In [1], the legends to Figure 2 and Figure 3 were published incorrectly. The corrected legends are as follows:
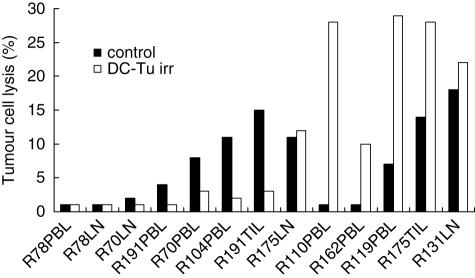
Fig. 2.
Cytotoxic activity of lymphocytes after stimulation by dendritic cells (DC) loaded with irradiated tumour cells. Peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL), lymph node lymphocytes (LNL) or tumour infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) were stimulated with autologous DC pulsed with irradiated tumour cells (DC-Tu irr). Cytotoxic activity of lymphocytes was evaluated against autologous tumour cells using 51Cr release assay. Effector: target ratio was 50: 1. Controls were non-stimulated lymphocytes. Data are individual percentage lysis values of 13 lymphocyte populations.
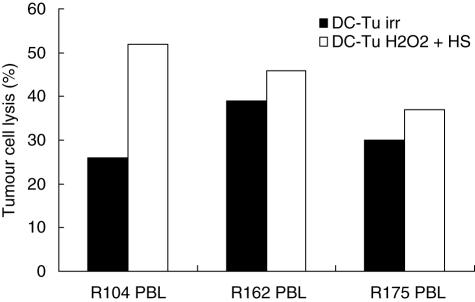
Fig. 3.
Cytotoxic activity of lymphocytes after stimulation by dendritic cells (DC) loaded with hydrogen peroxide + heat shock treated tumour cells. Peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL) were stimulated with autologous DC pulsed with tumour cells treated with hydrogen peroxide and heat shock (DC-Tu H2O2 + HS) or 75 grays irradiated (DC-Tu irr). Cytotoxic activity of lymphocytes stimulated was measured against autologous tumour cells using 51Cr release assay. Effector: target ratio was 50: 1. Data are individual percentage lysis values of three lymphocyte populations.
In [2], there was a typographical error in line 3 of the Summary. The incorrect sentence read ‘A defective T helper 1 (Th1) response and a long percentage of CD4+/CD25+ cells have been described in chronic brucellosis patients’. The corrected sentence should read ‘A defective T helper 1 (Th1) response and a low percentage of CD4+/CD25+ cells have been described in chronic brucellosis patients.’
We apologize for these errors.
References
- 1.Cabillic F, Bouet-Toussaint F, Toutirais O, et al. Interleukin-6 and vascular endothelial growth factor release by renal cell carcinoma cells impedes lymphocyte–dendritic cell cross-talk. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006;146:509–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03212.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Skendros P, Boura P, Kamaria F, Raptopoulou-Gigi M. CD80/CD28 co-stimulation in human brucellosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006;146:400–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03223.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]