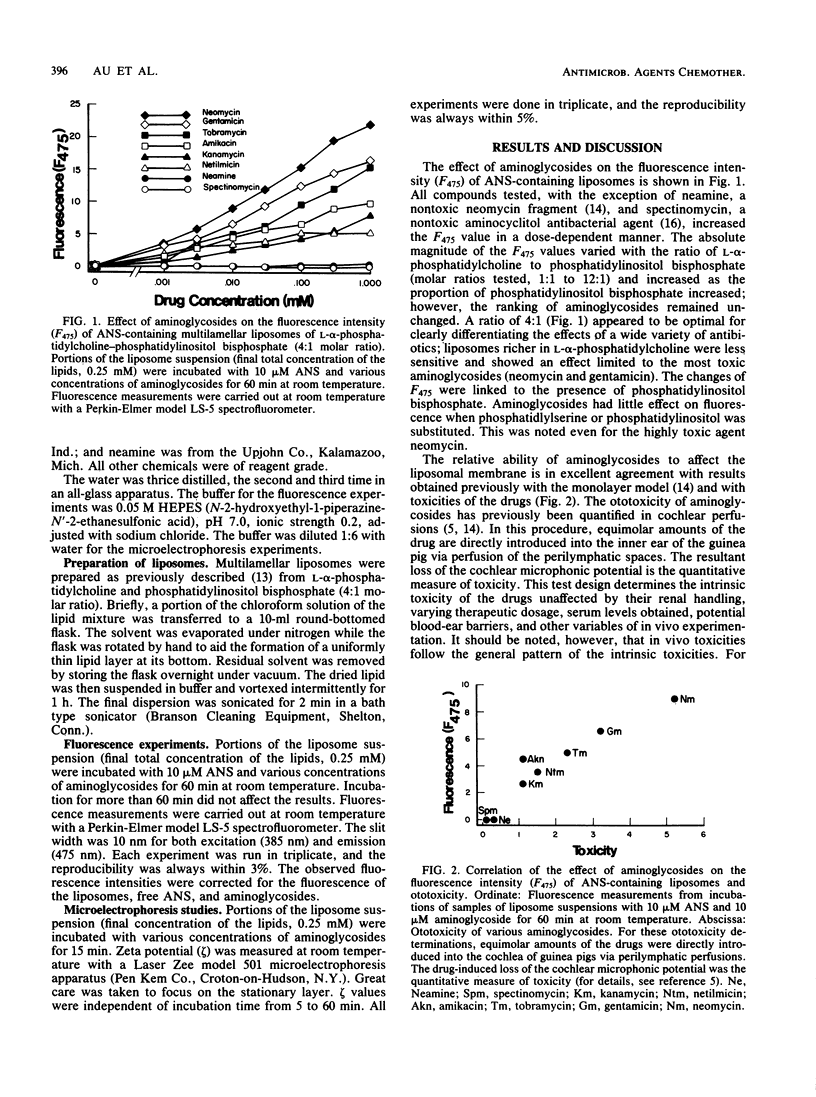
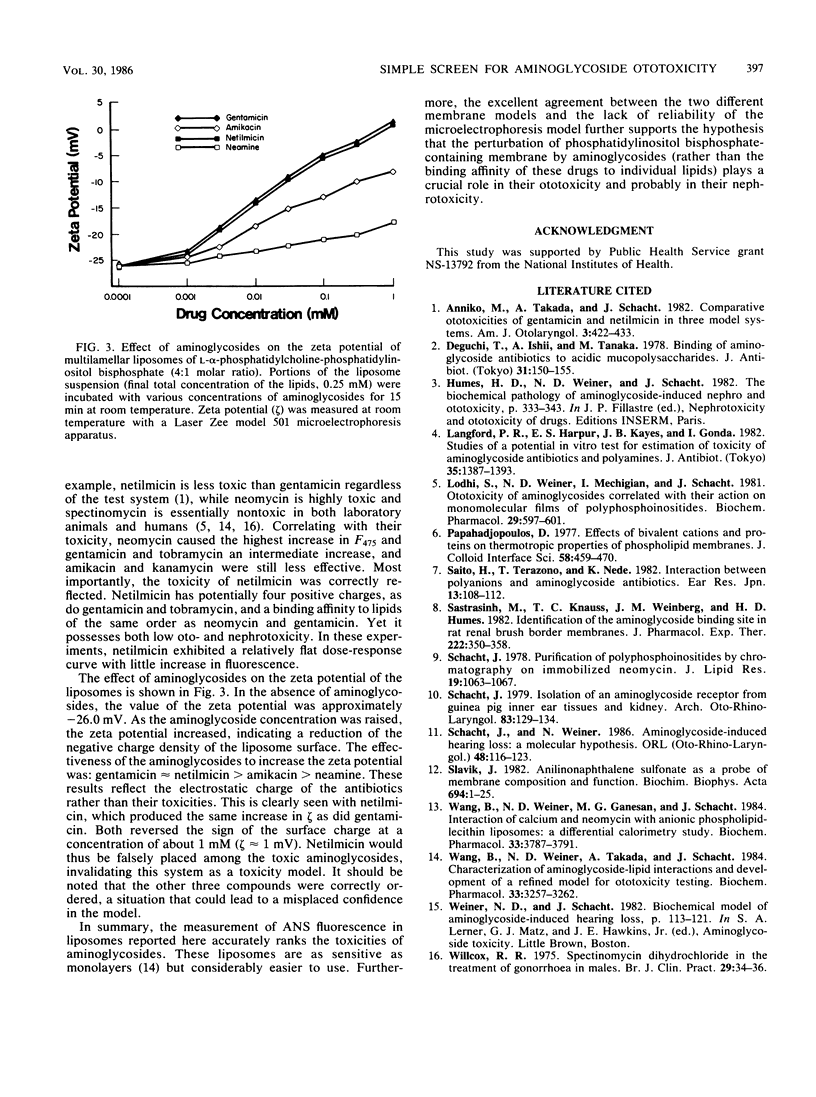
A simple test to assess the toxicity of aminoglycosides was designed based on the interaction of these drugs with phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate. The fluorescent probe 1-anilino-8-naphthalene sulfonate was incorporated into liposomes composed of L-alpha-phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate (4:1 molar ratio), and changes in fluorescence induced by the aminoglycosides were measured. The magnitude of these changes correlated well with the intrinsic ototoxicity of the drugs previously established in cochlear perfusions: neomycin greater than gentamicin approximately equal to tobramycin greater than amikacin approximately equal to kanamycin approximately equal to netilmicin greater than neamine approximately equal to spectinomycin. Correlations were not accurate when other phospholipids were substituted for phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate. An alternative in vitro test, measurement of the zeta potential of liposomes, ranked the drugs according to their electrostatic charge but not their toxicity. These results suggest that: a simple screen for aminoglycoside toxicity can be established and perturbation of membranes containing phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate is a key step in aminoglycoside ototoxicity.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anniko M., Takada A., Schacht J. Comparative ototoxicities of gentamicin and netilmicin in three model systems. Am J Otolaryngol. 1982 Nov-Dec;3(6):422–433. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0709(82)80020-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deguchi T., Ishi A., Tanaka M. Binding of aminoglycoside antibiotics to acidic mucopolysaccharides. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1978 Feb;31(2):150–155. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.31.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford P. R., Harpur E. S., Kayes J. B., Gonda I. Studies of a potential in vitro test for estimation of toxicity of aminoglycoside antibiotics and polyamines. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1982 Oct;35(10):1387–1393. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.35.1387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodhi S., Weiner N. D., Mechigian I., Schacht J. Ototoxicity of aminoglycosides correlated with their action on monomolecular films of polyphosphoinositides. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Feb 15;29(4):597–601. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90382-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastrasinh M., Knauss T. C., Weinberg J. M., Humes H. D. Identification of the aminoglycoside binding site in rat renal brush border membranes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Aug;222(2):350–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacht J. Isolation of an aminoglycoside receptor from guinea pig inner ear tissues and kidney. Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1979;224(1-2):129–134. doi: 10.1007/BF00455236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacht J. Purification of polyphosphoinositides by chromatography on immobilized neomycin. J Lipid Res. 1978 Nov;19(8):1063–1067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacht J., Weiner N. Aminoglycoside-induced hearing loss: a molecular hypothesis. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 1986;48(2):116–123. doi: 10.1159/000275856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slavík J. Anilinonaphthalene sulfonate as a probe of membrane composition and function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Aug 11;694(1):1–25. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(82)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B. M., Weiner N. D., Ganesan M. G., Schacht J. Interaction of calcium and neomycin with anionic phospholipid-lecithin liposomes. A differential scanning calorimetry study. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Dec 1;33(23):3787–3791. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B. M., Weiner N. D., Takada A., Schacht J. Characterization of aminoglycoside-lipid interactions and development of a refined model for ototoxicity testing. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Oct 15;33(20):3257–3262. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90087-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willcox R. R. Spectinomycin dihydrochloride in the treatment of gonorrhoea in males. Br J Clin Pract. 1975 Feb;29(2):34–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


