Abstract
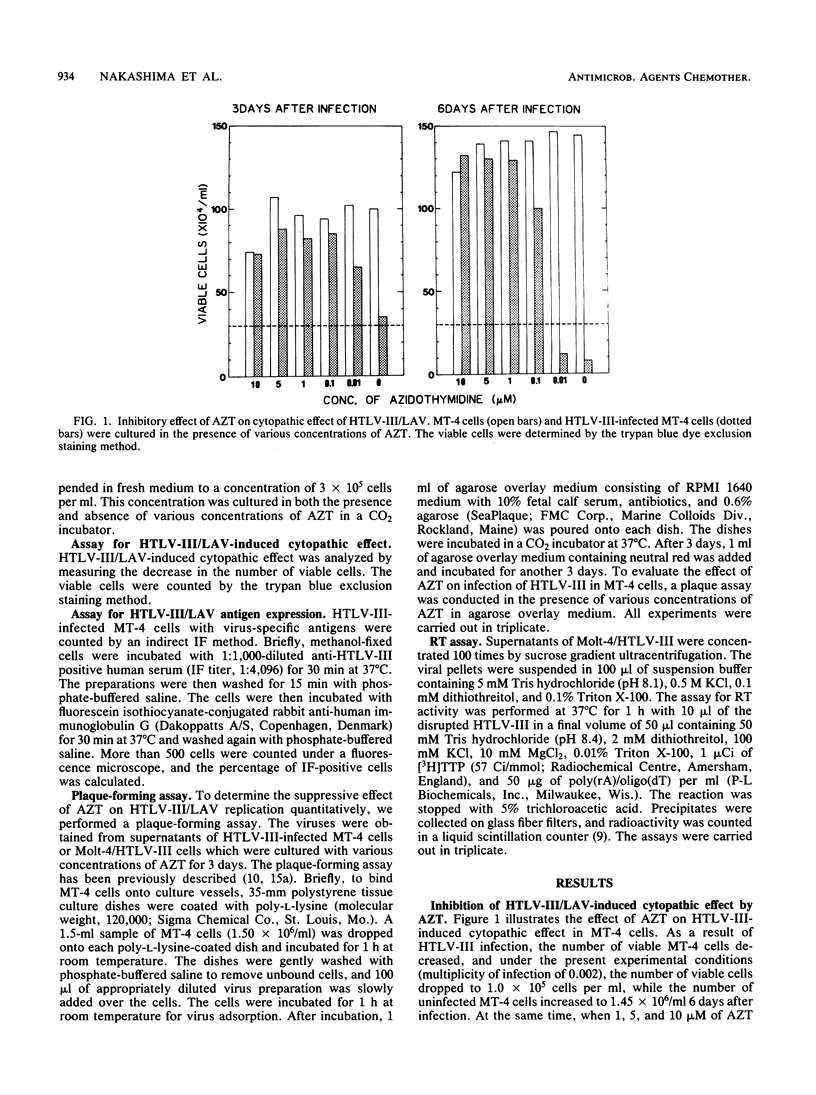
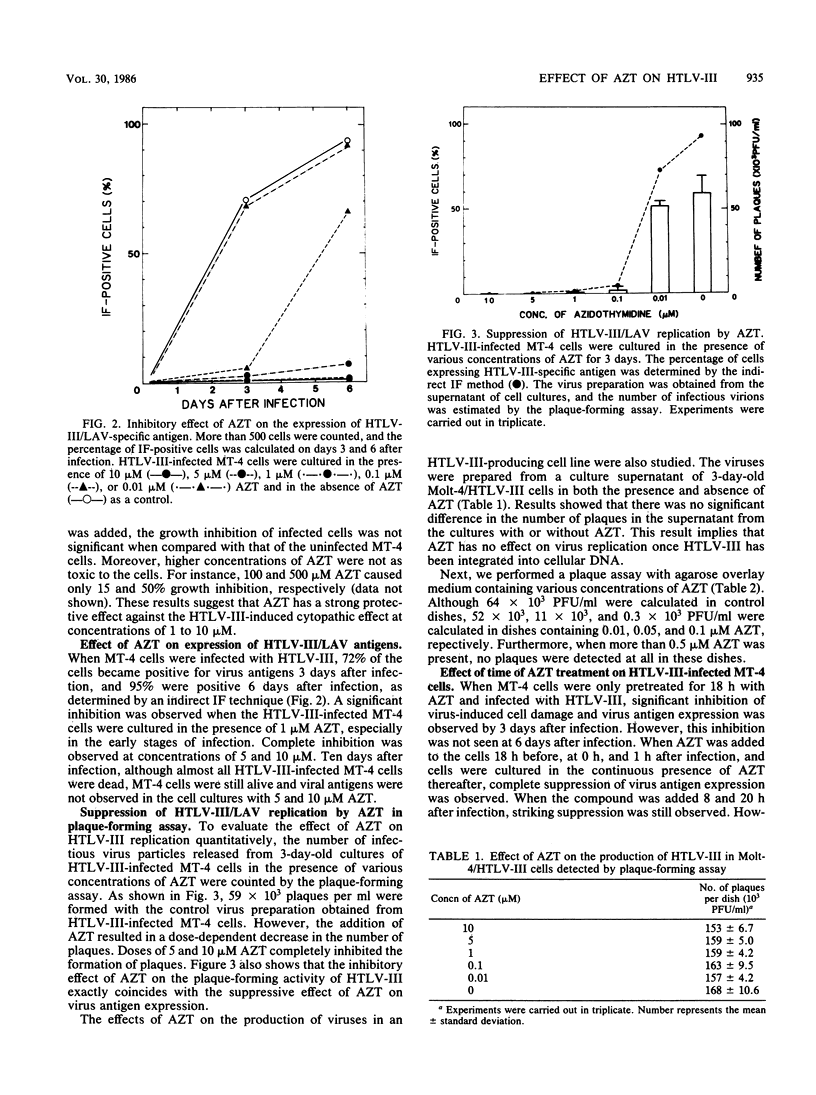
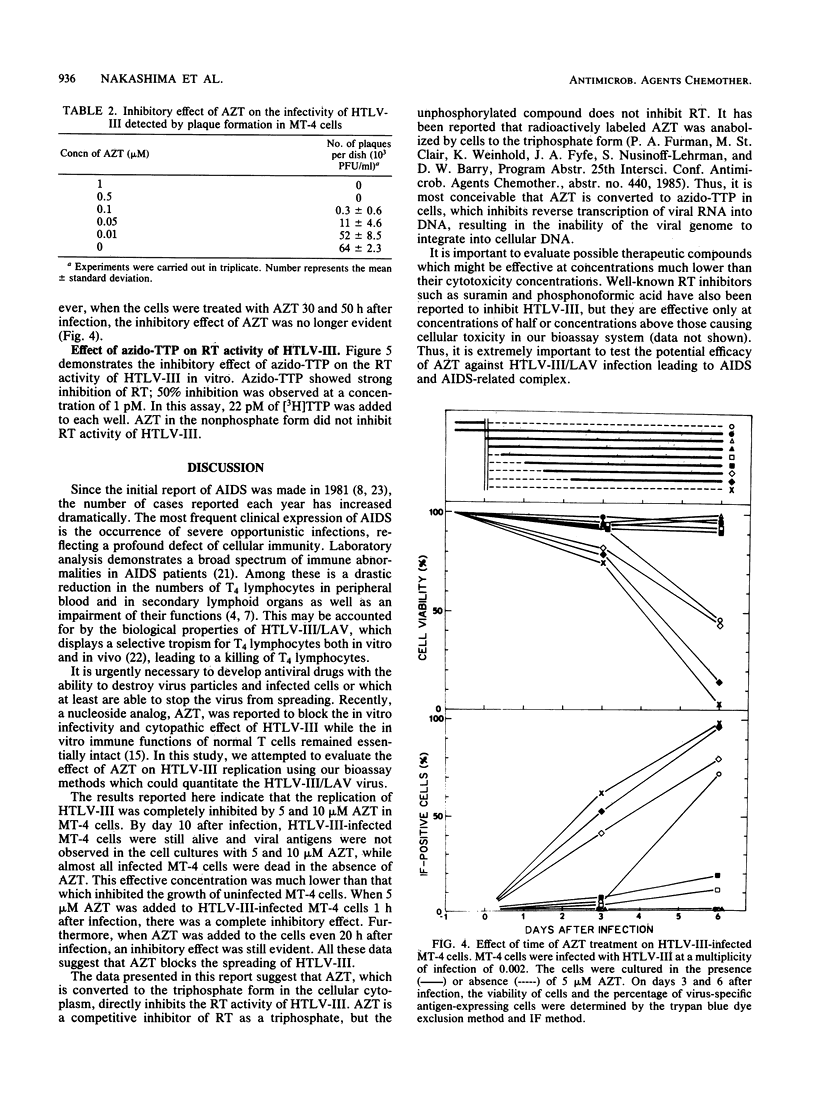
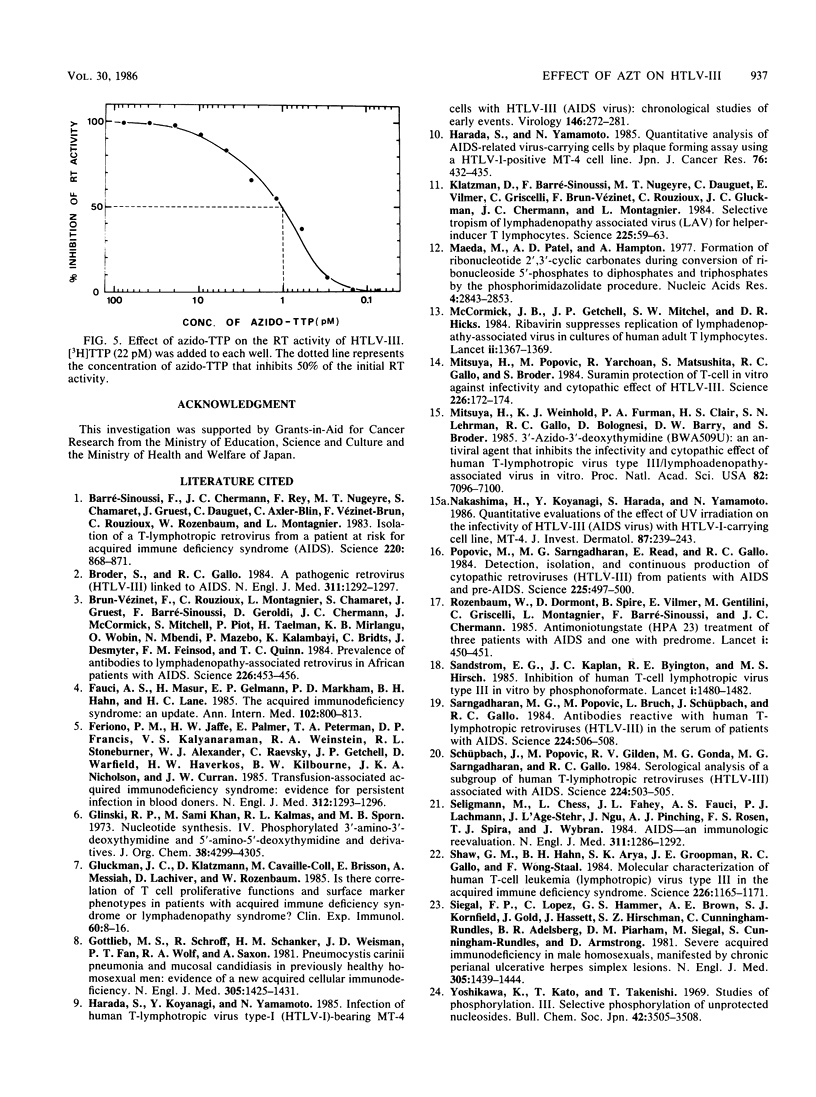
Human T cell lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III)/lymphadenopathy-associated virus is the etiologic agent of the acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) and AIDS-related complex. The effect of 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine (AZT) on the HTLV-III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus infection was quantitatively studied with HTLV type I-carrying MT-4 cells. The AZT compound inhibited HTLV-III-induced cytopathic effect and virus-specific antigen expression in MT-4 cells at concentrations of 5 and 10 microM. In addition, a plaque-forming assay was performed to assess the effect of AZT on virus replication in MT-4 cells freshly infected with HTLV-III and in continuous HTLV-III-producing Molt-4/HTLV-III cells. Results showed that AZT efficiently and effectively inhibited the replication of HTLV-III in infected MT-4 cells. AZT is a strong inhibitor of reverse transcriptase activity of HTLV-III as a triphosphate, to such a degree that even 1.0 pM azido-TTP inhibits 50% of reverse transcriptase activity. However, it did not show any effect in the HTLV-III-producing cell line Molt-4/HTLV-III. Thus, AZT has no effect on virus replication of an already integrated virus. When 5 microM AZT was added to HTLV-III-infected MT-4 within 20 h after infection, a striking suppressive effect was noticed. This concentration was much lower than that which inhibits the growth of MT-4 cells. These results confirm those found in a previous report (H. Mitsuya, K. J. Weinhold, P. S. Furman, H. S. Clair, S. N. Lehrman, R. C. Gallo, D. Bolognesi, D. W. Barry, and S. Broder, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:7096-7100, 1985) and suggest that AZT might be used as an experimental antiviral agent for AIDS and AIDS-related complex.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Rey F., Nugeyre M. T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broder S., Gallo R. C. A pathogenic retrovirus (HTLV-III) linked to AIDS. N Engl J Med. 1984 Nov 15;311(20):1292–1297. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198411153112006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun-Vézinet F., Rouzioux C., Montagnier L., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Barré-Sinoussi F., Geroldi D., Chermann J. C., McCormick J., Mitchell S. Prevalence of antibodies to lymphadenopathy-associated retrovirus in African patients with AIDS. Science. 1984 Oct 26;226(4673):453–456. doi: 10.1126/science.6238406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Masur H., Gelmann E. P., Markham P. D., Hahn B. H., Lane H. C. NIH conference. The acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: an update. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Jun;102(6):800–813. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-102-6-800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feorino P. M., Jaffe H. W., Palmer E., Peterman T. A., Francis D. P., Kalyanaraman V. S., Weinstein R. A., Stoneburner R. L., Alexander W. J., Raevsky C. Transfusion-associated acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Evidence for persistent infection in blood donors. N Engl J Med. 1985 May 16;312(20):1293–1296. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198505163122005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glinski R. P., Khan M. S., Kalamas R. L., Sporn M. B. Nucleotide synthesis. IV. Phosphorylated 3'-amino-3'-deoxythymidine and 5'-amino-5'-deoxythymidine and derivatives. J Org Chem. 1973 Dec 14;38(25):4299–4305. doi: 10.1021/jo00964a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluckman J. C., Klatzmann D., Cavaille-Coll M., Brisson E., Messiah A., Lachiver D., Rozenbaum W. Is there correlation of T cell proliferative functions and surface marker phenotypes in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome or lymphadenopathy syndrome? Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Apr;60(1):8–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb M. S., Schroff R., Schanker H. M., Weisman J. D., Fan P. T., Wolf R. A., Saxon A. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia and mucosal candidiasis in previously healthy homosexual men: evidence of a new acquired cellular immunodeficiency. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1425–1431. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada S., Koyanagi Y., Yamamoto N. Infection of human T-lymphotropic virus type-I (HTLV-I)-bearing MT-4 cells with HTLV-III (AIDS virus): chronological studies of early events. Virology. 1985 Oct 30;146(2):272–281. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada S., Yamamoto N. Quantitative analysis of AIDS-related virus-carrying cells by plaque-forming assay using an HTLV-I-positive MT-4 cell line. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1985 Jun;76(6):432–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D., Barré-Sinoussi F., Nugeyre M. T., Danquet C., Vilmer E., Griscelli C., Brun-Veziret F., Rouzioux C., Gluckman J. C., Chermann J. C. Selective tropism of lymphadenopathy associated virus (LAV) for helper-inducer T lymphocytes. Science. 1984 Jul 6;225(4657):59–63. doi: 10.1126/science.6328660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda M., Patel A. D., Hampton A. Formation of ribonucleotide 2',3'-cyclic carbonates during conversion of ribonucleoside 5'-phosphates to diphosphates and triphosphates by the phosphorimidazolidate procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2843–2853. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick J. B., Getchell J. P., Mitchell S. W., Hicks D. R. Ribavirin suppresses replication of lymphadenopathy-associated virus in cultures of human adult T lymphocytes. Lancet. 1984 Dec 15;2(8416):1367–1369. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuya H., Popovic M., Yarchoan R., Matsushita S., Gallo R. C., Broder S. Suramin protection of T cells in vitro against infectivity and cytopathic effect of HTLV-III. Science. 1984 Oct 12;226(4671):172–174. doi: 10.1126/science.6091268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuya H., Weinhold K. J., Furman P. A., St Clair M. H., Lehrman S. N., Gallo R. C., Bolognesi D., Barry D. W., Broder S. 3'-Azido-3'-deoxythymidine (BW A509U): an antiviral agent that inhibits the infectivity and cytopathic effect of human T-lymphotropic virus type III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7096–7100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima H., Koyanagi Y., Harada S., Yamamoto N. Quantitative evaluations of the effect of UV irradiation on the infectivity of HTLV-III (AIDS virus) with HTLV-I-carrying cell line, MT-4. J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Aug;87(2):239–243. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12696622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Sarngadharan M. G., Read E., Gallo R. C. Detection, isolation, and continuous production of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and pre-AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):497–500. doi: 10.1126/science.6200935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozenbaum W., Dormont D., Spire B., Vilmer E., Gentilini M., Griscelli C., Montagnier L., Barre-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C. Antimoniotungstate (HPA 23) treatment of three patients with AIDS and one with prodrome. Lancet. 1985 Feb 23;1(8426):450–451. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandstrom E. G., Kaplan J. C., Byington R. E., Hirsch M. S. Inhibition of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III in vitro by phosphonoformate. Lancet. 1985 Jun 29;1(8444):1480–1482. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92255-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarngadharan M. G., Popovic M., Bruch L., Schüpbach J., Gallo R. C. Antibodies reactive with human T-lymphotropic retroviruses (HTLV-III) in the serum of patients with AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):506–508. doi: 10.1126/science.6324345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüpbach J., Popovic M., Gilden R. V., Gonda M. A., Sarngadharan M. G., Gallo R. C. Serological analysis of a subgroup of human T-lymphotropic retroviruses (HTLV-III) associated with AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):503–505. doi: 10.1126/science.6200937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann M., Chess L., Fahey J. L., Fauci A. S., Lachmann P. J., L'Age-Stehr J., Ngu J., Pinching A. J., Rosen F. S., Spira T. J. AIDS--an immunologic reevaluation. N Engl J Med. 1984 Nov 15;311(20):1286–1292. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198411153112005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G. M., Hahn B. H., Arya S. K., Groopman J. E., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Molecular characterization of human T-cell leukemia (lymphotropic) virus type III in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Science. 1984 Dec 7;226(4679):1165–1171. doi: 10.1126/science.6095449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegal F. P., Lopez C., Hammer G. S., Brown A. E., Kornfeld S. J., Gold J., Hassett J., Hirschman S. Z., Cunningham-Rundles C., Adelsberg B. R. Severe acquired immunodeficiency in male homosexuals, manifested by chronic perianal ulcerative herpes simplex lesions. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1439–1444. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



