Abstract
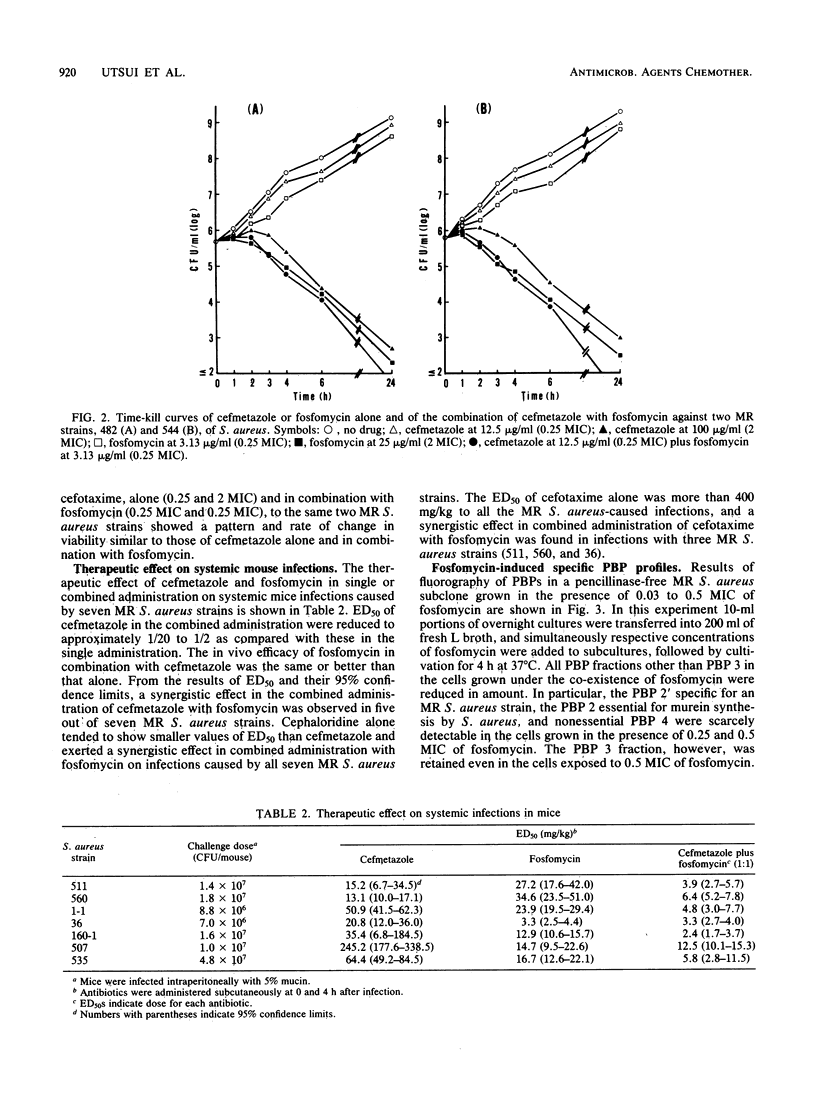
In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities of cefmetazole alone and in combination with fosfomycin against methicillin- and cephem-resistant (MR) strains of Staphylococcus aureus were investigated, and the mechanism of synergistic effect between cefmetazole and fosfomycin was also studied. Cefmetazole inhibited the growth of 71 strains of MR S. aureus at concentrations ranging from 1.56 to 50 micrograms/ml; the antibacterial activity of cefmetazole against these strains was enhanced approximately 4 times with the addition of fosfomycin at a concentration of 1.56 micrograms/ml. The binding affinity of cefmetazole for the penicillin-binding protein 2' fraction specific for MR S. aureus was higher than that of methicillin, cloxacillin, cefazolin, and cefotaxime. A synergy experiment in vitro was performed by checkerboard titration with Mueller-Hinton agar plates containing various concentrations and ratios of cefmetazole and fosfomycin. The fractional inhibitory concentration index ranged from 0.09 to 0.75. Exposure of cefmetazole plus fosfomycin to exponentially growing cultures at a concentration at which both antibiotics had no bactericidal effect when given alone exerted bactericidal action. Combined administration of cefmetazole with fosfomycin at a ratio of 1:1 against systemic MR S. aureus infections with mice showed an excellent therapeutic efficacy as compared with administration of either antibiotic alone. Penicillin-binding protein 2', 2, and 4 fractions were scarcely detectable in MR S. aureus strains grown in the presence of fosfomycin at concentrations of 0.25 MIC and 0.5 MIC, respectively.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarez S., Jones M., Berk S. L. In vitro activity of fosfomycin, alone and in combination, against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Nov;28(5):689–690. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.5.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayers L. W., Jones R. N., Barry A. L., Thornsberry C., Fuchs P. C., Gavan T. L., Gerlach E. H., Sommers H. M. Cefotetan, a new cephamycin: comparison of in vitro antimicrobial activity with other cephems, beta-lactamase stability, and preliminary recommendations for disk diffusion testing. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Nov;22(5):859–877. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.5.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven D. E., Kollisch N. R., Hsieh C. R., Connolly M. G., Jr, McCabe W. R. Vancomycin treatment of bacteremia caused by oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: comparison with beta-lactam antibiotic treatment of bacteremia caused by oxacillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jan;147(1):137–143. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.1.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deguchi K., Kawamura S., Sugita R., Fujimaki Y., Ohsawa H. [Sensitivity to second-generation cephem agents of clinically isolated strains of bacteria in otorhinolaryngological field (author's transl)]. Jpn J Antibiot. 1982 Mar;35(3):812–820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deguchi K. [Sensitivity of Staphylococcus aureus isolated clinically to CEPs. Results obtained with strains originating in superficial abscess in infants (author's transl)]. Jpn J Antibiot. 1982 Mar;35(3):807–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELION G. B., SINGER S., HITCHINGS G. H. Antagonists of nucleic acid derivatives. VIII. Synergism in combinations of biochemically related antimetabolites. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jun;208(2):477–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopapadakou N. H., Liu F. Y. Binding of beta-lactam antibiotics to penicillin-binding proteins of Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus faecalis: relation to antibacterial activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):834–836. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guenthner S. H., Wenzel R. P. In vitro activities of teichomycin, fusidic acid, flucloxacillin, fosfomycin, and vancomycin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):268–269. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman B. J., Tomasz A. Low-affinity penicillin-binding protein associated with beta-lactam resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):513–516. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.513-516.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan F. M., Kahan J. S., Cassidy P. J., Kropp H. The mechanism of action of fosfomycin (phosphonomycin). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):364–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozarich J. W., Strominger J. L. A membrane enzyme from Staphylococcus aureus which catalyzes transpeptidase, carboxypeptidase, and penicillinase activities. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1272–1278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAY J. W., HOUGHTON R. H., PERRET C. J. THE EFFECT OF GROWTH AT ELEVATED TEMPERATURES ON SOME HERITABLE PROPERTIES OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Nov;37:157–169. doi: 10.1099/00221287-37-2-157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muytjens H. L., van der Ros-van de Repe J. Comparative activities of 13 beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jun;21(6):925–934. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.6.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Kamimura T. Synergy of fosmidomycin (FR-31564) and other antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Oct;22(4):560–563. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.4.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock J. E., Jr, Moorman D. R., Wenzel R. P., Mandell G. L. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: microbiologic characteristics, antimicrobial susceptibilities, and assessment of virulence of an epidemic strain. J Infect Dis. 1981 Dec;144(6):575–582. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.6.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Schumacher-Perdreau F., Pulverer G. Vergleich der Staphylokokken- und Mikrokokken-Wirksamkeit von Fosfomycin, Oxacillin und Penicillin G. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1980 Oct 31;105(44):1541–1543. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1070908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapico F. L., Montgomerie J. Z., Canawati H. N., Aeilts G. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteriuria. Am J Med Sci. 1981 Mar-Apr;281(2):101–109. doi: 10.1097/00000441-198103000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Distinct penicillin binding proteins involved in the division, elongation, and shape of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. L., Cabezudo I., Wenzel R. P. Epidemiology of nosocomial infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Sep;97(3):309–317. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-3-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. L., Wenzel R. P. International recognition of methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Dec;97(6):925–926. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-6-925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipper D. J., Strominger J. L. Mechanism of action of penicillins: a proposal based on their structural similarity to acyl-D-alanyl-D-alanine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Oct;54(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.4.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ubukata K., Yamashita N., Konno M. Occurrence of a beta-lactam-inducible penicillin-binding protein in methicillin-resistant staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):851–857. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
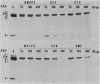
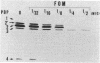
- Utsui Y., Yokota T. Role of an altered penicillin-binding protein in methicillin- and cephem-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Sep;28(3):397–403. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.3.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbist L., Verhaegen J. Effect of temocillin in combination with other beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jan;25(1):142–144. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.1.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanakunakorn C. Treatment of infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Sep;97(3):376–378. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-3-376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyke A. W., Ward J. B., Hayes M. V., Curtis N. A. A role in vivo for penicillin-binding protein-4 of Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Oct;119(2):389–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]