Abstract
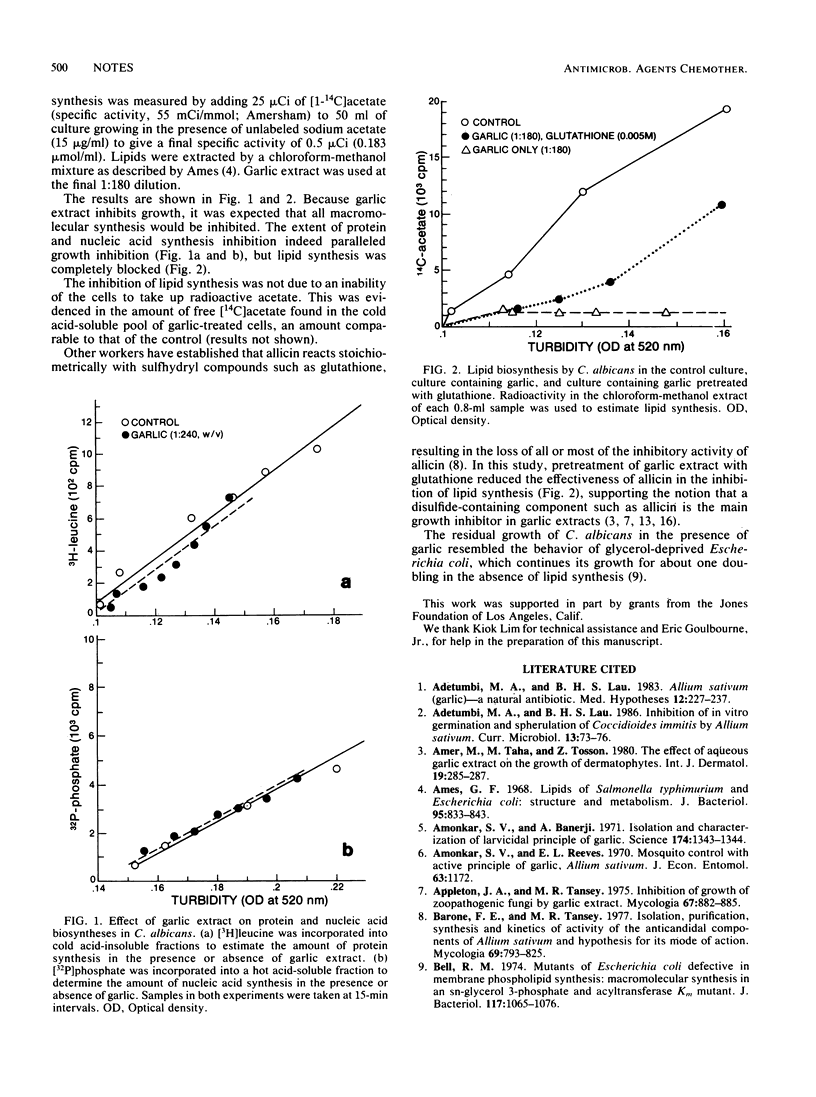
The effect of aqueous garlic extract on the macromolecular synthesis of Candida albicans was studied. Protein and nucleic acid syntheses were inhibited to the same extent as growth, but lipid synthesis was completely arrested. Blockage of lipid synthesis is likely an important component of the anticandidal activity of garlic.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adetumbi M. A., Lau B. H. Allium sativum (garlic)--a natural antibiotic. Med Hypotheses. 1983 Nov;12(3):227–237. doi: 10.1016/0306-9877(83)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amer M., Taha M., Tosson Z. The effect of aqueous garlic extract on the growth of dermatophytes. Int J Dermatol. 1980 Jun;19(5):285–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4362.1980.tb00331.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F. Lipids of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli: structure and metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):833–843. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.833-843.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amonkar S. V., Banerji A. Isolation and characterization of larvicidal principle of garlic. Science. 1971 Dec 24;174(4016):1343–1344. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4016.1343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amonkar S. V., Reeves E. L. Mosquito control with active principle of garlic, Allium sativum. J Econ Entomol. 1970 Aug;63(4):1172–1175. doi: 10.1093/jee/63.4.1172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appleton J. A., Tansey M. R. Inhibition of growth of zoopathogenic fungi by garlic extract. Mycologia. 1975 Jul-Aug;67(4):882–885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barone F. E., Tansey M. R. Isolation, purification, identification, synthesis, and kinetics of activity of the anticandidal component of Allium sativum, and a hypothesis for its mode of action. Mycologia. 1977 Jul-Aug;69(4):793–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. M. Mutants of Escherichia coli defective in membrane phospholipid synthesis: macromolecular synthesis in an sn-glycerol 3-phosphate acyltransferase Km mutant. J Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;117(3):1065–1076. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.3.1065-1076.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delaha E. C., Garagusi V. F. Inhibition of mycobacteria by garlic extract (Allium sativum). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):485–486. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Pong Chong R. Right to health. Nouv Com Int Cathol Infirm Assist Med Soc. 1986;(2-3):73–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. S., Atkins R. D. The fungicidal and fungistatic effects of an aqueous garlic extract on medically important yeast-like fungi. Mycologia. 1977 Mar-Apr;69(2):341–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma V. D., Sethi M. S., Kumar A., Rarotra J. R. Antibacterial property of Allium sativum Linn.: in vivo & in vitro studies. Indian J Exp Biol. 1977 Jun;15(6):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tansey M. R., Appleton J. A. Inhibition of fungal growth by garlic extract. Mycologia. 1975 Mar-Apr;67(2):409–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLS E. D. Enzyme inhibition by allicin, the active principle of garlic. Biochem J. 1956 Jul;63(3):514–520. doi: 10.1042/bj0630514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


