Abstract
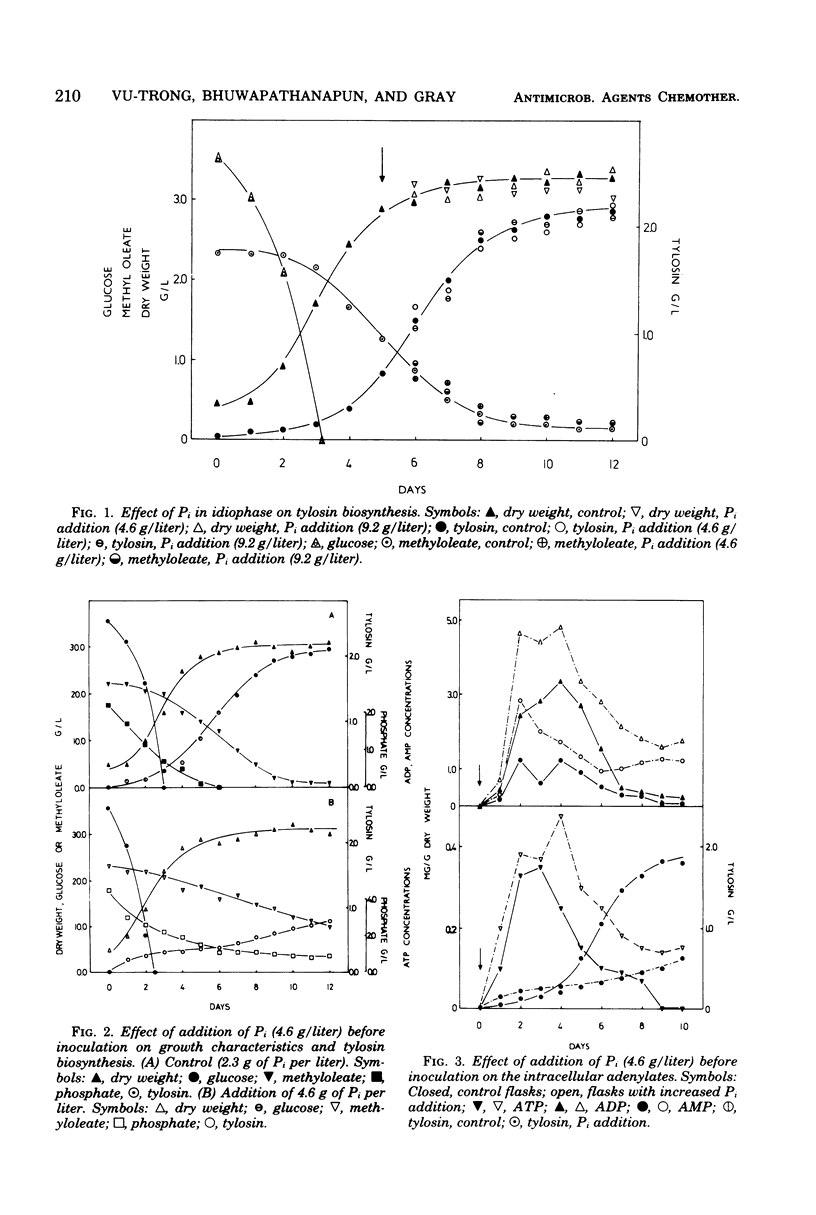
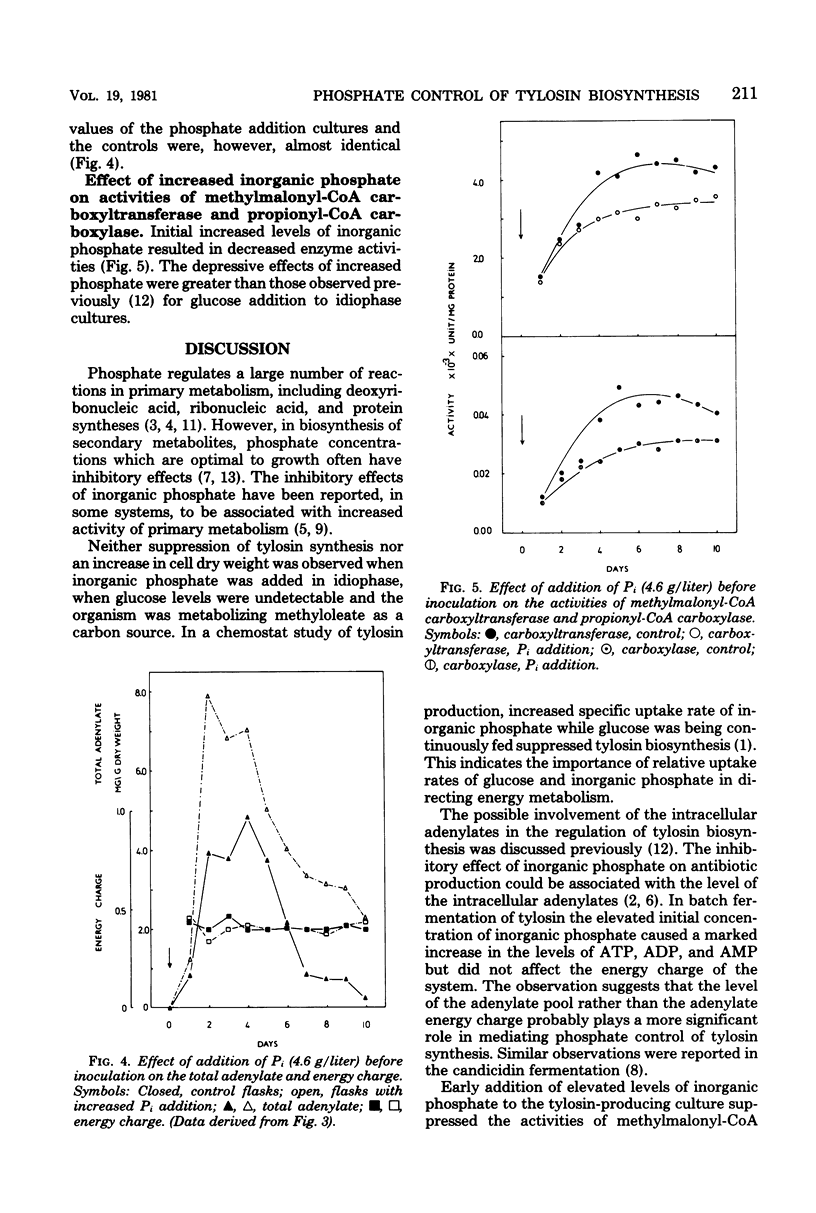
The effects of increased concentration of inorganic phosphate on the biosynthesis of tylosin, the level of the intracellular adenylates, the energy charge, and the activities of enzymes involved in the synthesis of tylonolide precursors were studied in Streptomyces fradiae NRRL 2702. No metabolic response was observed when elevated levels of inorganic phosphate were added in idiophase. Increased initial levels of inorganic phosphate suppressed tylosin production and markedly increased the levels of the adenylates, although the adenylate energy charge was unchanged. Higher growth and glucose uptake rates were also observed. The activities of methylmalonyl-coenzyme A carboxyltransferase (EC 2.1.3.1) and propionyl-coenzyme A carboxylase (EC 6.4.1.3) were suppressed by the increased concentration of inorganic phosphate. The results indicated that the rate of tylosin synthesis was inversely related to the absolute level of the adenylates rather than to the energy charge.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Curdová E., Kremen A., Vanek Z., Hostálek Z. Regulation and biosynthesis of secondary metabolites. XVIII. Adenylate level and chlorotetracycline production in Streptomyces aureofaciens. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1976;21(6):481–487. doi: 10.1007/BF02876940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOSTALEK Z. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM OF STREPTOMYCES AUREOFACIENS AND THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF CHLORTETRACYCLINE. I. THE EFFECT OF INTERRUPTED AERATION, INORGANIC PHOSPHATE AND BENZYL THIOCYANATE ON CHLORTETRACYCLINE BIOSYNTHESIS. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1964 Mar;18:78–88. doi: 10.1007/BF02868788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu D. M., McDaniel L. E., Schaffner C. P. Factors affecting the production of candicidin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Feb;7(2):196–202. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.2.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. F., McDaniel L. E. Production of polyene macrolide antibiotics. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1977;21:1–52. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70037-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martín J. F., Liras P., Demain A. L. ATP and adenylate energy charge during phosphate-mediated control of antibiotic synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 14;83(3):822–828. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91468-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz F. P., Doolin L. E. The effect of inorganic phosphate on the biosynthesis of vancomycin. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Feb;19(2):263–270. doi: 10.1139/m73-040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERLMAN D., WAGMAN G. H. Studies on the utilization of lipids by streptomyces griseus. J Bacteriol. 1952 Feb;63(2):253–262. doi: 10.1128/jb.63.2.253-262.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu-Trong K., Bhuwapathanapun S., Gray P. P. Metabolic regulation in tylosin-producing Streptomyces fradiae: regulatory role of adenylate nucleotide pool and enzymes involved in biosynthesis of tylonolide precursors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Apr;17(4):519–525. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.4.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



