Abstract
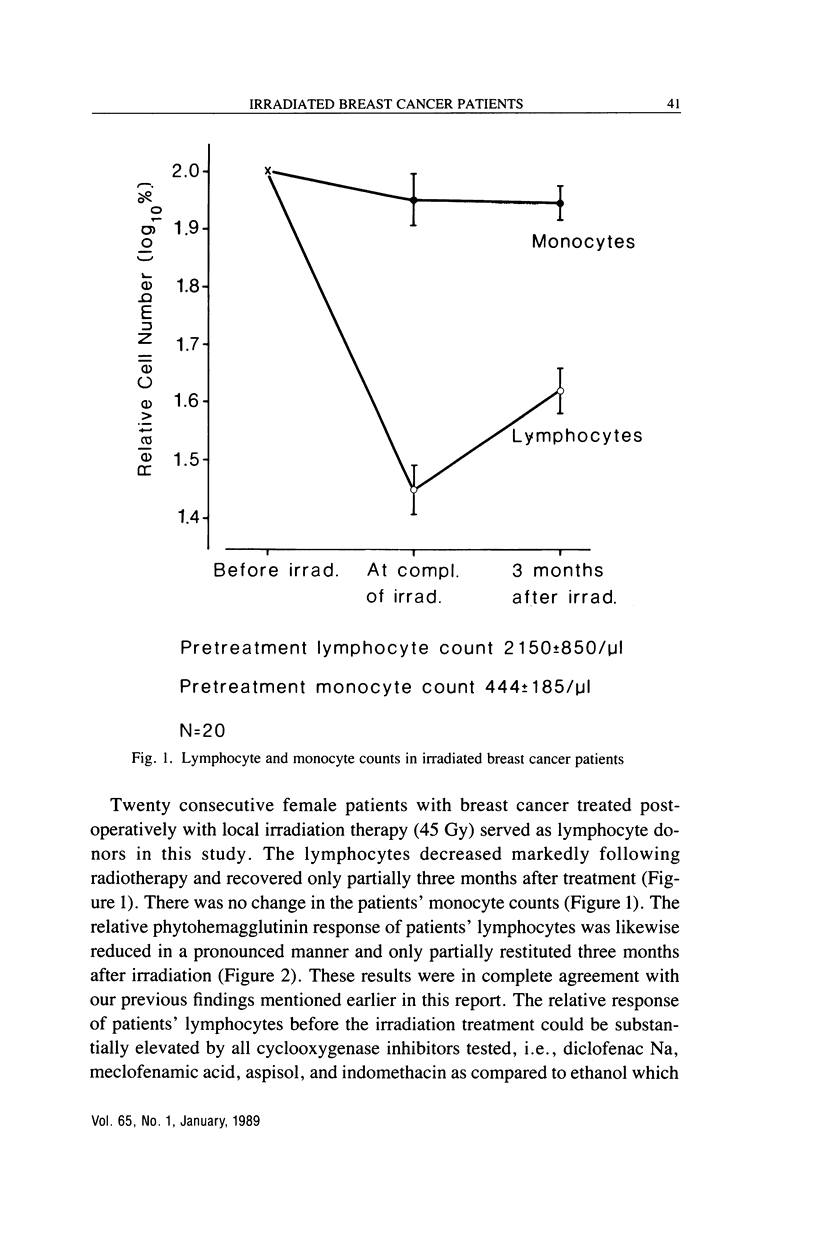
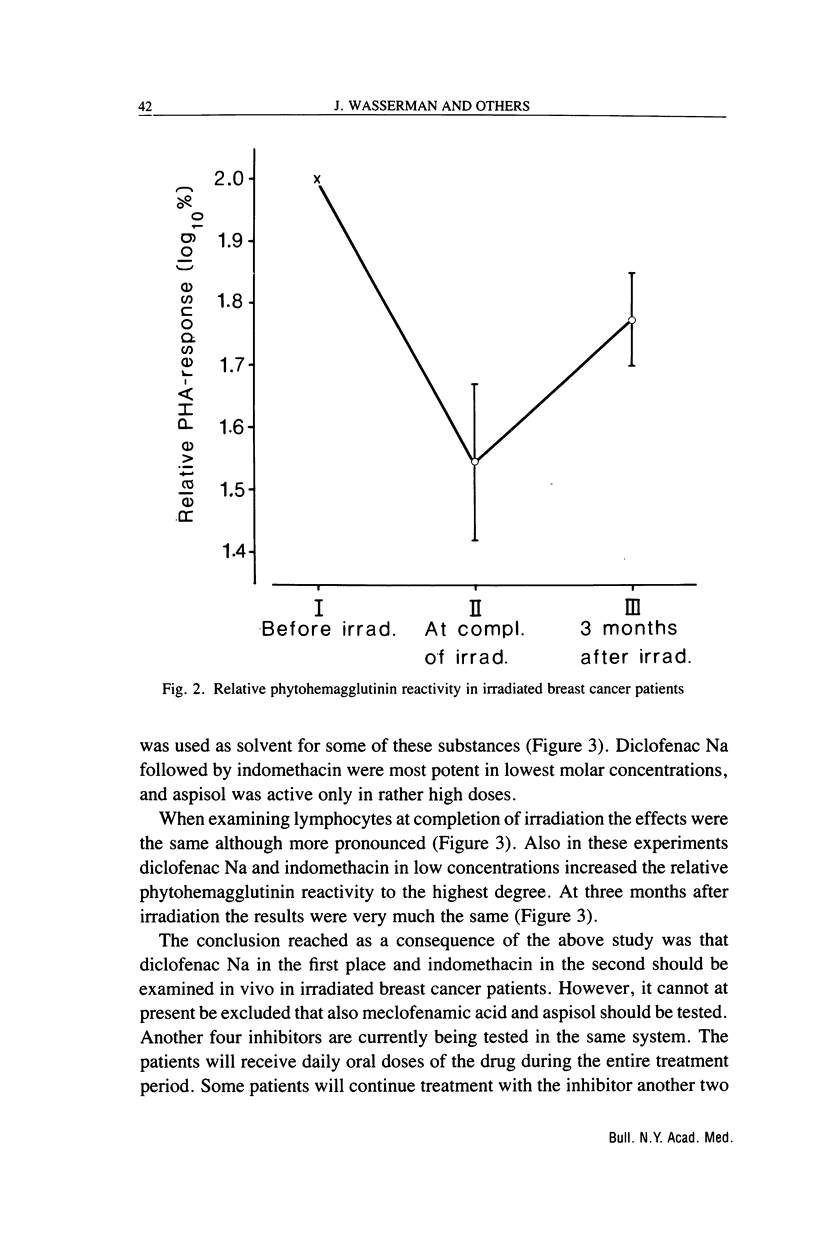
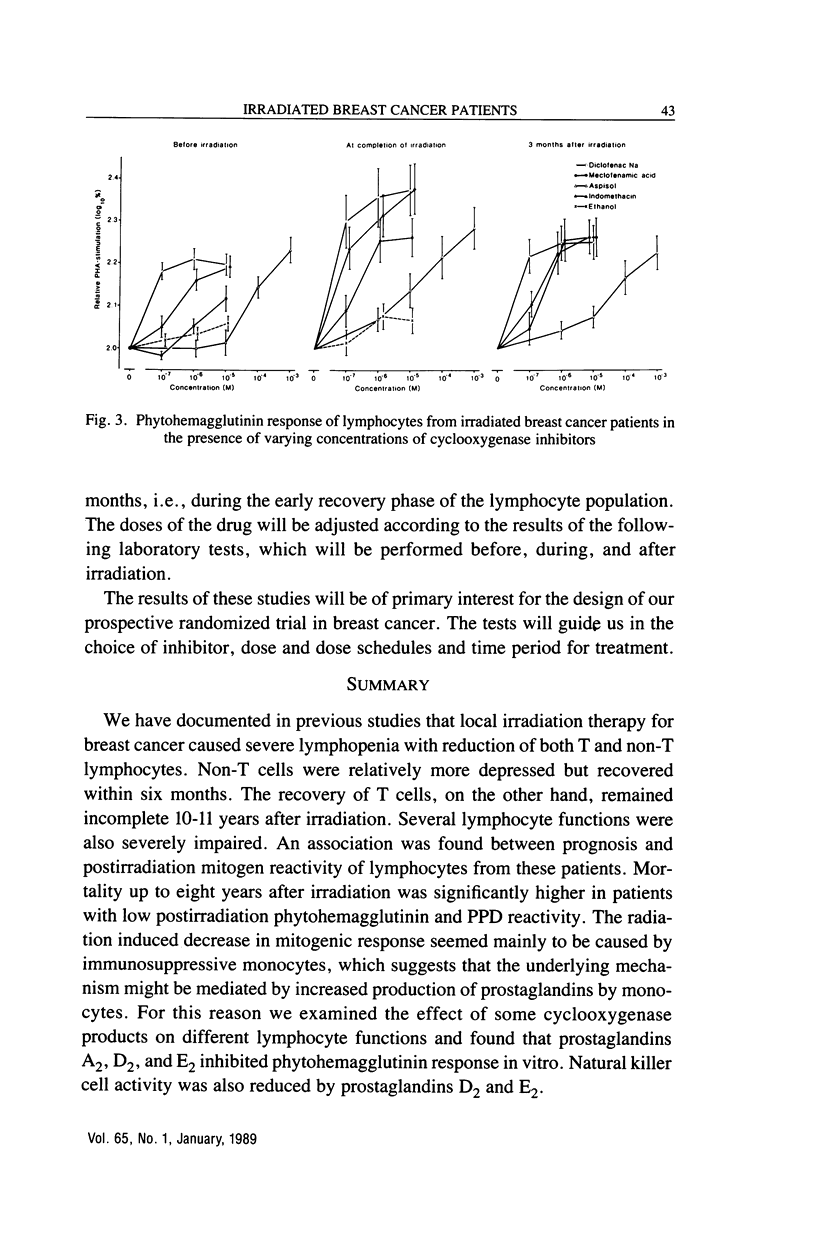
We have documented in previous studies that local irradiation therapy for breast cancer caused severe lymphopenia with reduction of both T and non-T lymphocytes. Non-T cells were relatively more depressed but recovered within six months. The recovery of T cells, on the other hand, remained incomplete 10-11 years after irradiation. Several lymphocyte functions were also severely impaired. An association was found between prognosis and postirradiation mitogen reactivity of lymphocytes from these patients. Mortality up to eight years after irradiation was significantly higher in patients with low postirradiation phytohemagglutinin and PPD reactivity. The radiation induced decrease in mitogenic response seemed mainly to be caused by immunosuppressive monocytes, which suggests that the underlying mechanism might be mediated by increased production of prostaglandins by monocytes. For this reason we examined the effect of some cyclooxygenase products on different lymphocyte functions and found that prostaglandins A2, D2, and E2 inhibited phytohemagglutinin response in vitro. Natural killer cell activity was also reduced by prostaglandins D2 and E2. The next step was to examine various inhibitors of cyclooxygenase in respect to their capacity to revert irradiation-induced suppression of in vitro mitogen response in lymphocytes from breast cancer patients. It was demonstrated that Diclofenac Na (Voltaren), Meclofenamic acid, Indomethacin, and lysin-mono-acetylsalicylate (Aspisol) could enhance mitogen responses both before and after radiation therapy. This effect was most pronounced at completion of irradiation. On a molar basis, Diclofenac Na was most effective followed by Indomethacin, Meclofenamic acid, and lysin-monoacetylsalicylate.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blomgren H., Hammarström S., Wasserman J., Petrini B. Prostaglandin sensitivity of the PHA-response of blood lymphocytes following radiation therapy for breast cancer. Radiother Oncol. 1986 Oct;7(2):141–145. doi: 10.1016/s0167-8140(86)80093-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomgren H., Hammarström S., Wasserman J. Synergistic enhancement of mitogen responses of human lymphocytes by inhibitors of cyclo-oxygenase and 5,8,11-eicosatriynoic acid, an inhibitor of 12-lipoxygenase and leukotriene biosynthesis. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1987;83(3):247–255. doi: 10.1159/000234304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomgren H., Wasserman J., Baral E., Petrini B. Evidence for the appearance of non-specific suppressor cells in the blood after local radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1978 Mar-Apr;4(3-4):249–253. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(78)90145-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomgren H., Wasserman J., Edsmyr F., Baral E., Petrini B. Reductions of responder and stimulator capacities of peripheral lymphoid cells in the mixed lymphocyte culture following external radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1977 Mar-Apr;2(3-4):297–305. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(77)90088-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomgren H., Wasserman J., Rotstein S., Petrini B., Baral E. Possible role of prostaglandin producing monocytes in the depression of mitogenic responses of blood lymphocytes following radiation therapy. Radiother Oncol. 1984 Jan;1(3):255–261. doi: 10.1016/s0167-8140(84)80008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarstrand C., Petrini B., Wasserman J., Blomgren H., Strender L. E. Increased reduction of nitroblue tetrazolium by human blood monocytes following post-operative radiation therapy for breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 1982 Jul-Aug;2(4):209–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotstein S., Blomgren H., Petrini B., Wasserman J., Baral E. Long term effects on the immune system following local radiation therapy for breast cancer. I. Cellular composition of the peripheral blood lymphocyte population. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1985 May;11(5):921–925. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(85)90114-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman J., Blomgren H., Petrini B., Baral E., Strender L. E., Jarstrand C., von Stedingk L. V. Effect of radiation therapy and in vitro x-ray exposure on lymphocyte subpopulations and their functions. Am J Clin Oncol. 1982 Apr;5(2):195–208. doi: 10.1097/00000421-198204000-00069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman J., Hammarström S., Petrini B., Blomgren H., von Stedingk L. V., Vedin I. Effects of some prostaglandins and leukotrienes on lymphocytes, monocytes and their activity in vitro. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1987;83(1):39–43. doi: 10.1159/000234328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman J., Wallgren A., Blomgren H., Baral E., Petrini B. Prognostic relevance of postirradiation lymphocyte reactivity in breast cancer patients. Cancer. 1986 Jul 15;58(2):348–351. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19860715)58:2<348::aid-cncr2820580225>3.0.co;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



