Abstract
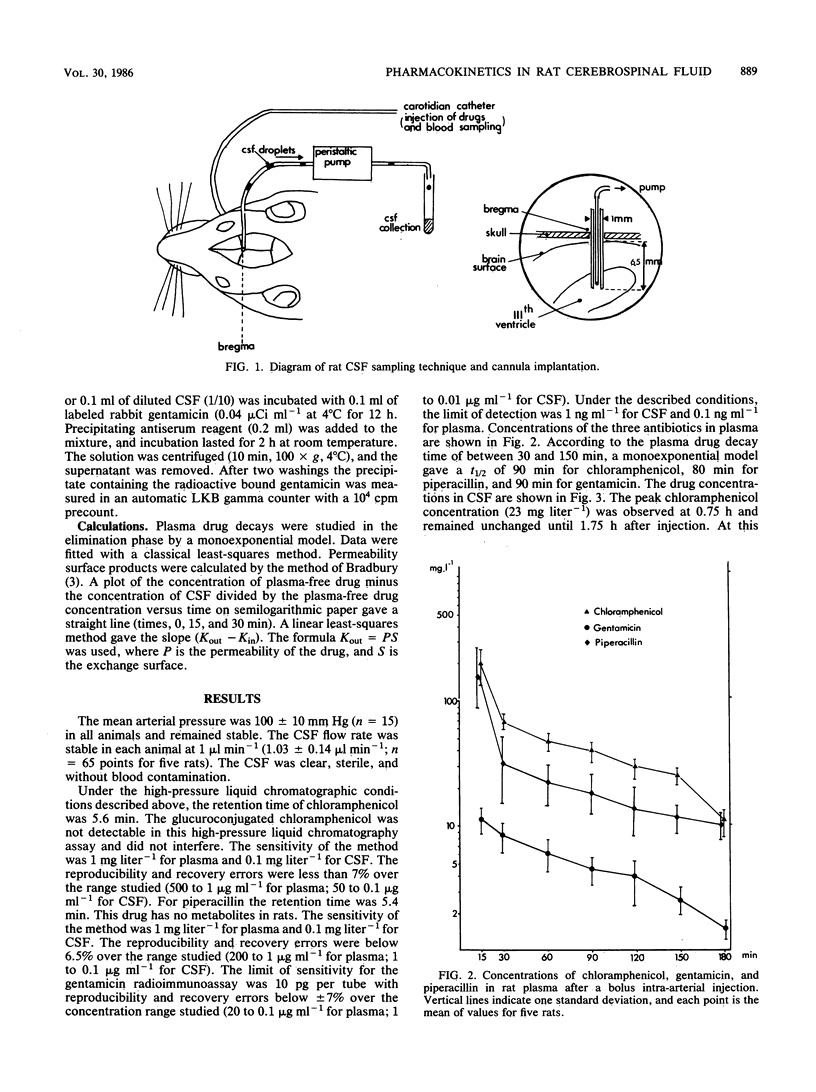
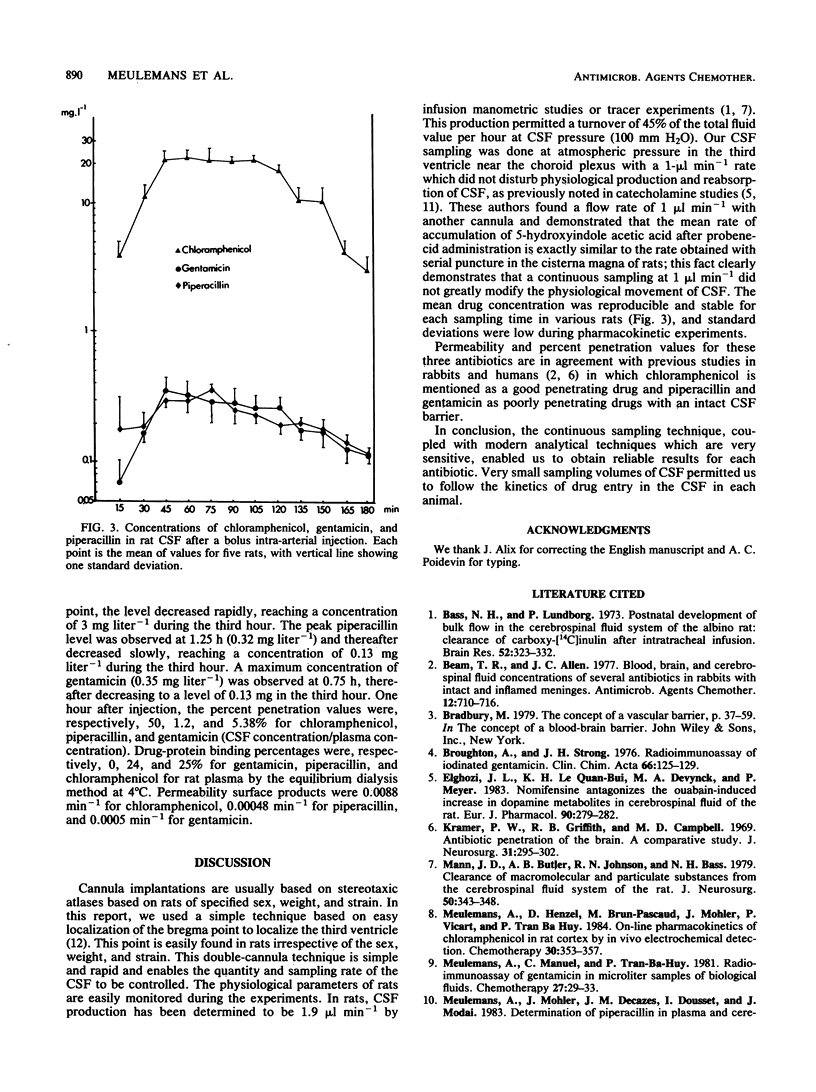
A method for determining drug concentration relationships between plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in rats is described. Continuous CSF samples were collected directly from the third anterior ventricle with an indwelling cannula inserted through the bregma point, and drug concentrations were determined by high-pressure liquid chromatography and radioimmunoassay micromethods. Three antibiotics with different abilities to cross the blood-CSF barrier (chloramphenicol, piperacillin, and gentamicin) were tested. This method was found to be reproducible for each drug even if the antibiotic levels were low and the sample volumes very small. Peak CSF concentrations occurred between 0.75 and 1.25 h after injection for all three antibiotics. Percent penetration values at 1 h were 50, 1.2, and 5.4% for chloramphenicol, piperacillin, and gentamicin, respectively.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bass N. H., Lundborg P. Postnatal development of bulk flow in the cerebrospinal fluid system of the albino rat: clearance of carboxyl-( 14 C)inulin after intrathecal infusion. Brain Res. 1973 Mar 30;52:323–332. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90668-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beam T. R., Jr, Allen J. C. Blood, brain, and cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of several antibiotics in rabbits with intact and inflamed meninges. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Dec;12(6):710–716. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.6.710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broughton A., Strong J. E. Radioimmunoassay of iodinated gentamicin. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Jan 2;66(1):125–129. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90379-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elghozi J. L., Le Quan-Bui K. H., Devynck M. A., Meyer P. Nomifensine antagonizes the ouabain-induced increase in dopamine metabolites in cerebrospinal fluid of the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun 3;90(2-3):279–282. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90250-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer P. W., Griffith R. S., Campbell R. L. Antibiotic penetration of the brain. A comparative study. J Neurosurg. 1969 Sep;31(3):295–302. doi: 10.3171/jns.1969.31.3.0295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann J. D., Butler A. B., Johnson R. N., Bass N. H. Clearance of macromolecular and particulate substances from the cerebrospinal fluid system of the rat. J Neurosurg. 1979 Mar;50(3):343–348. doi: 10.3171/jns.1979.50.3.0343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meulemans A., Henzel D., Brun-Pacaud M., Mohler J., Vicart P., Huy P. T. On-line pharmacokinetics of chloramphenicol in rat cortex by in vivo electrochemical detection. Chemotherapy. 1984;30(6):353–357. doi: 10.1159/000238293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meulemans A., Manuel C., Tran Ba Huy P. Radioimmunoassay of gentamicin in microliter and nanoliter samples of biological fluids. Chemotherapy. 1981;27(1):29–33. doi: 10.1159/000237951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignot E., Laude D., Elghozi J. L. Kinetics of drug-induced changes in dopamine and serotonin metabolite concentrations in the CSF of the rat. J Neurochem. 1984 Mar;42(3):819–825. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb02754.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paxinos G., Watson C., Pennisi M., Topple A. Bregma, lambda and the interaural midpoint in stereotaxic surgery with rats of different sex, strain and weight. J Neurosci Methods. 1985 Apr;13(2):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(85)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ylitalo P., Heikkinen E. R., Myllylä V. V. Evaluation of sucessive collections of cisternal cerebrospinal fluid in rats, rabbits, and cats. Exp Neurol. 1976 Feb;50(2):330–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(76)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



