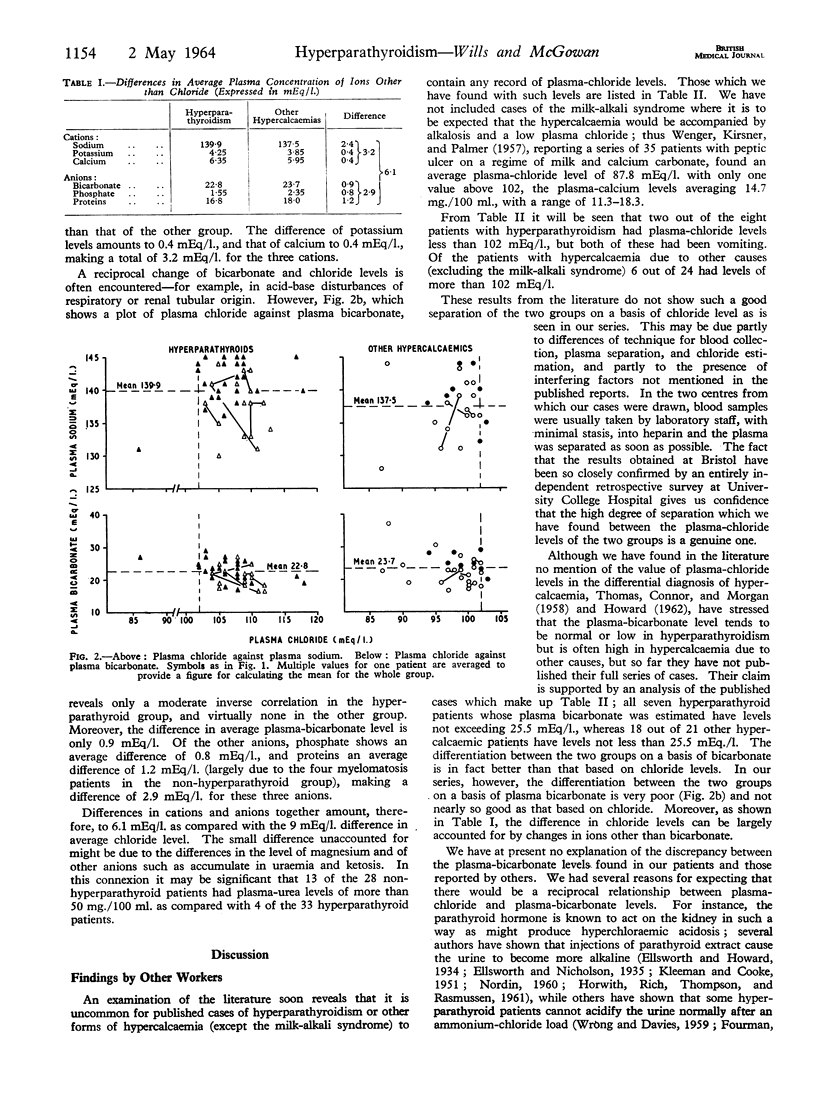
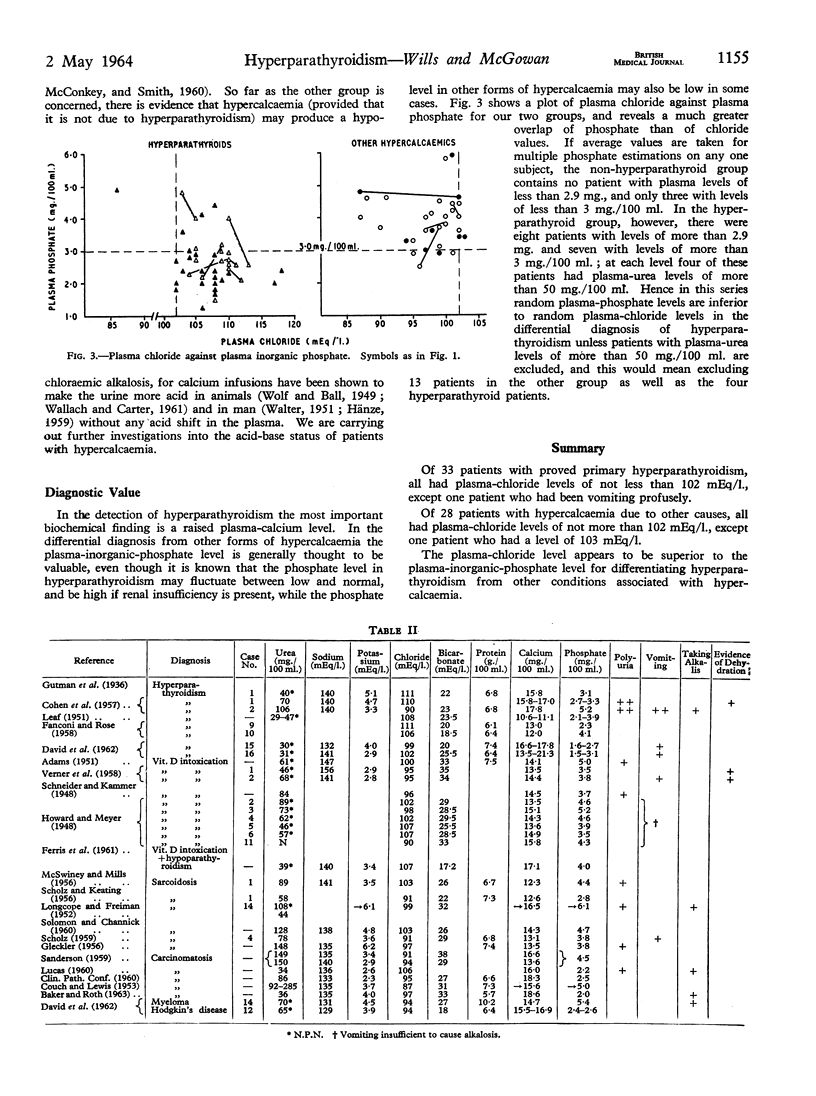
Full text
PDF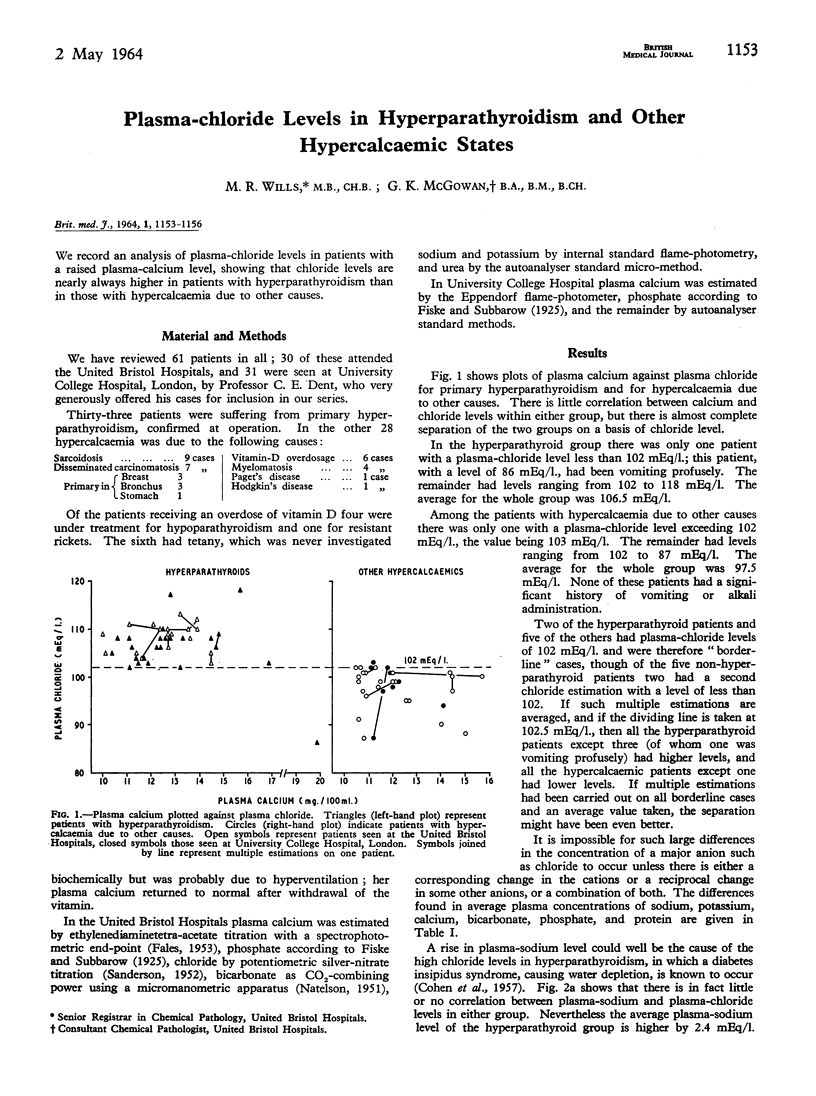

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADAMS F. D. Reversible uremia with hypercalcemia due to vitamin D intoxication. N Engl J Med. 1951 Apr 19;244(16):590–592. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195104192441604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S. I., FITZGERALD M. G., FOURMAN P., GRIFFITHS W. J., DE WARDENER H. E. Polyuria in hyperparathyroidism. Q J Med. 1957 Oct;26(104):423–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COUCH R. S. C., LEWIS A. A. G. A case of nephrocalcinosis. Arch Middx Hosp. 1953 Apr;3(2):84–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVID N. J., VERNER J. V., ENGEL F. L. The diagnostic spectrum of hypercalcemia. Case reports and discussion. Am J Med. 1962 Jul;33:88–110. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(62)90280-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellsworth R., Nicholson W. M. FURTHER OBSERVATIONS UPON THE CHANGES IN THE ELECTROLYTES OF THE URINE FOLLOWING THE INJECTION OF PARATHYROID EXTRACT. J Clin Invest. 1935 Nov;14(6):823–827. doi: 10.1172/JCI100730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FANCONI A., ROSE G. A. The ionized, complexed, and protein-bound fractions of calcium in plasma; an investigation of patients with various diseases which affect calcium metabolism, with an additional study of the role of calcium ions in the prevention of tetany. Q J Med. 1958 Oct;27(108):463–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERRIS T., KASHGARIAN M., LEVITIN H., BRANDT I., EPSTEIN F. H. Renal tubular acidosis and renal potassium wasting acquired as a result of hypercalcemic nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 1961 Nov 9;265:924–928. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196111092651902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOURMAN P., McCONKEY B., SMITH J. W. Defects of water reabsorption and of hydrogen-ion excretion by the renal tubules in hyperparathyroidism. Lancet. 1960 Mar 19;1(7125):619–623. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(60)90503-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLECKLER W. J. Hypercalcemia and renal insufficiency due to sarcoidosis: treatment with cortisone. Ann Intern Med. 1956 Jan;44(1):174–179. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-44-1-174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEEMAN C. R., COOKE R. E. The acute effects of parathyroid hormone on the metabolism of endogenous phosphate. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 Jul;38(1):112–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LONGCOPE W. T., FREIMAN D. G. A study of sarcoidosis; based on a combined investigation of 160 cases including 30 autopsies from The Johns Hopkins Hospital and Massachusetts General Hospital. Medicine (Baltimore) 1952 Feb;31(1):1–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUCAS P. F. Acute hypercalcaemia from carcinomatosis without bone metastasis. Br Med J. 1960 Apr 30;1(5182):1330–1331. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5182.1330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCSWINEY R. R., MILLS I. H. Hypercalcaemia due to sarcoidosis; treatment with cortisone. Lancet. 1956 Oct 27;271(6948):862–866. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(56)91039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NATELSON S. Routine use of ultramicro methods in the clinical laboratory; estimation of sodium, potassium, chloride, protein, hematocrit value, sugar, urea and nonprotein nitrogen in fingertip blood; construction of ultramicro pipets; a practical microgasometer for estimation of carbon dioxide. Am J Clin Pathol. 1951 Dec;21(12):1153–1172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORDIN B. E. The effect of intravenous parathyroid extract on urinary pH, bicarbonate and electrolyte excretion. Clin Sci. 1960 May;19:311–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDERSON P. H. Potentiometric determination of chloride in biological fluids. Biochem J. 1952 Nov;52(3):502–505. doi: 10.1042/bj0520502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERNER J. V., Jr, ENGEL F. L., McPHERSON H. T. Vitamin D intoxication: report of two cases treated with cortisone. Ann Intern Med. 1958 Apr;48(4):765–773. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-48-4-765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLACH S., CARTER A. C. Metabolic and renal effects of acute hypercalcemia in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1961 Feb;200:359–366. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.2.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALTER O. Beobachtungen bei intravenösen Kalzium-Injektionsserien. Z Gesamte Inn Med. 1951 Nov;6(21-22):664–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WENGER J., KIRSNER J. B., PALMER W. L. The milk-alkali syndrome; hypercalcemia, alkalosis and azotemia following calcium carbonate and milk therapy of peptic ulcer. Gastroenterology. 1957 Nov;33(5):745–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRONG O., DAVIES H. E. The excretion of acid in renal disease. Q J Med. 1959 Apr;28(110):259–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


