Abstract
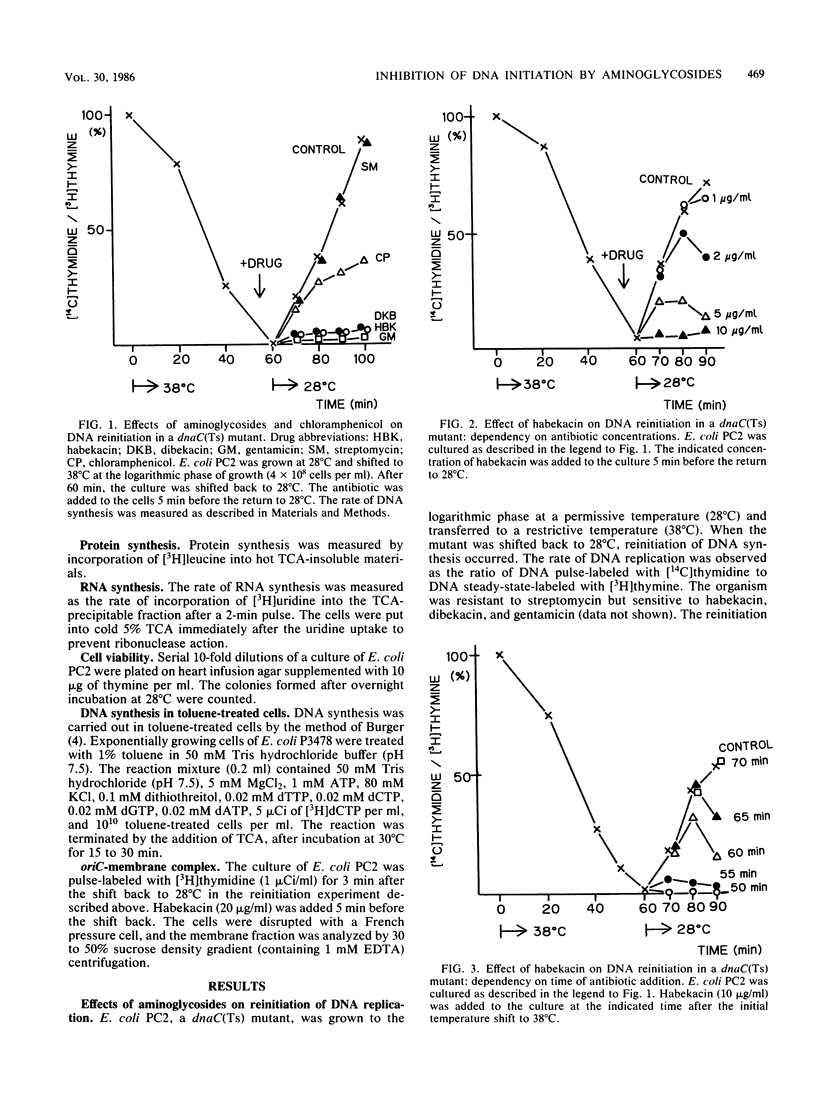
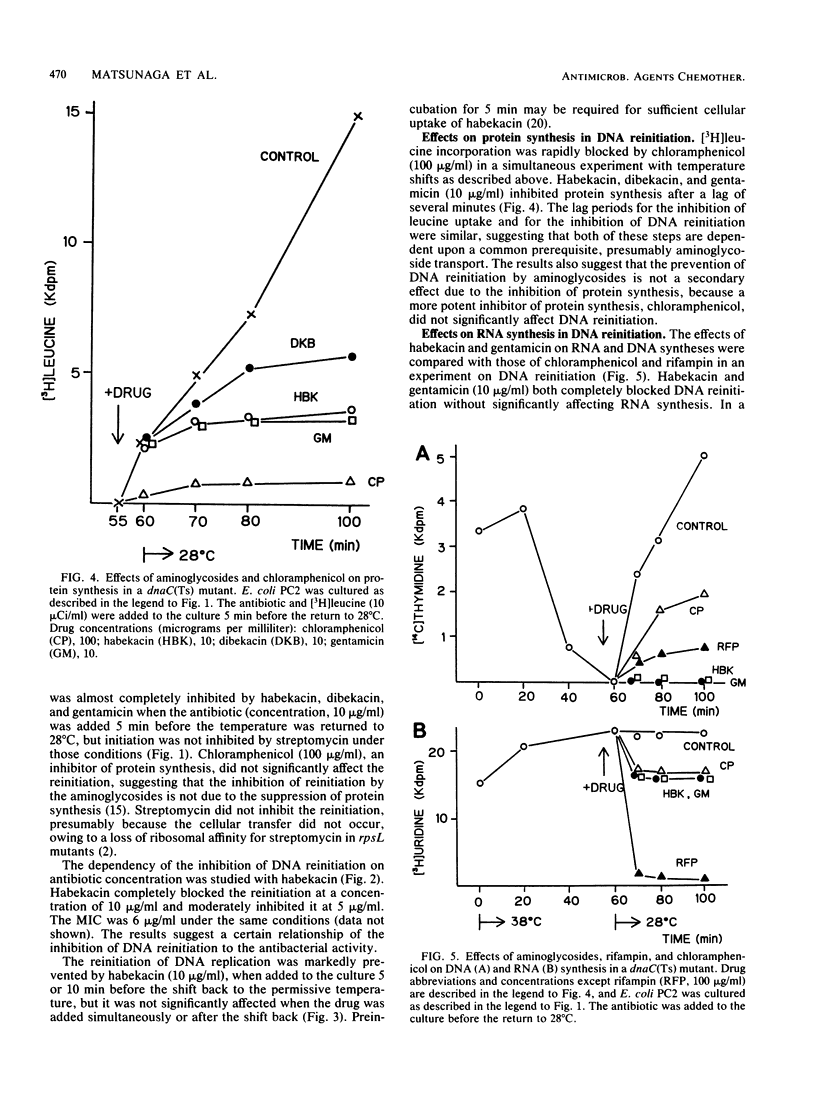
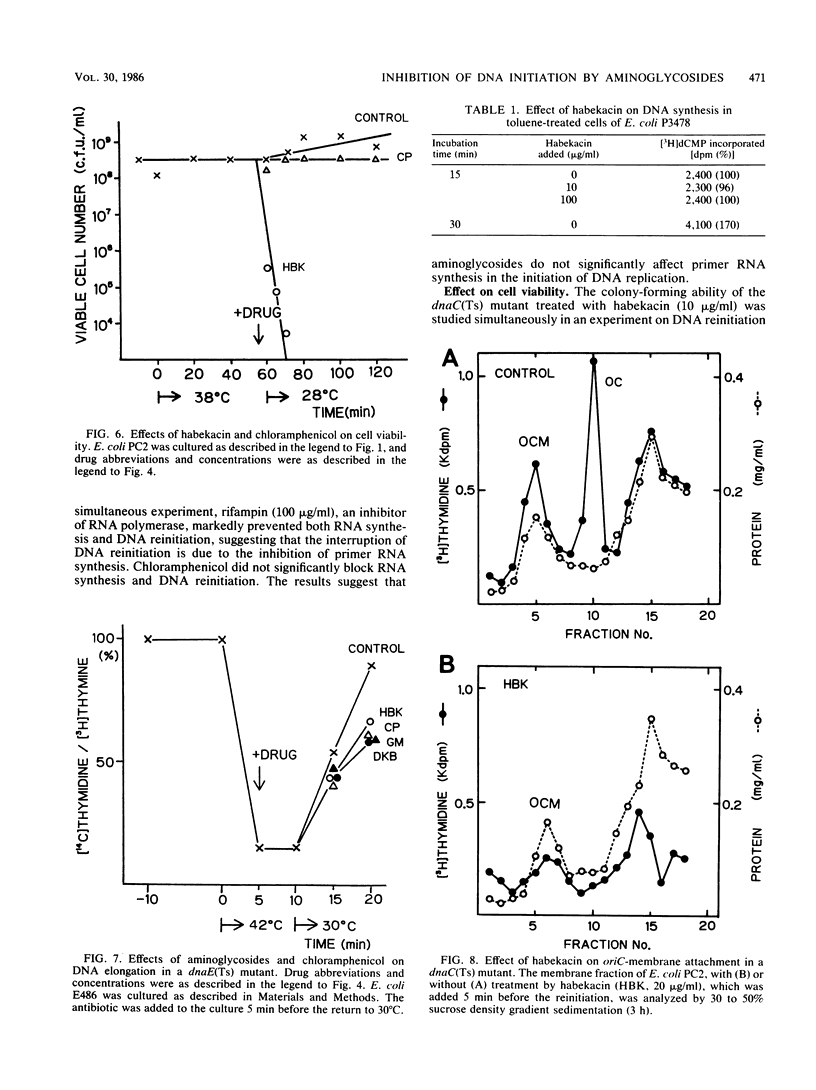
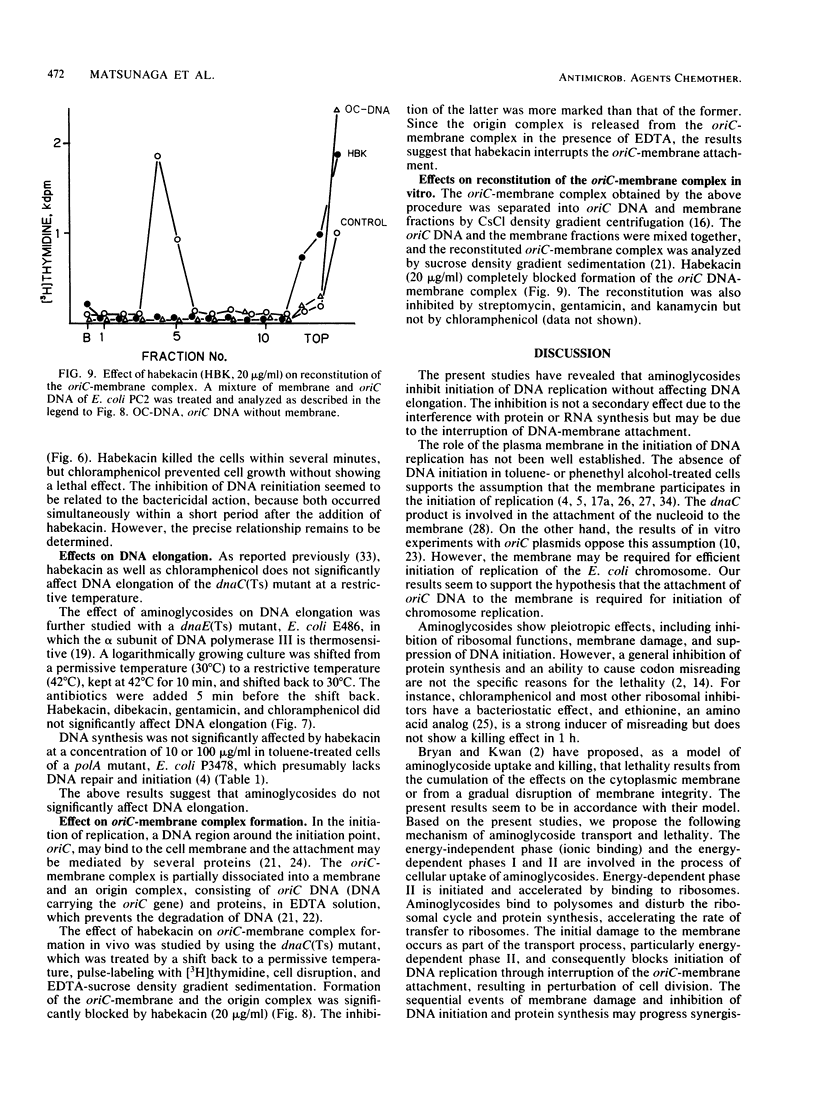
The reinitiation of DNA replication induced by a temperature shift in a dnaC(Ts) mutant of Escherichia coli was markedly inhibited by aminoglycoside antibiotics around the MIC in a short period. Protein synthesis continued for several minutes after the addition of aminoglycosides but was immediately blocked by chloramphenicol, suggesting that the inhibition of initiation of replication by aminoglycosides is not a secondary effect due to the interruption of protein synthesis. Aminoglycosides did not significantly affect RNA synthesis, suggesting that primer RNA synthesis for DNA initiation is not blocked by the agents. The lethal action of habekacin was observed simultaneously with the inhibition of DNA reinitiation. DNA elongation demonstrated with a dnaE(Ts) mutant or toluene-treated cells of a polA mutant was not significantly affected by aminoglycosides. The oriC-membrane complex formation was markedly interrupted by habekacin in the dnaC(Ts) mutant, and the in vitro reconstitution of the oriC-membrane complex was completely blocked by aminoglycosides. The present studies show that aminoglycosides block initiation of DNA replication and suggest that the inhibition is caused by the interruption of oriC-membrane attachment.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bryan L. E., Kwan S. Roles of ribosomal binding, membrane potential, and electron transport in bacterial uptake of streptomycin and gentamicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):835–845. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Van den Elzen H. M. Streptomycin accumulation in susceptible and resistant strains of Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jun;9(6):928–938. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.6.928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger R. M., Glaser D. A. Effect of nalidixic acid on DNA replication by toluene-treated Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):1955–1958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger R. M. Toluene-treated Escherichia coli replicate only that DNA which was about to be replicated in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2124–2126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi E. C., Nishimura T., Tanaka N. Mutational alterations of either large or small ribosomal subunit for the kanamycin resistance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jun 16;94(3):755–762. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91299-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBIN D. T., HANCOCK R., DAVIS B. D. THE SEQUENCE OF SOME EFFECTS OF STREPTOMYCIN IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 13;74:476–489. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91390-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lucia P., Cairns J. Isolation of an E. coli strain with a mutation affecting DNA polymerase. Nature. 1969 Dec 20;224(5225):1164–1166. doi: 10.1038/2241164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K. Biology of bacterial deoxyribonucleic acid topoisomerases. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Dec;48(4):273–289. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.4.273-289.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freda C. E., Nass M. M., Cohen S. S. T6r+-induced proteins and nucleic acids in Escherichia coli infected in the presence of streptomycin. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1382–1399. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1382-1399.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Kaguni J. M., Kornberg A. Enzymatic replication of the origin of the Escherichia coli chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7370–7374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOSS W. A., DEITZ W. H., COOK T. M. MECHANISM OF ACTION OF NALIDIXIC ACID ON ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1112–1118. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1112-1118.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gefter M. L., Hirota Y., Kornberg T., Wechsler J. A., Barnoux C. Analysis of DNA polymerases II and 3 in mutants of Escherichia coli thermosensitive for DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3150–3153. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E. Aminoglycoside uptake and mode of action--with special reference to streptomycin and gentamicin. I. Antagonists and mutants. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Oct;8(4):249–276. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.4.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E. Aminoglycoside uptake and mode of action-with special reference to streptomycin and gentamicin. II. Effects of aminoglycosides on cells. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8(6):429–445. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.6.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna M. H., Carl P. L. Reinitiation of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis by deoxyribonucleic acid initiation mutants of Escherichia coli: role of ribonucleic acid synthesis, protein synthesis, and cell division. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):219–226. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.219-226.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson W. G., Kusano T., Yamaki H., Balakrishnan R., King M., Murchie J., Schaechter M. Binding of the origin of replication of Escherichia coli to the outer membrane. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):915–923. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90296-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida K., Koike M. Cell wall alterations of gram-negative bacteria by aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jan;5(1):95–97. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lark K. G., Lark C. Regulation of chromosome replication in Escherichia coli: a comparison of the effects of phenethyl alcohol treatment with those of amino acid starvation. J Mol Biol. 1966 Sep;20(1):9–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90113-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Mount D. W. The SOS regulatory system of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga K., Nishimura T., Tanaka N. Bacterial uptake of habekacin, a novel aminoglycoside antibiotic. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1984 May;37(5):596–601. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.37.596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai K., Hendrickson W., Balakrishnan R., Yamaki H., Boyd D., Schaechter M. Isolation of a replication origin complex from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):262–266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaidis A. A., Holland I. B. Evidence for the specific association of the chromosomal origin with outer membrane fractions isolated from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):178–189. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.178-189.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nüsslein-Crystalla V., Scheefers-Borchel U. In vitro replication of a DNA fragment containing the vicinity of the origin of E. coli DNA replication. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 16;169(1):35–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00267542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen W. L., Heidrich H. G., Hannig K., Hofschneider P. H. Deoxyribonucleic acid-envelope complexes isolated from Escherichia coli by free-flow electrophoresis: biochemical and electron microscope characterization. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):646–653. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.646-653.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine M. J. Comparative physiological effects of incorporated amino acid analogs in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Apr;13(4):676–685. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.4.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson A. G., Leach F. R. The effect of phenethyl alcohol on Bacillus subtilis transformation. I. Characterization of the effect. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jan 21;174(1):264–275. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90250-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson A. G., Pierson D. L., Leach F. R. The effect of phenethyl alcohol on Bacillus subtilis transformation. II. Transport of DNA and precursors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jan 21;174(1):276–281. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90251-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder O. A., Smith D. W. Properties of membrane-associated folded chromosomes of E. coli related to initiation and termination of DNA replication. Cell. 1975 Apr;4(4):337–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90154-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern J. L., Barner H. D., Cohen S. S. The lethality of streptomycin and the stimulation of RNA synthesis in the absence of protein synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):188–217. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80103-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREICK R. W., KONETZKA W. A. PHYSIOLOGICAL STATE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI AND THE INHIBITION OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIS BY PHENETHYL ALCOHOL. J Bacteriol. 1964 Dec;88:1580–1584. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.6.1580-1584.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka N., Matsunaga K., Hirata A., Matsuhisa Y., Nishimura T. Mechanism of action of habekacin, a novel amino acid-containing aminoglycoside antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Nov;24(5):797–802. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.5.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka N., Matsunaga K., Yamaki H., Nishimura T. Inhibition of initiation of DNA synthesis by aminoglycoside antibiotics. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 18;122(1):460–465. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90498-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMAKI H., TANAKA N. EFFECTS OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS INHIBITORS ON THE LETHAL ACTION OF KANAMYCIN AND STREPTOMYCIN. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1963 Nov;16:222–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


