Abstract
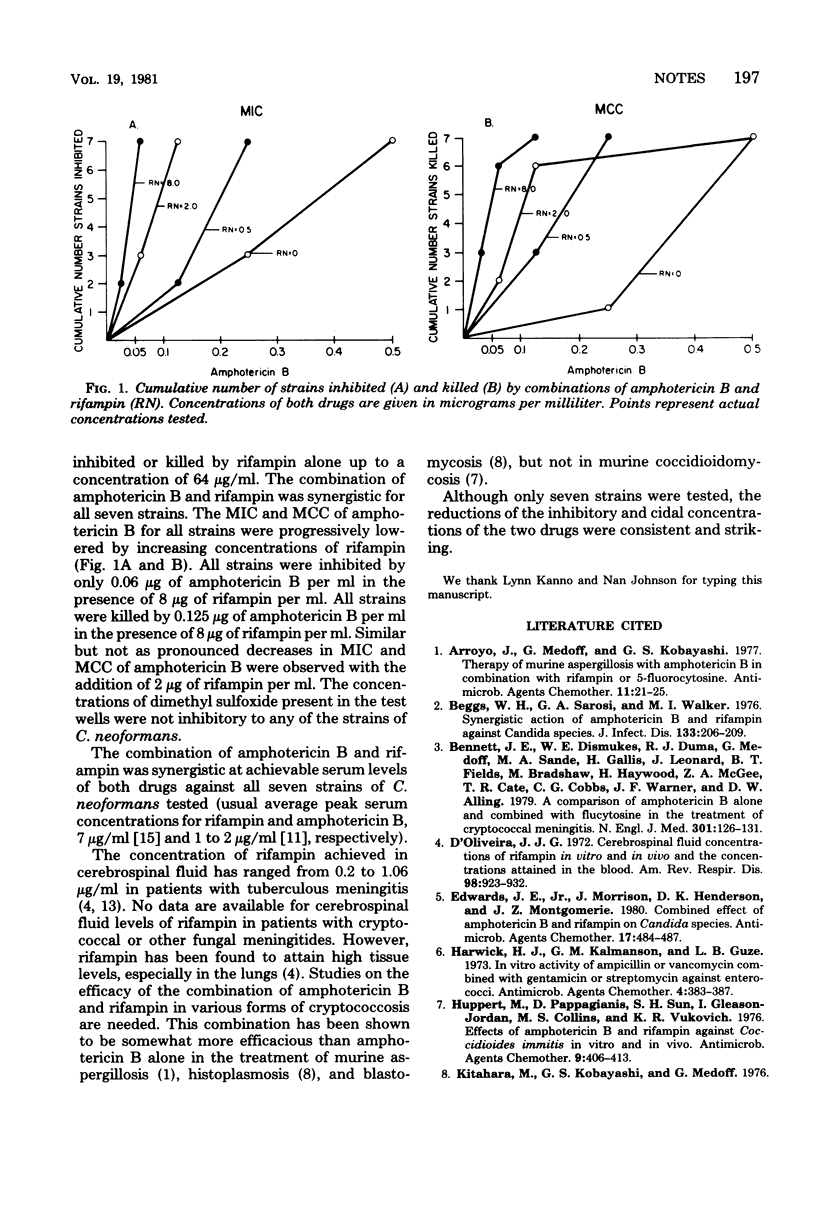
The combination of amphotericin B and rifampin was synergistic in vitro in both inhibiting and killing seven strains of Cryptococcus neoformans by the checkerboard microtitration technique.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arroyo J., Medoff G., Kobayashi G. S. Therapy of murine aspergillosis with amphotericin B in combination with rifampin of 5-fluorocytosine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jan;11(1):21–25. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beggs W. H., Sarosi G. A., Walker M. I. Synergistic action of amphotericin B and rifampin against Candida species. J Infect Dis. 1976 Feb;133(2):206–209. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.2.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. E., Dismukes W. E., Duma R. J., Medoff G., Sande M. A., Gallis H., Leonard J., Fields B. T., Bradshaw M., Haywood H. A comparison of amphotericin B alone and combined with flucytosine in the treatment of cryptoccal meningitis. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jul 19;301(3):126–131. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197907193010303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. E., Jr, Morrison J., Henderson D. K., Montgomerie J. Z. Combined effect of amphotericin B and rifampin on Candida species. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Mar;17(3):484–487. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.3.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwick H. J., Kalmanson G. M., Guze L. B. In vitro activity of ampicillin or vancomycin combined with gentamicin or streptomycin against enterococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Oct;4(4):383–387. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.4.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppert M., Pappagianis D., Sun S. H., Gleason-Jordan I., Collins M. S., Vukovich K. R. Effect of amphotericin B and rifampin against Coccidioides immitis in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Mar;9(3):406–413. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.3.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobbayashi G. S., Medoff G., Schlessinger D., Kwan C. N., Musser W. E. Amphotericin B potentiation of rifampicin as an antifungal agent against the yeast phase of Histoplasma capsulatum. Science. 1972 Aug 25;177(4050):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4050.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medoff G., Kobayashi G. S., Kwan C. N., Schlessinger D., Venkov P. Potentiation of rifampicin and 5-fluorocytosine as antifungal antibiotics by amphotericin B (yeast-membrane permeability-ribosomal RNA-eukaryotic cell-synergism). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):196–199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomerie J. Z., Edwards J. E., Jr, Guze L. B. Synergism of amphotericin B and 5-fluorocytosine for candida species. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jul;132(1):82–86. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.1.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkind D., Crowder E. D., Hyland R. N. In vitro inhibition of Coccidioides immitis strains with amphotericin B plus rifampin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Dec;6(6):783–784. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.6.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippel J. E., Mikhail I. A., Girgis N. I., Youssef H. H. Rifampin concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with tuberculous meningitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974 May;109(5):579–580. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1974.109.5.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utz J. P., Garriques I. L., Sande M. A., Warner J. F., Mandell G. L., McGehee R. F., Duma R. J., Shadomy S. Therapy of cryptococcosis with a combination of flucytosine and amphotericin B. J Infect Dis. 1975 Oct;132(4):368–373. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.4.368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbist L., Gyselen A. Antituberculous activity of rifampin in vitro and in vivo and the concentrations attained in human blood. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1968 Dec;98(6):923–932. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1968.98.6.923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



