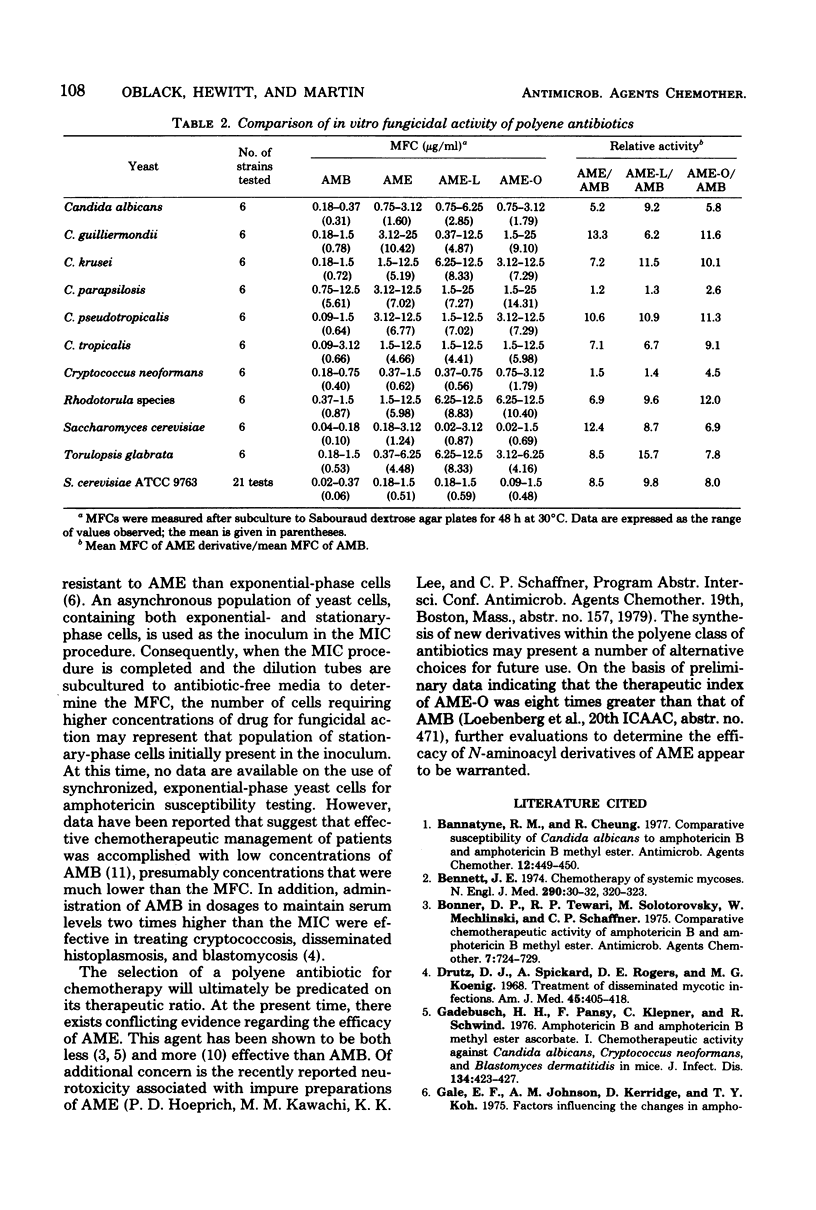
Abstract
The in vitro antifungal activities of two N-aminoacyl derivatives of amphotericin B methyl ester (AME) were compared by tube dilution with those of amphotericin B and AME, using 60 isolates representing 10 yeast species. A total of 70% of the strains were inhibited by concentrations of the N-aminoacyl AME derivatives that were within a twofold dilution of the amphotericin B or AME minimum inhibitory concentration. The fungicidal activity of the N-aminoacyl AME derivatives was 3- to 16-fold lower than that of amphotericin B for 8 of 10 species. A considerable spectrum of antifungal activity was observed for N-aminoacyl derivatives of AME, which represents a new class of water-soluble polyene antibiotics.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bannatyne R. M., Cheung R. Comparative susceptibility of Candida albicans to amphotericin B and amphotericin B methyl ester. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Oct;12(4):449–450. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.4.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. E. Chemotherapy of systemic mycoses (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1974 Feb 7;290(6):320–323. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197402072900607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner D. P., Tewari R. P., Solotorovsky M., Mechlinski W., Schaffner C. P. Comparative chemotherapeutic activity of amphotericin B and amphotericine B methy ester. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jun;7(6):724–729. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.6.724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drutz D. J., Spickard A., Rogers D. E., Koenig M. G. Treatment of disseminated mycotic infectioons. A new approach to amphotericin B therapy. Am J Med. 1968 Sep;45(3):405–418. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(68)90075-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadebusch H. H., Pansy F., Klepner C., Schwind R. Amphotericin B and amphotericin B methyl ester ascorbate. I. Chemotherapeutic activity against Candida albicans, Cryptococcus neoformans, and Blastomyces dermatitidis in mice. J Infect Dis. 1976 Nov;134(5):423–427. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.5.423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale E. F., Johnson A. M., Kerridge D., Koh T. Y. Factors affecting the changes in amphotericin sensitivity of Candida albicans during growth. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Mar;87(1):20–36. doi: 10.1099/00221287-87-1-20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howarth W. R., Tewari R. P., Solotorovsky M. Comparative in vitro antifungal activity of amphotericin B and amphotericin B methyl ester. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jan;7(1):58–63. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.1.58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huston A. C., Hoeprich P. D. Comparative susceptibility of four kinds of pathogenic fungi to amphotericin B and amphotericin B methyl ester. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jun;13(6):905–909. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.6.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keim G. R., Sibley P. L., Yoon Y. H., Kulesza J. S., Zaidi I. H., Miller M. M., Poutsiaka J. W. Comparative toxicological studies of amphotericin B methyl ester and amphotericin B in mice, rats, and dogs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):687–690. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence R. M., Hoeprich P. D. Comparison of amphotericin B and amphotericin B methyl ester: efficacy in murine coccidioidomycosis and toxicity. J Infect Dis. 1976 Feb;133(2):168–174. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.2.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medoff G., Dismukes W. E., Meade R. H., 3rd, Moses J. M. A new therapeutic approach to Candida infections. A preliminary report. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Aug;130(2):241–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



